java.lang.Boolean logicalXor(boolean a, boolean b)
Description
| First Value | Second Value | Result |
|---|---|---|
| true | true | false |
| true | false | false |
| false | true | false |
| false | false | true |
As a general rule, in performing a logical XOR operator, the two operand should not have the same values for it to return true.
Method Syntax
public static boolean logicalXor(boolean a, boolean b)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| boolean | a | the first operand |
| boolean | b | the second operand |
Method Returns
The logicalXor(boolean a, boolean b) method of Boolean class returns the logical XOR of a and b.
Discussion
Java Boolean logicalXor(boolean a, boolean b) Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of logicalXor() method of Boolean class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* logicalXOr(boolean a, boolean b) method of Boolean class.
*/
public class BooleanLogicalXORExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize Scanner object
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
// ask for user input
System.out.print("Enter first boolean value:");
// parse the user input into boolean
boolean firstInput = Boolean.parseBoolean(s.nextLine());
// ask for another user input
System.out.print("Enter second boolean value:");
// parse the second user input as boolean
boolean secondInput = Boolean.parseBoolean(s.nextLine());
/*
* get the logical XOR result
* true | true = false
* true | false = true
* false | false = false
* false | true = true
*/
boolean result = Boolean.logicalXor(firstInput, secondInput);
System.out.print(firstInput + " XOR " + secondInput
+ " = " + result );
// close the scanner object
s.close();
}
}
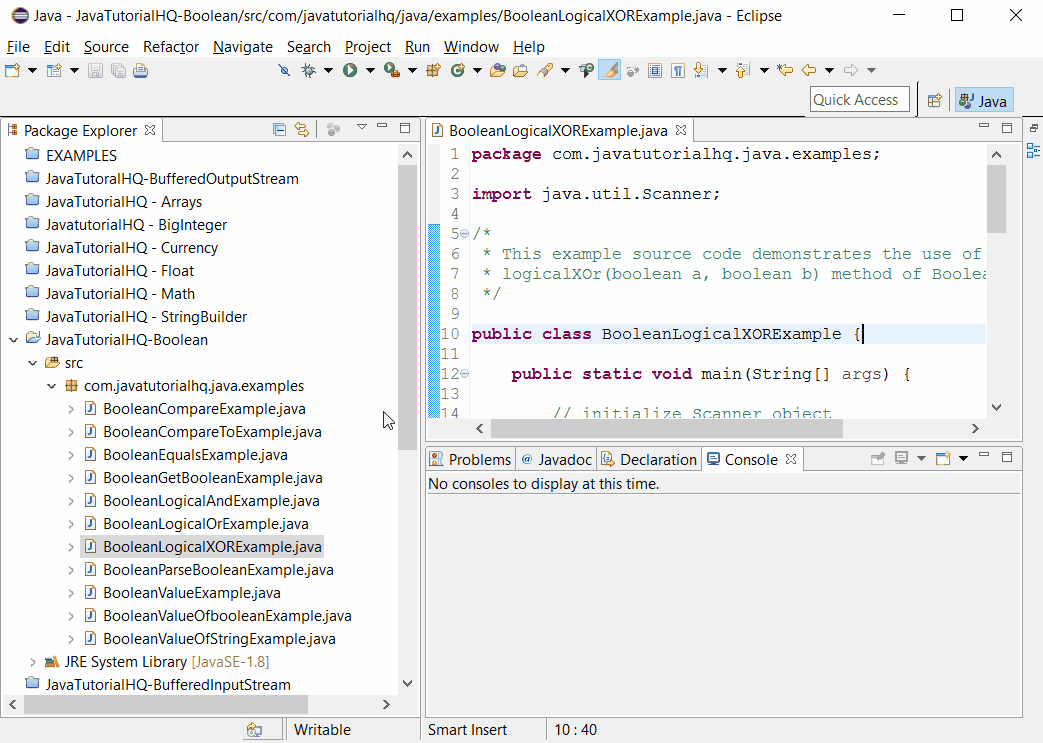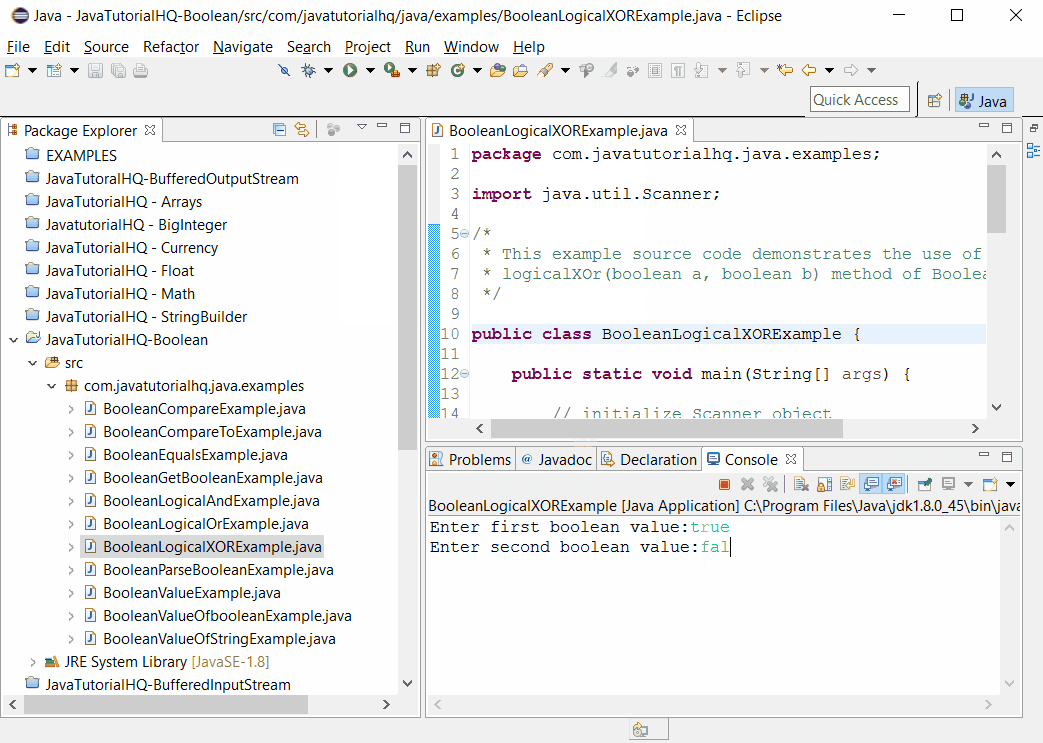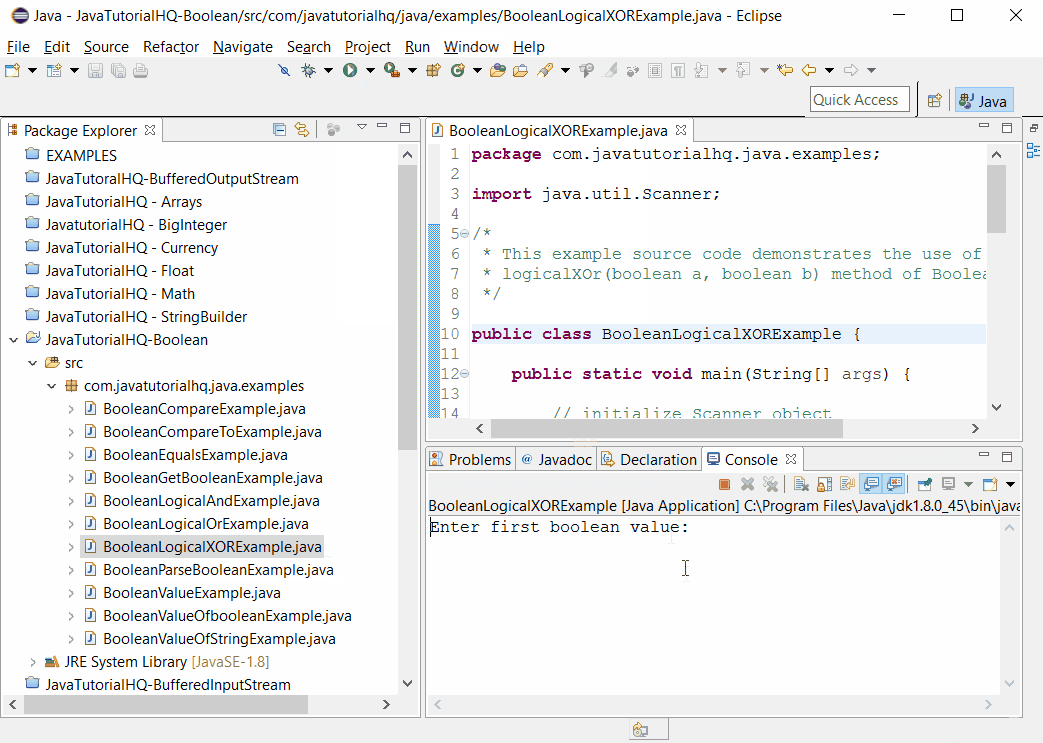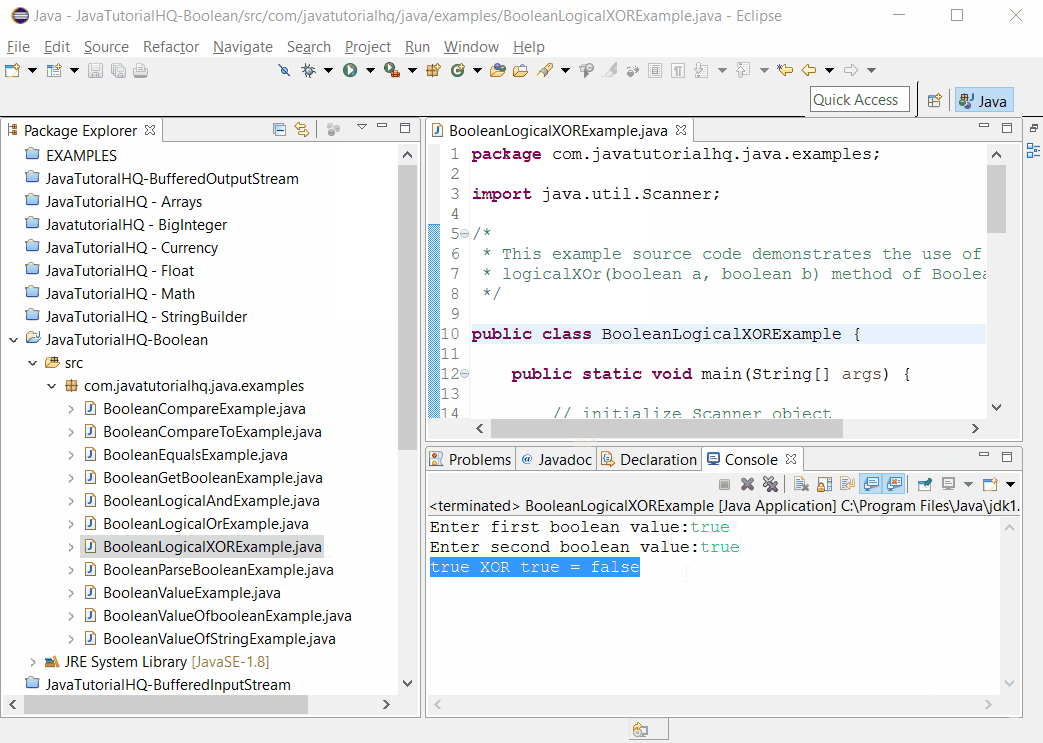
To fully demonstrate the behaviour of logicalXor() method, the program above is designed in such a way that user can enter two boolean values and then the result of logicalXor() method is displayed based on the two user input. On this way, the user can experiment on different values as input.
Sample Output
Below is the sample output when you run the above example.