java.io.BufferedReader read()
Description :
This java tutorial shows how to use the read() method of BufferedReader class of java.io package. This method reads a single character and converted it into int as a method return. This BufferedReader method is widely used in reading characters from the InputStream as input on this class constructor.
Method Syntax :
public int read() throws IOException
Parameter Input :
| DataType | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method Returns :
The Scanner read() method return the int equivalent of character read by the BufferedReader’s object. The int return range from 0 to 65535. If there is no character to be read because it already reaches the end of the stream, the method returns -1.
Compatibility Version :
Requires Java 1.1 and up
Exception :
IOException
– This method will throw IOException if the operation encounter an I/O exception.
Discussion :
The read() method of BufferedReader class is inherited from Reader class which is the parent of BufferedReader. This reader class is widely used usually in reading characters either from a file or from the console.
Java Code Example :
This java example source code demonstrates the use of read() method of BufferedReader class. Basically it just reads a character from the console input of the user and then prints the result in int data type and also in char data type. This is only a simple program that can be modified to a more complex logic, however for you to appreciate the use of this method, below is for beginner’s example of read() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/*
* Java example source code that uses the read() method of
* BufferedReader class
* This example java program reads a user input and then we print
* the char that has been read
*/
public class BufferedReaderReadMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Do you want to Continue? ");
// declare the BufferedReader Class
// used the InputStreamReader to read the console input
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
System.in));
int readVal;
// catch the possible IOException by the read() method
try {
// assign the return value of the read() method to a variable
readVal = reader.read();
// print the read char converted in int
System.out.println("Character from console in int:" + readVal);
// print the char read from console input
// by the BufferedReader class
System.out.println("Character from console in char:"
+ (char) readVal);
// close the BufferedReader object
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
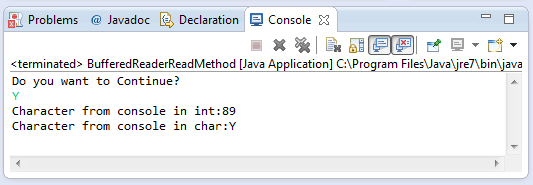
Sample Output :
Running the read() method example source code of BufferedReader class will give you the following output.
Exception Scenario :
N/A
Similar Method :
- N/A