java.lang.Boolean valueOf(String s)
Description
Make a note that the valueOf(String s) method of Boolean class is static thus it should be accessed statically. What I mean to say is that we should use this method such as below:
Boolean.valueOf(method args)
Non static method is usually called by just declaring method_name(argument) however in this case since the method is static, it should be called by appending the class name as suffix. We will be encountering a compilation problem if we call the java valueOf(String s) method non statically.
Method Syntax
public static Boolean valueOf(String s)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| String | s | a String. |
Method Returns
The valueOf(String s) method of Boolean class returns the Boolean value represented by the string.
Java Boolean valueOf(String s) Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of valueOf(String s) method of Boolean class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* valueOf(String s) method of Boolean class.
*/
public class BooleanValueOfStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ask for user input
System.out.print("Are you single (true/false)?");
// read the user input
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
String value = s.nextLine();
s.close();
// convert the user input into boolean
Boolean answer = Boolean.valueOf(value);
// evaluate the user input
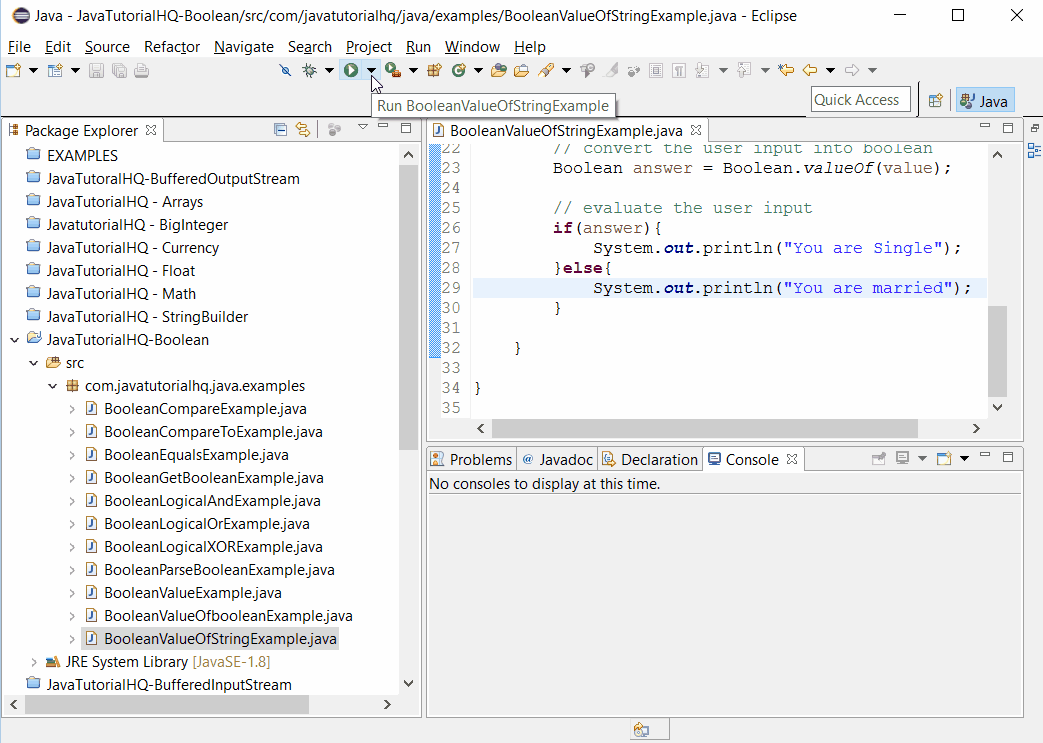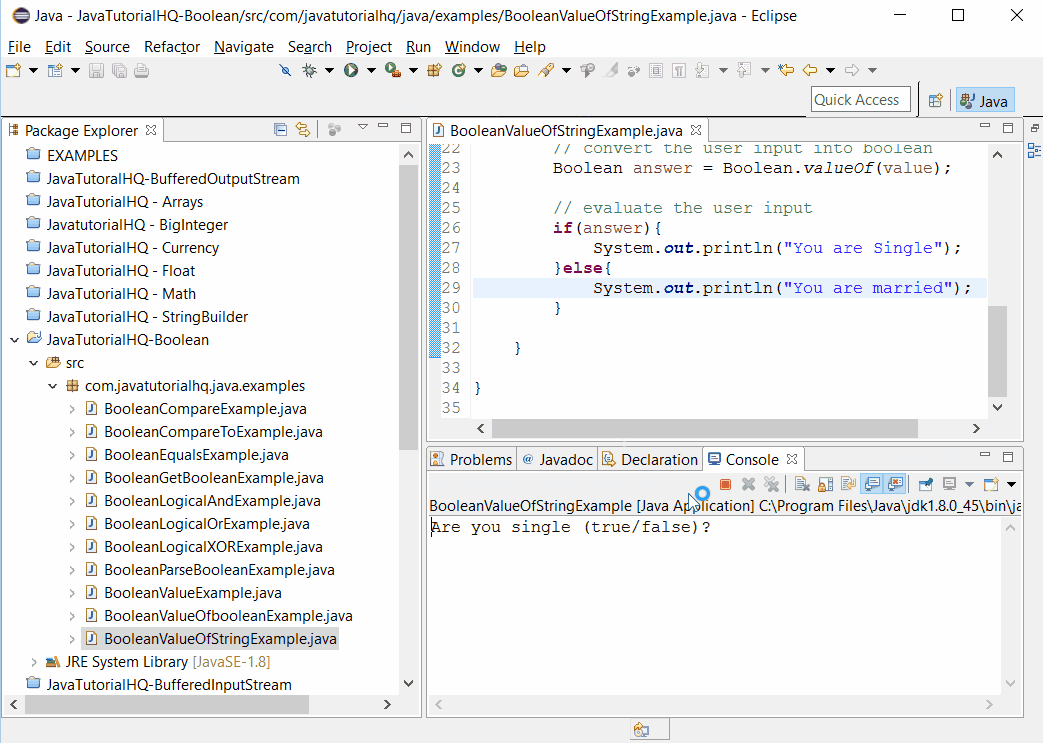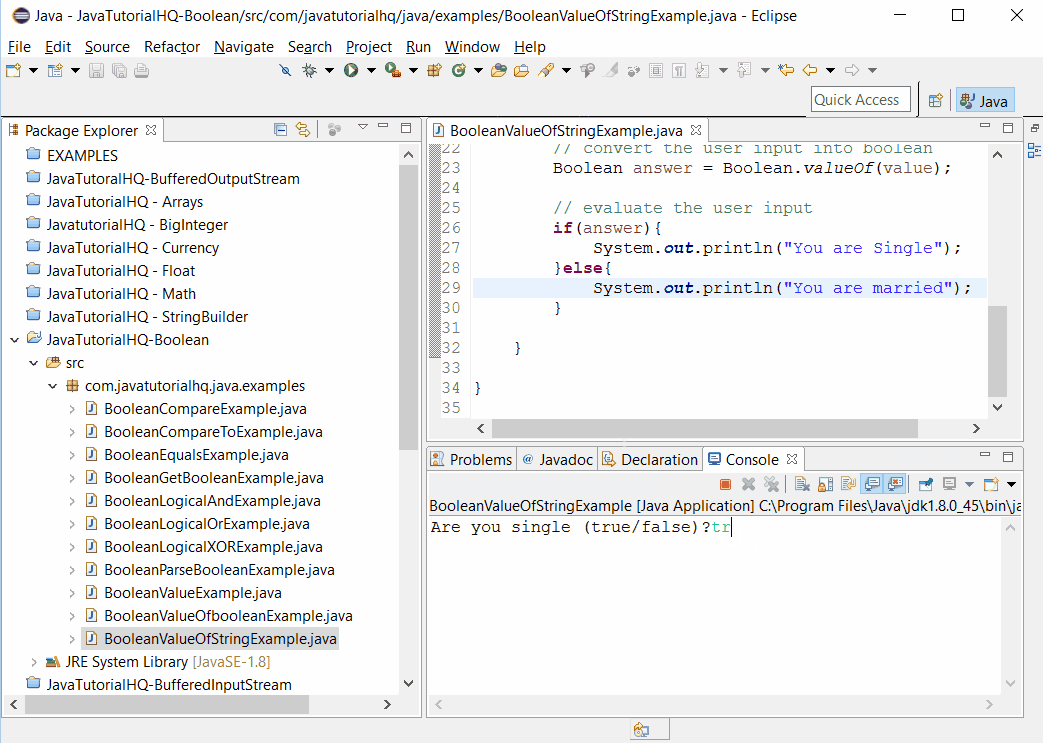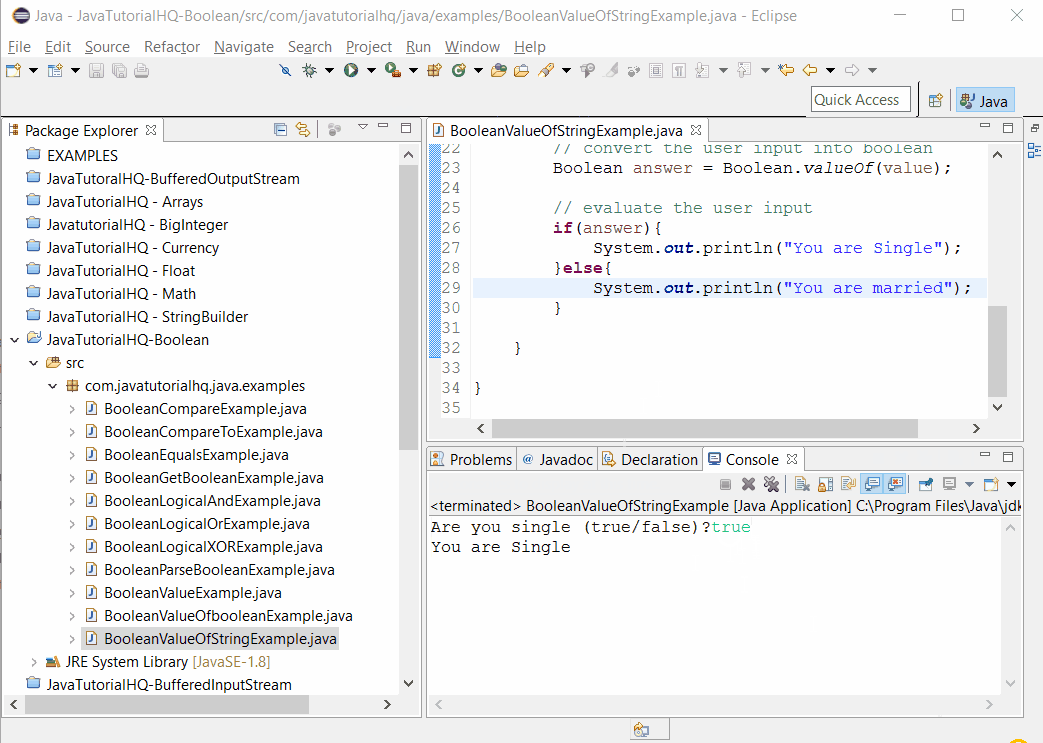
if(answer){
System.out.println("You are Single");
}else{
System.out.println("You are married");
}
}
}
Sample Output
Below is the sample output when you run the above example.