java.io.BufferedInputStream read()
Description
On this document we will be showing a java example on how to use the flush() method of BufferedInputStream Class. This method reads the next byte of data from the input stream. The value byte is returned as an int in the range 0 to 255. If no byte is available because the end of the stream has been reached, the value -1 is returned. This method blocks until input data is available, the end of the stream is detected, or an exception is thrown.
A subclass must provide an implementation of this method.
A subclass must provide an implementation of this method.
Override by:
- read in class FilterInputStream
Throws:
- IOException – if this input stream has been closed by invoking its close() method, or an I/O error occurs.
Method Syntax
public int read()
throws IOException
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method Returns
This method returns the next byte of data, or -1 if the end of the stream is reached.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.0 and up
Java BufferedInputStream read() Example
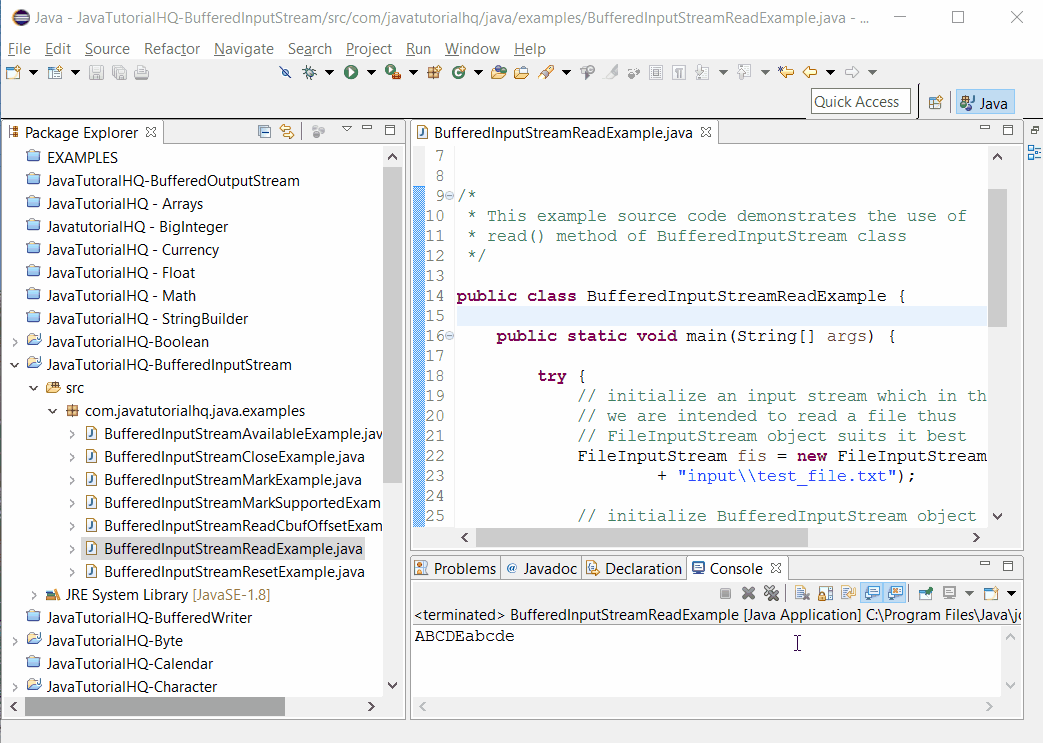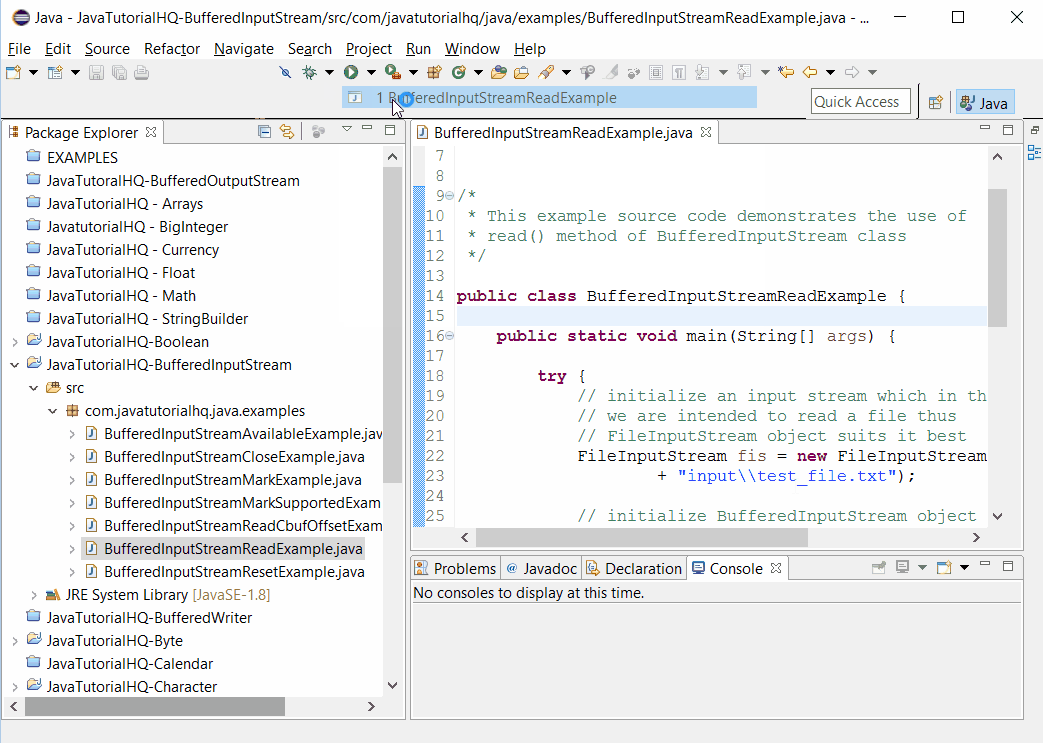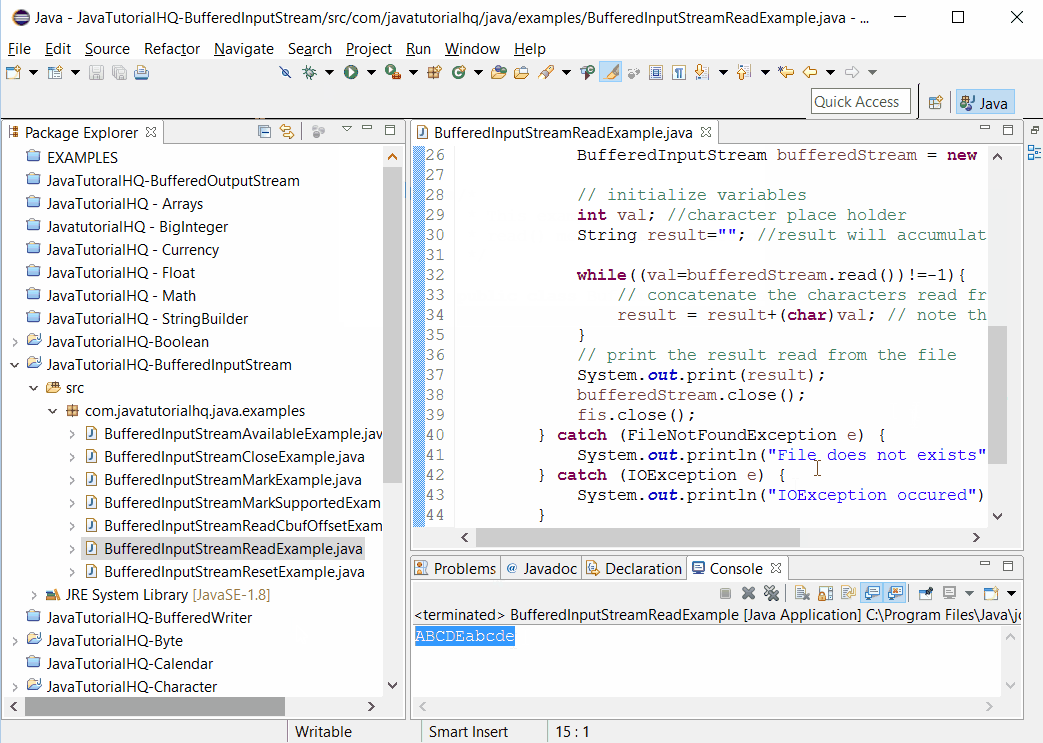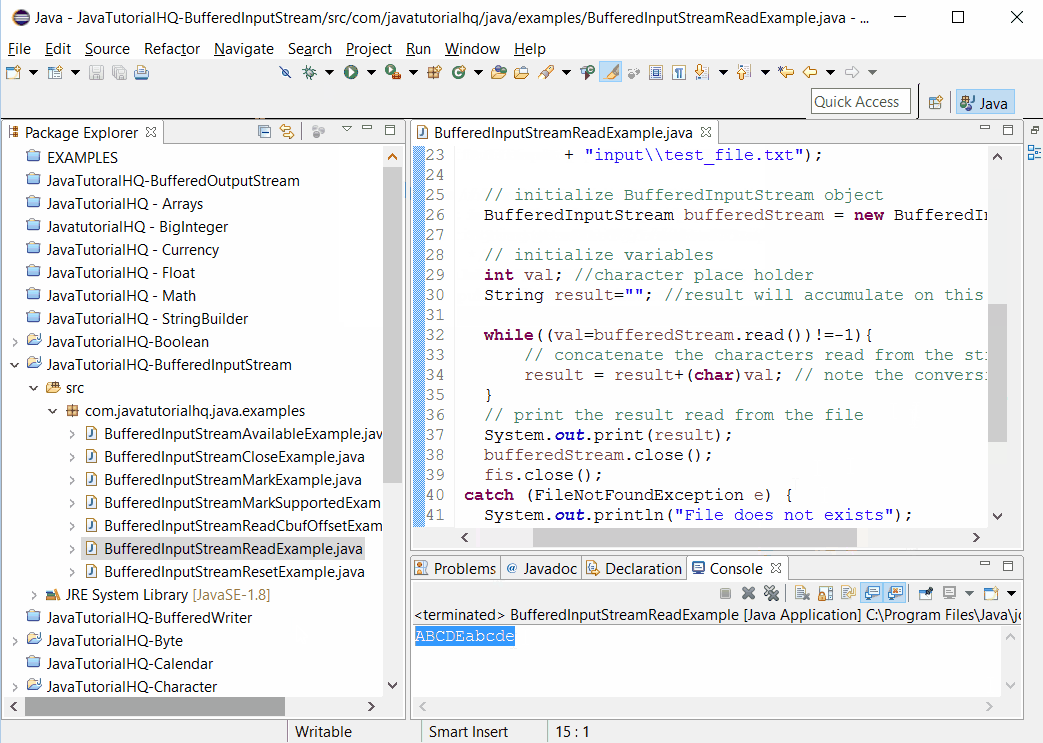
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of read() method of BufferedInputStream class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behaviour of the read().
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* read() method of BufferedInputStream class
*/
public class BufferedInputStreamReadExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// initialize an input stream which in this case
// we are intended to read a file thus
// FileInputStream object suits it best
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:javatutorialhq"
+ "inputtest_file.txt");
// initialize BufferedInputStream object
BufferedInputStream bufferedStream = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
// initialize variables
int val; //character place holder
String result=""; //result will accumulate on this variable
while((val=bufferedStream.read())!=-1){
// concatenate the characters read from the stream
result = result+(char)val; // note the conversion of int to char
}
// print the result read from the file
System.out.print(result);
bufferedStream.close();
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("File does not exists");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException occured");
}
}
}