java.lang.Boolean parseBoolean(String s)
Description
Boolean.parseBoolean(method args)
Non static method is usually called by just declaring method_name(argument) however in this case since the method is static, it should be called by appending the class name as suffix. We will be encountering a compilation problem if we call the java parseboolean method non statically.
Method Syntax
public static boolean parseBoolean(String s)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| String | s | the String containing the boolean representation to be parsed |
Method Returns
The parseBoolean() method of Boolean class returns the boolean represented by the string argument.
Discussion
Example: Boolean.parseBoolean("True") returns true.Example: Boolean.parseBoolean("yes") returns false.
Java Boolean parseBoolean(String s) Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of parseBoolean(String s) method of Boolean class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* parseBoolean(String s) method of Boolean class.
*/
public class BooleanParseBooleanExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ask for user input
System.out.print("Are you single (true/false)?");
// read the user input
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
String value = s.nextLine();
s.close();
// convert the user input into boolean
boolean answer = Boolean.parseBoolean(value);
// evaluate the user input
if(answer){
System.out.println("You are Single");
}else{
System.out.println("You are married");
}
}
}
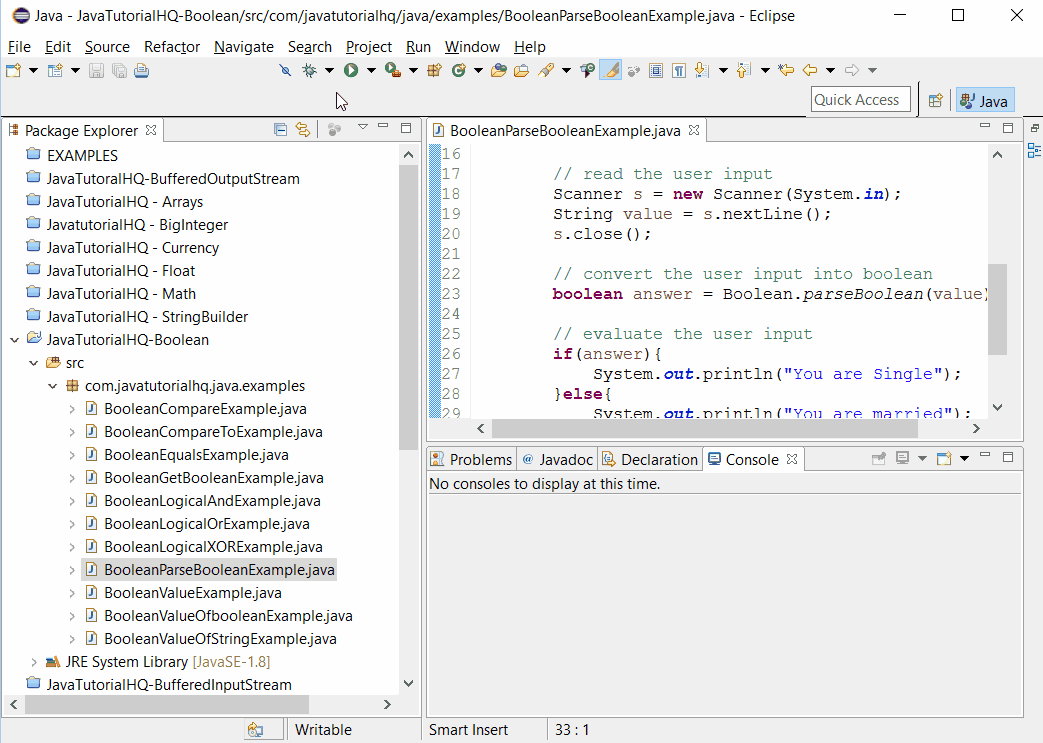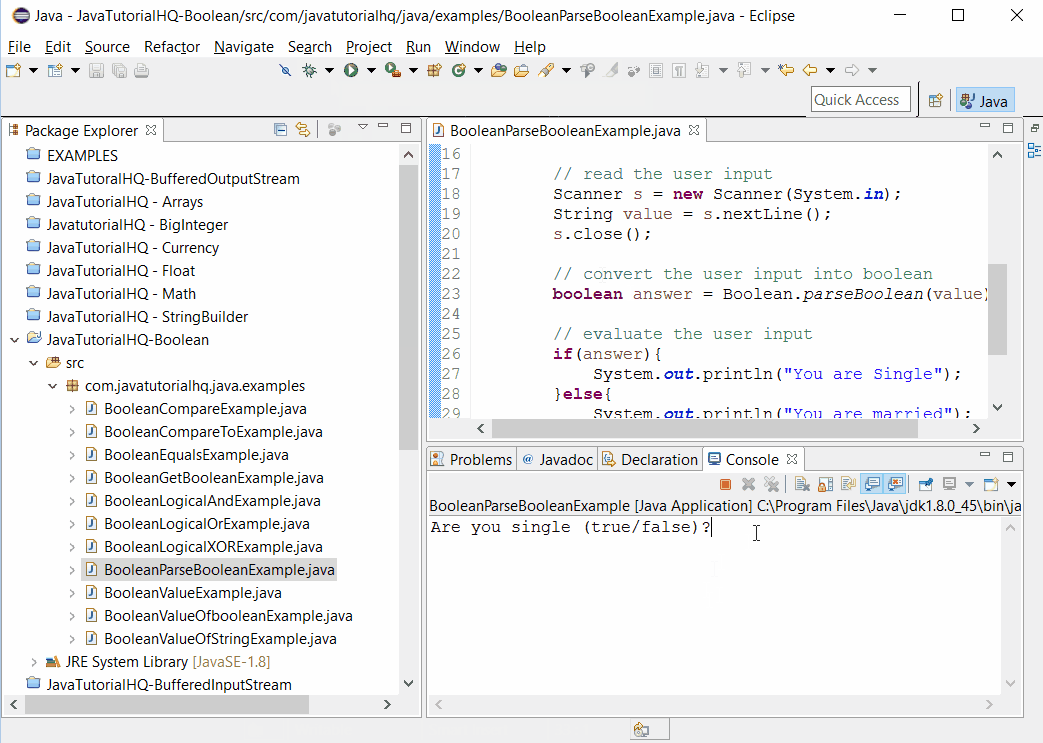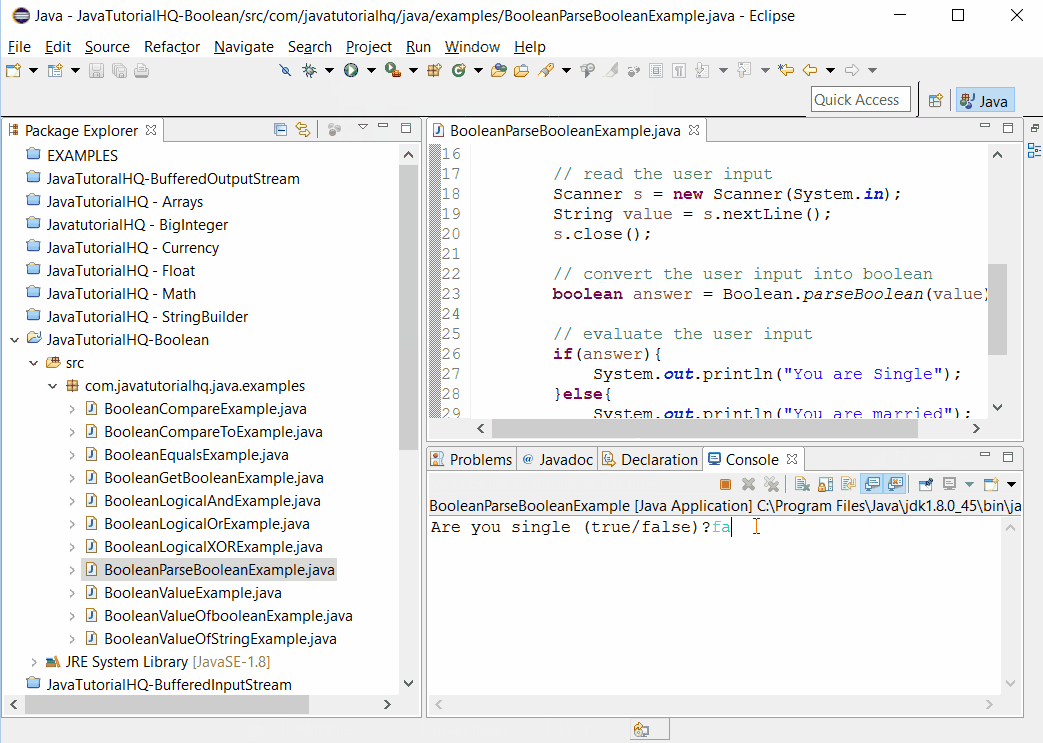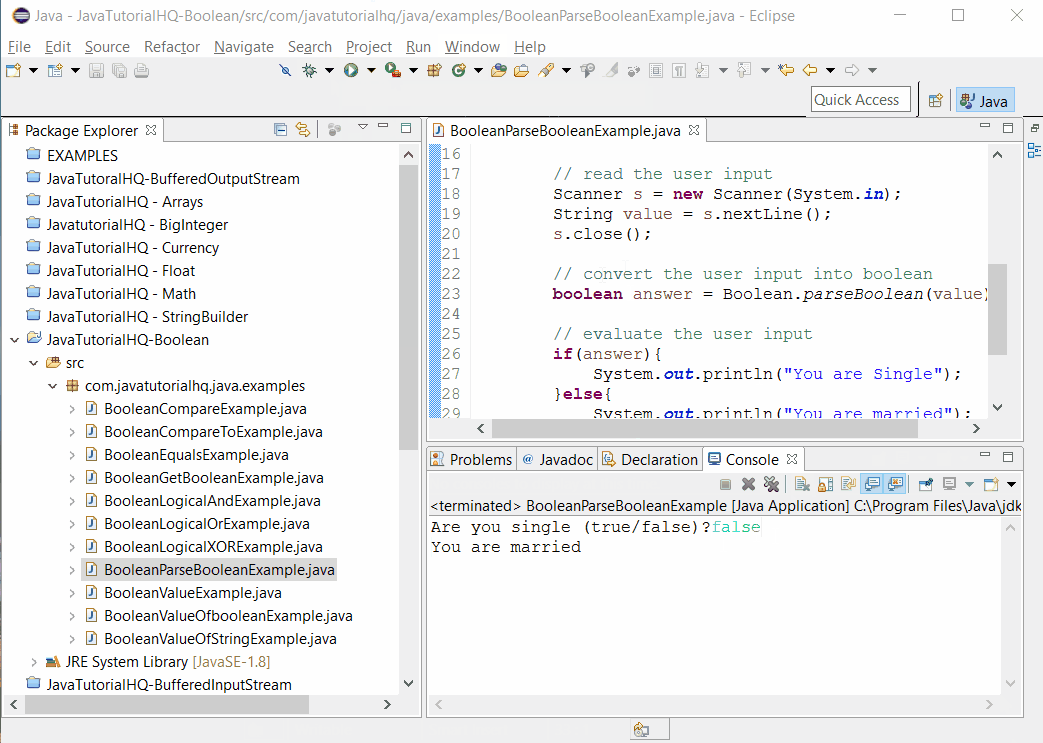
To fully demonstrate the behaviour of parseBoolean(String s) method, the program above is designed in such a way that user can enter two boolean values and then the result of parseBoolean(String s) method has been evaluated using if else and appropriate message were displayed on the console. On this way, the user can experiment on different values as input.
Sample Output
Below is the sample output when you run the above example.