java.io.InputStreamReader ready()
Description
Overrides:
ready in class Reader
Throws:
- IOException – If an I/O error occurs
Method Syntax
public boolean ready()
throws IOException
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method Returns
This method returns boolean, true if the next read() is guaranteed not to block for input, false otherwise. Note that returning false does not guarantee that the next read will block.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.2 and up
Java InputStreamReader ready() Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of ready() method of InputStreamReader class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behaviour of the ready() method of InputStreamReader class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* ready() method of InputStreamReader class
*/
public class InputStreamReaderReadyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// initialize an input stream which in this case
// we are intended to read a file thus
// FileInputStream object suits it best
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:javatutorialhq"
+ "inputtest_file.txt");
// initialize InputStreamReader object
InputStreamReader is = new InputStreamReader(fis);
// initialize variables
int val; //character place holder
while((val=is.read())!=-1){
// convert the integer value to character
char result = (char)val;
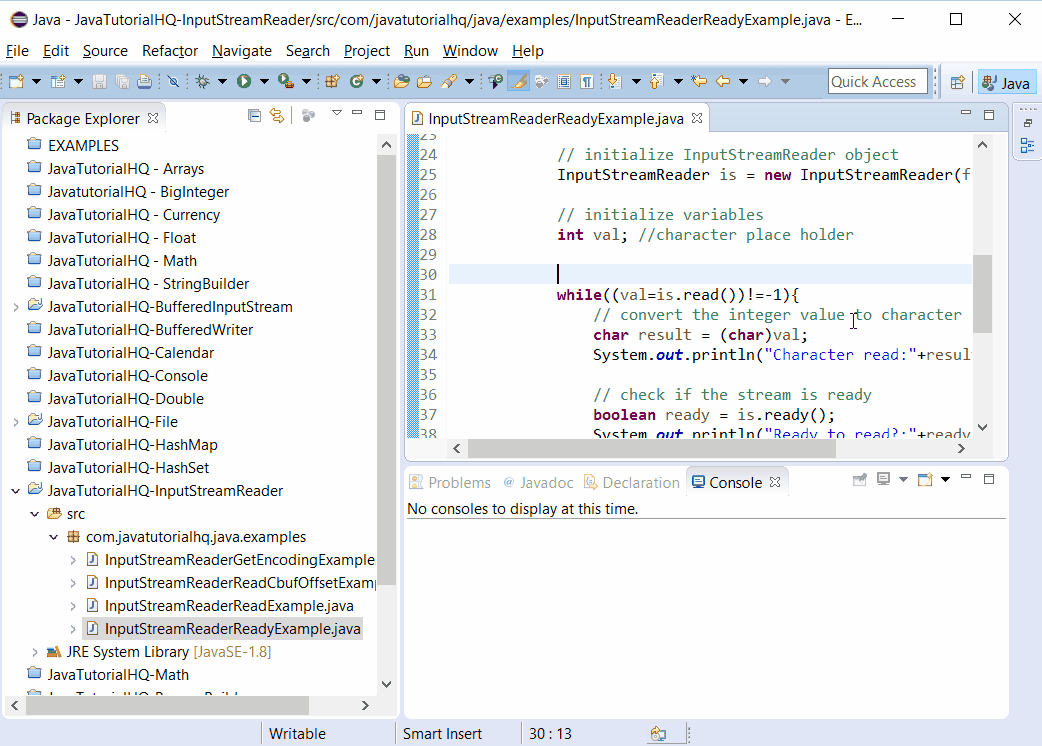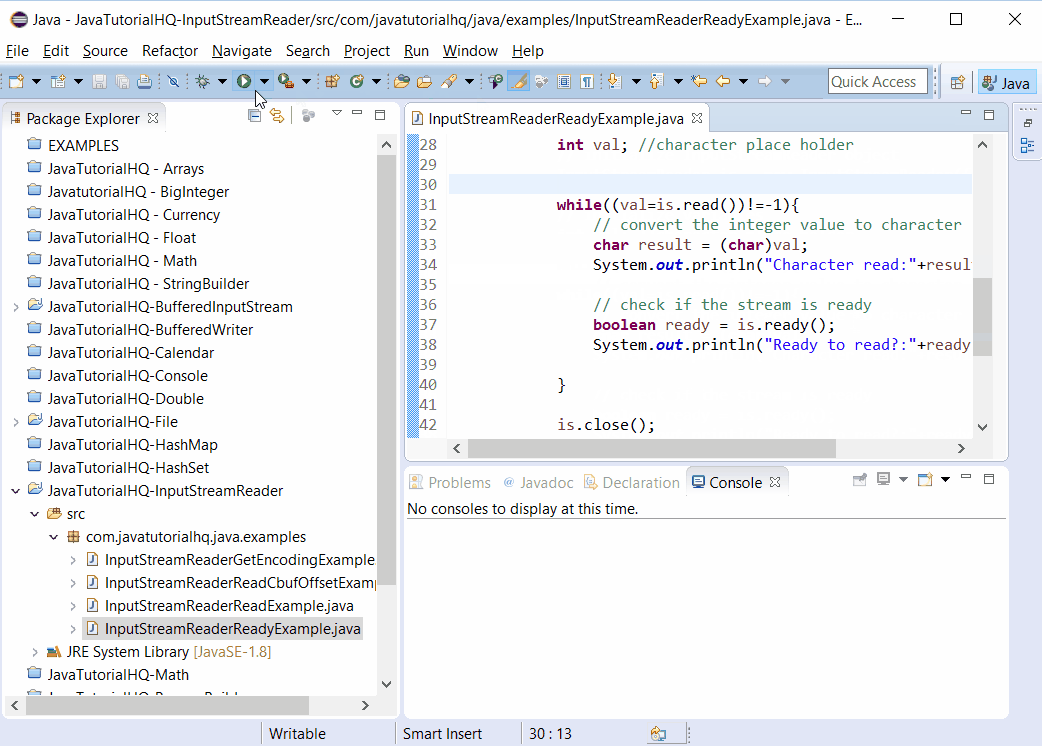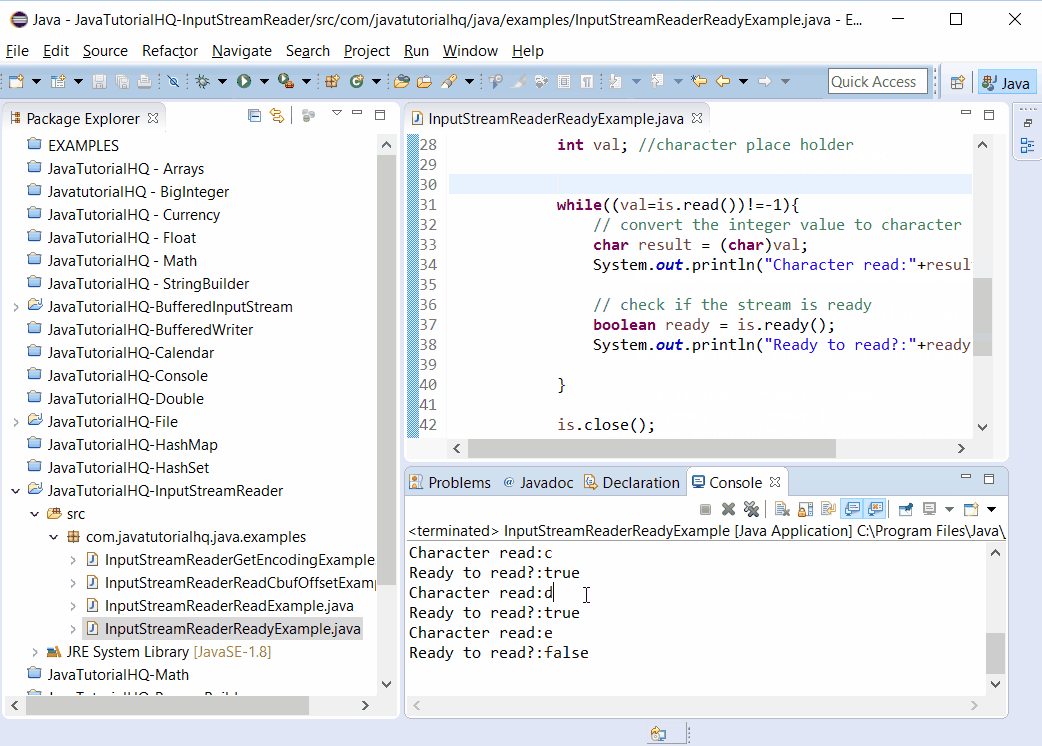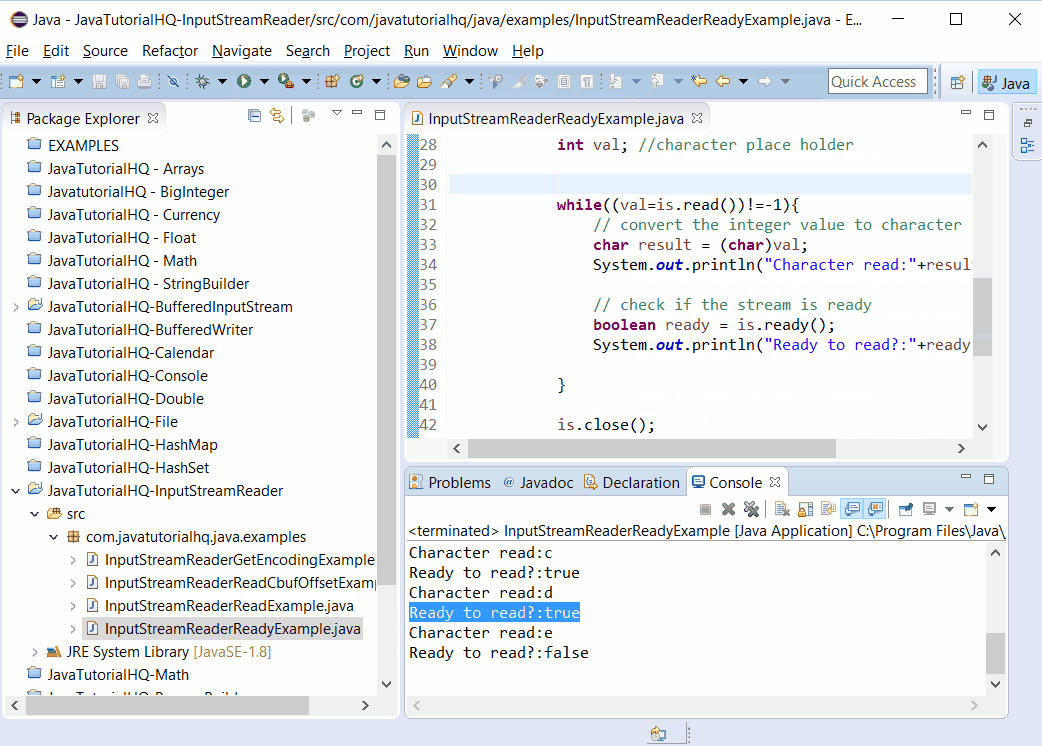
System.out.println("Character read:"+result);
// check if the stream is ready
boolean ready = is.ready();
System.out.println("Ready to read?:"+ready);
}
is.close();
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("File does not exists");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException occured");
}
}
}