java.io.BufferedOutputStream write(int b)
Description
On this document we will be showing a java example on how to use the write(int b) method of BufferedOutputStream Class. This method writes the specified byte to this buffered output stream.
Override by:
write in class FilterOutputStream
Throws:
- IOException – If an I/O error occurs
Method Syntax
public void write(int b)
throws IOException
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| int | b | the byte to be written. |
Method Returns
This method returns void.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.0 and up
Java BufferedOutputStream write(int b) Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of write(int b) method of BufferedOutputStream class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behaviour of the write(int b) method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* write() method of BufferedOutputStream class
*/
public class BufferedOutputStreamWriteExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// initialize File object
File f = new File("C:javatutorialhqoutputtest_out.txt");
// instantiate a new FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
// using the above FileOutputStream
// instantiate a BufferedOutputStream object
BufferedOutputStream buffOut = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
// initialize variables
String writeString = "This is a test string";
// convert above String to character array
char[] value = writeString.toCharArray();
// write the values of the character array
for(char c:value){
buffOut.write((int)c);
}
// close the BufferedOutputStream
buffOut.flush();
buffOut.close();
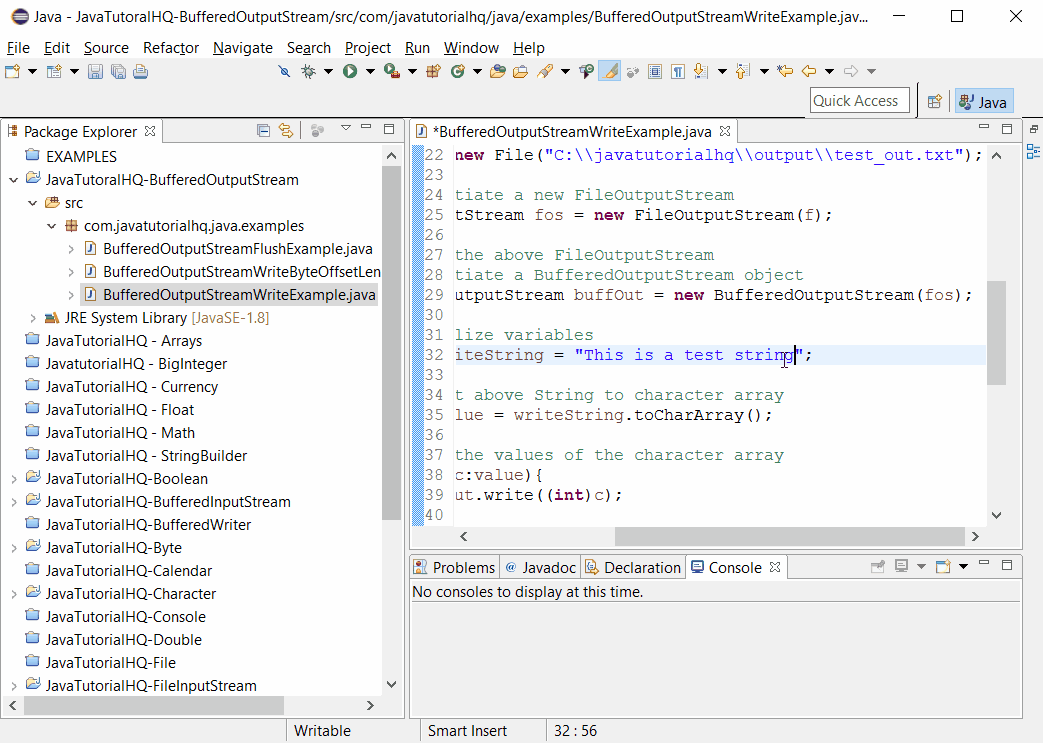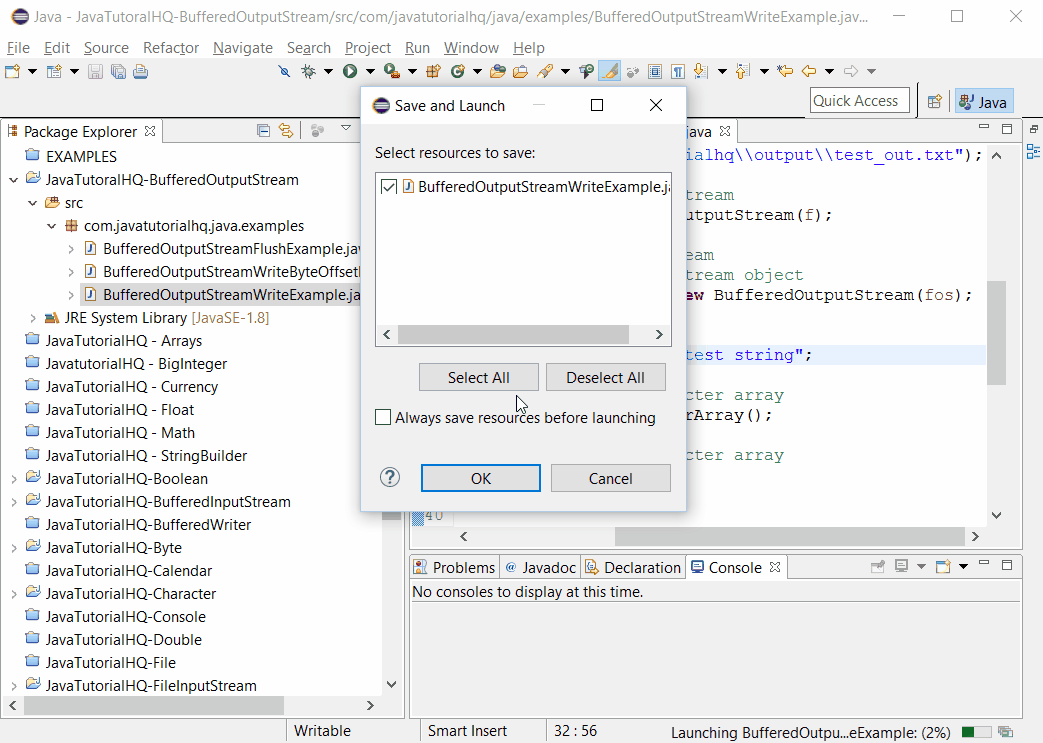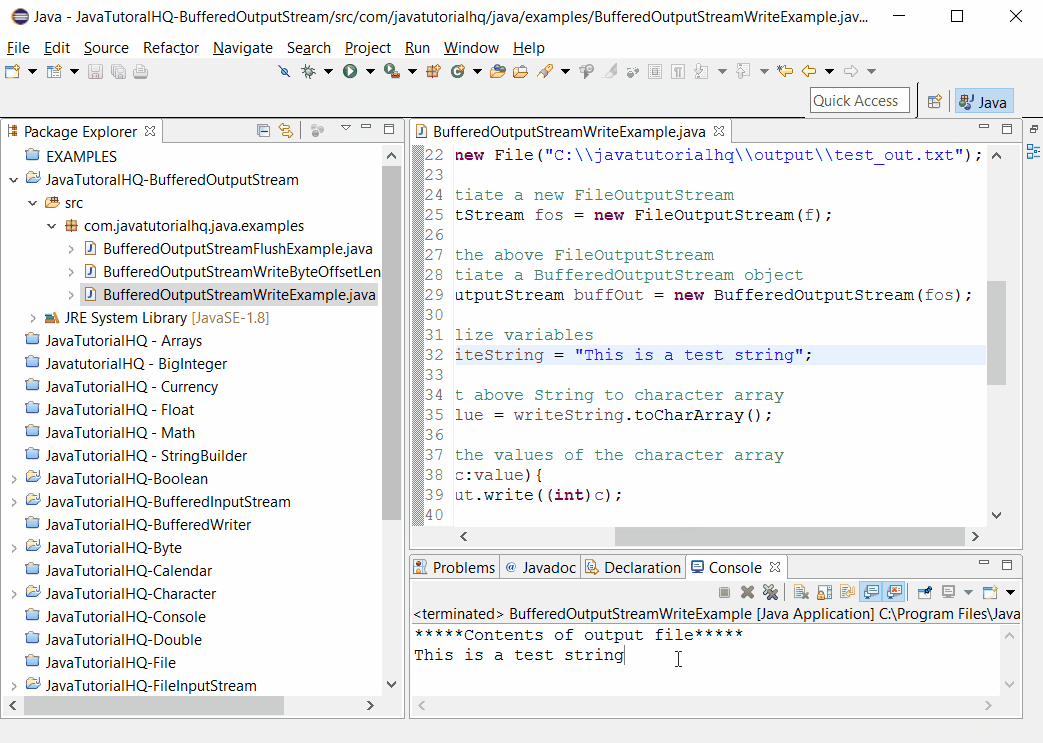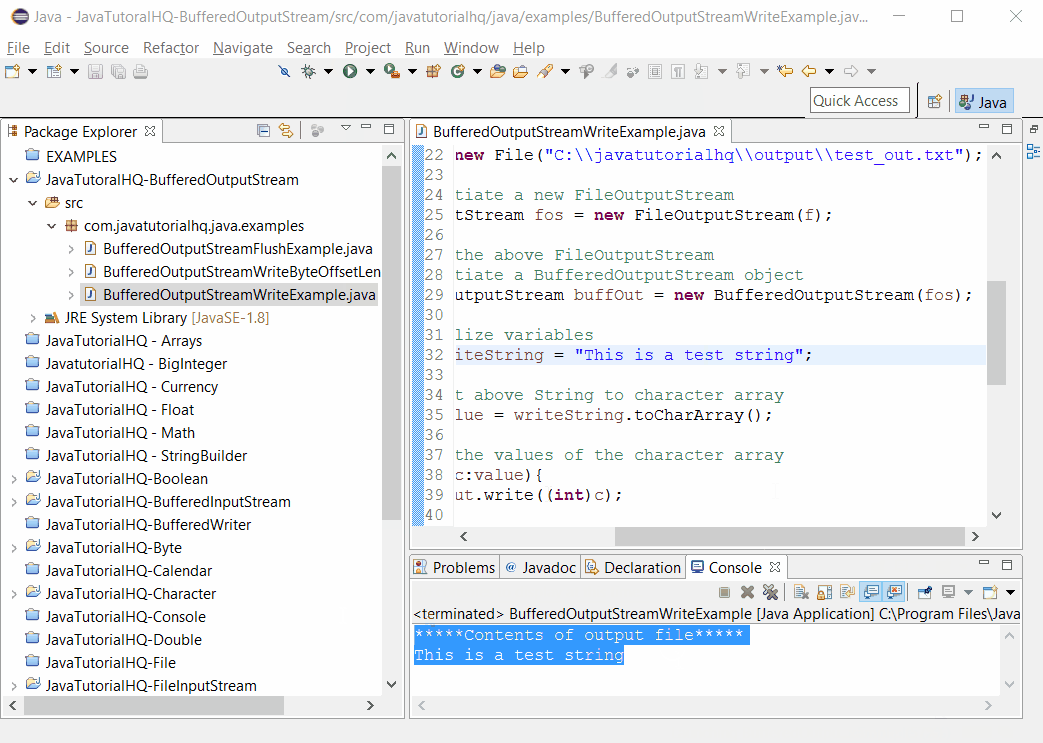
// read the output file
System.out.println("*****Contents of output file*****");
Scanner s = new Scanner(f);
while(s.hasNextLine()){
System.out.println(s.nextLine());
}
s.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("File path not found");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException occured");
}
}
}