java.lang.StrictMath addExact(long x, long y)
Description
The addExact(long x, long y) method of StrictMath class returns the sum of its arguments, throwing an exception if the result overflows a long.
Notes:
The addExact(long x, long y) method of StrictMath class is static thus it should be accessed statically which means the we would be calling this method in this format:
StrictMath.addExact(long x, long y)
Non static method is usually called by just declaring method_name(argument) however in this case since the method is static, it should be called by appending the class name as suffix. We will be encountering a compilation problem if we call the java compare method non statically.
Method Syntax
public static long addExact(long x, long y)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| long | x | the first value |
| long | y | the second value |
Method Returns
The addExact(long x, long y) method returns the sum of the arguments.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.8 and up
Java StrictMath addExact(long x, long y) Example
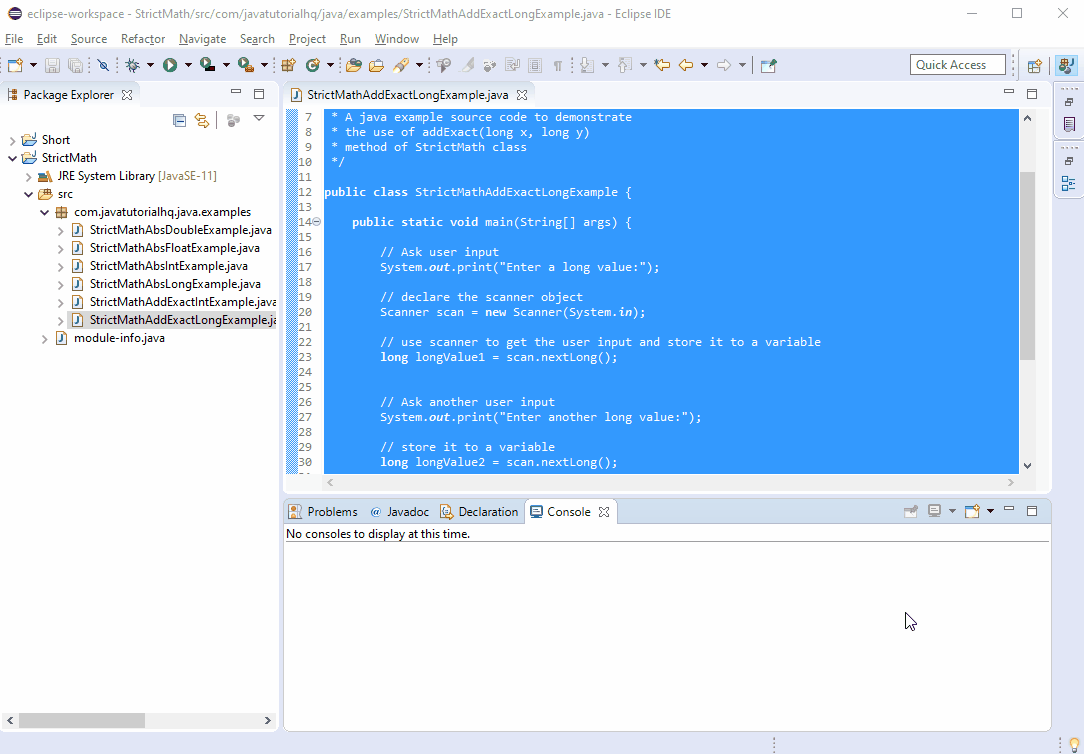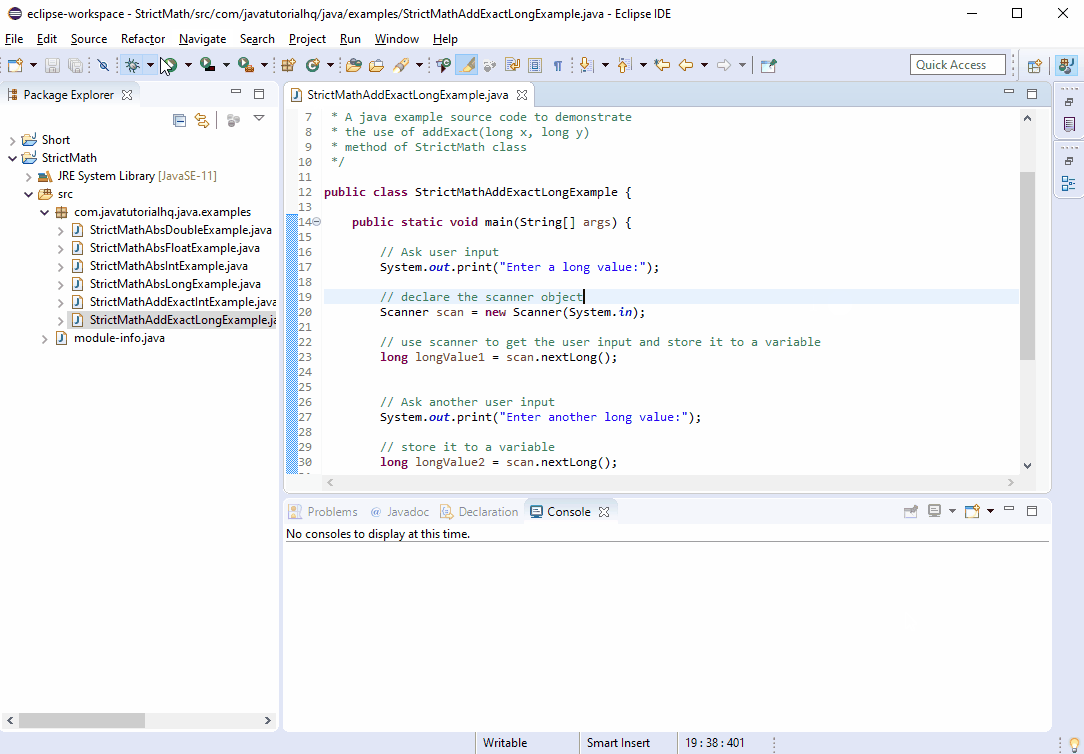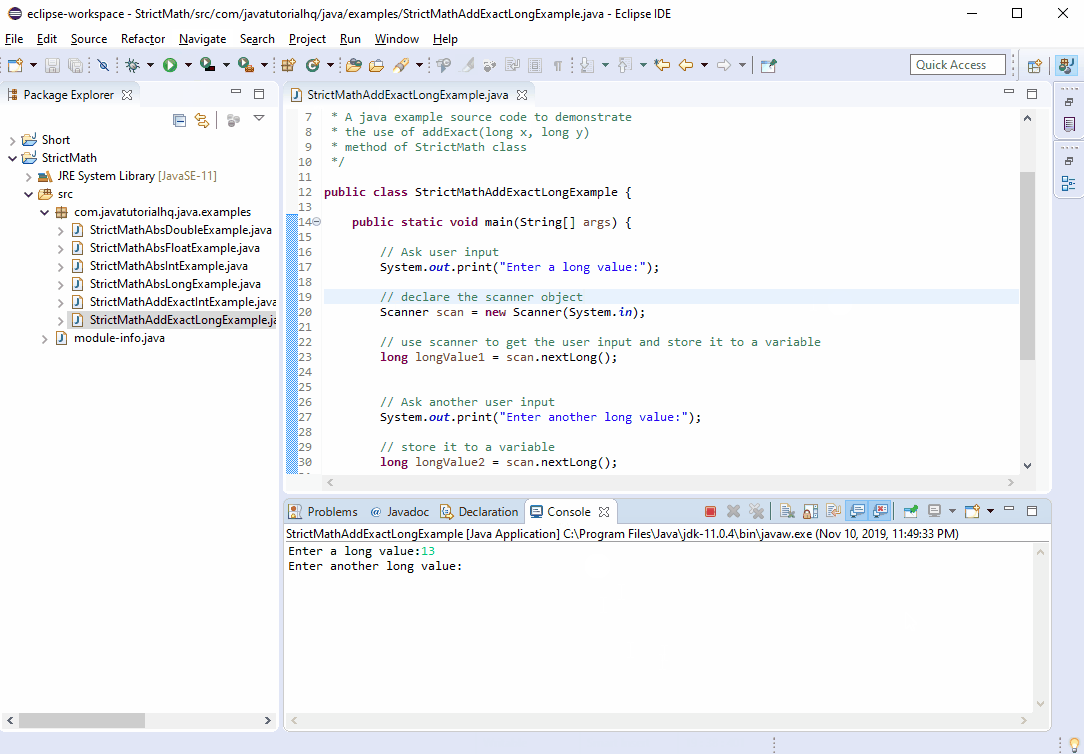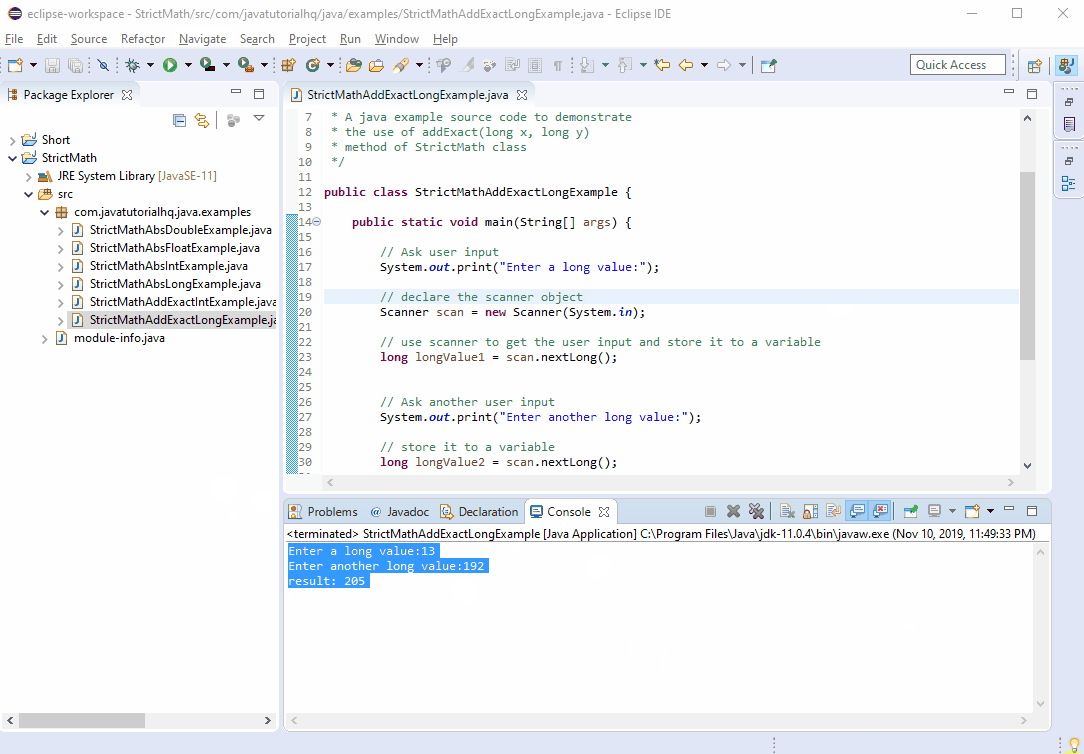
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of addExact(long x, longy) method of StrictMath class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of addExact(long x, long y)
* method of StrictMath class
*/
public class StrictMathAddExactLongExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Ask user input
System.out.print("Enter a long value:");
// declare the scanner object
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// use scanner to get the user input and store it to a variable
long longValue1 = scan.nextLong();
// Ask another user input
System.out.print("Enter another long value:");
// store it to a variable
long longValue2 = scan.nextLong();
// close the scanner object
scan.close();
// get the result
long result = StrictMath.addExact(longValue1, longValue2);
// print the result
System.out.println("result: "+result);
}
}