java.lang.Byte byteValue()
Description
Important Notes:
- The method
byteValue()overrides byteValue in class Number
Method Syntax
public byte byteValue()
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method Returns
The byteValue() method of Byte class returns the numeric value represented by this object after conversion to type byte.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.1 and up
Java Byte byteValue() Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of byteValue() method of Byte class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* byteValue() method of Byte class.
*/
public class ByteValueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// instantiate a new Byte object
Byte byteObject = new Byte("12");
// convert byteObject to byte primitive
byte bytePrimitive = byteObject.byteValue();
// print the result
System.out.print("Byte object " + byteObject +
" primitive value is " + bytePrimitive);
}
}
Basically on the above example, we have declared a new Byte object and then eventually converted into primitive byte. As you would have noticed already, the printed value is the same as the instantiated Byte object. But remember that the result is now a primitive type. Anyway because of autoxing and unboxing features which have been introduced at the newer version of java, the byteValue() method renders as obsolete.
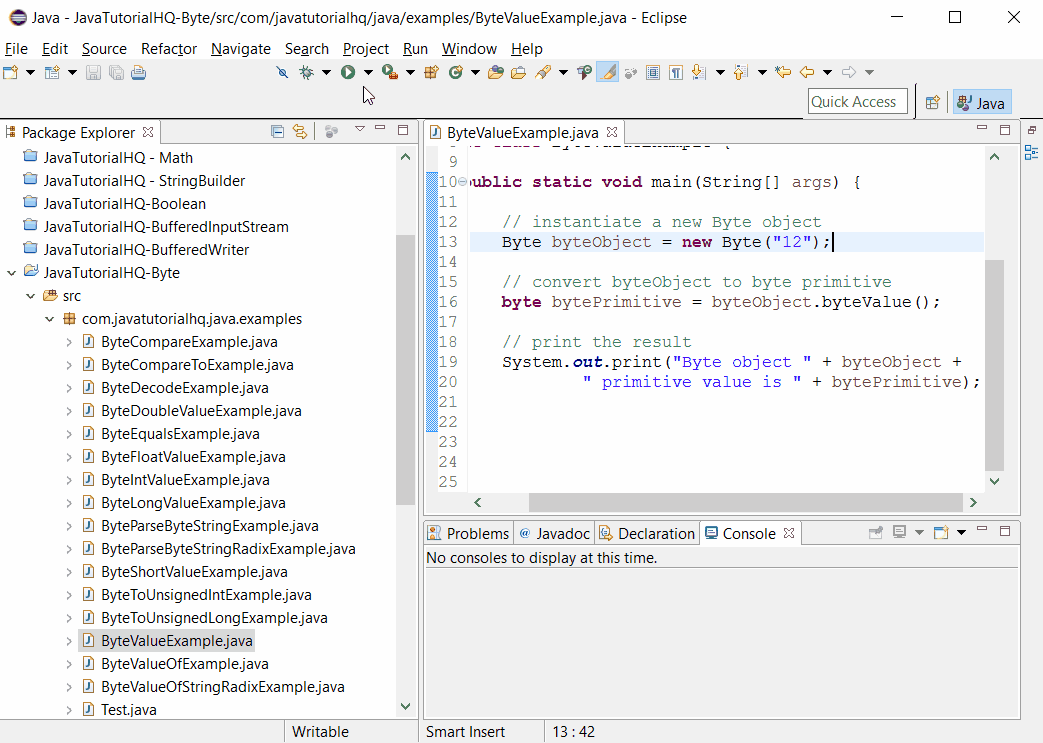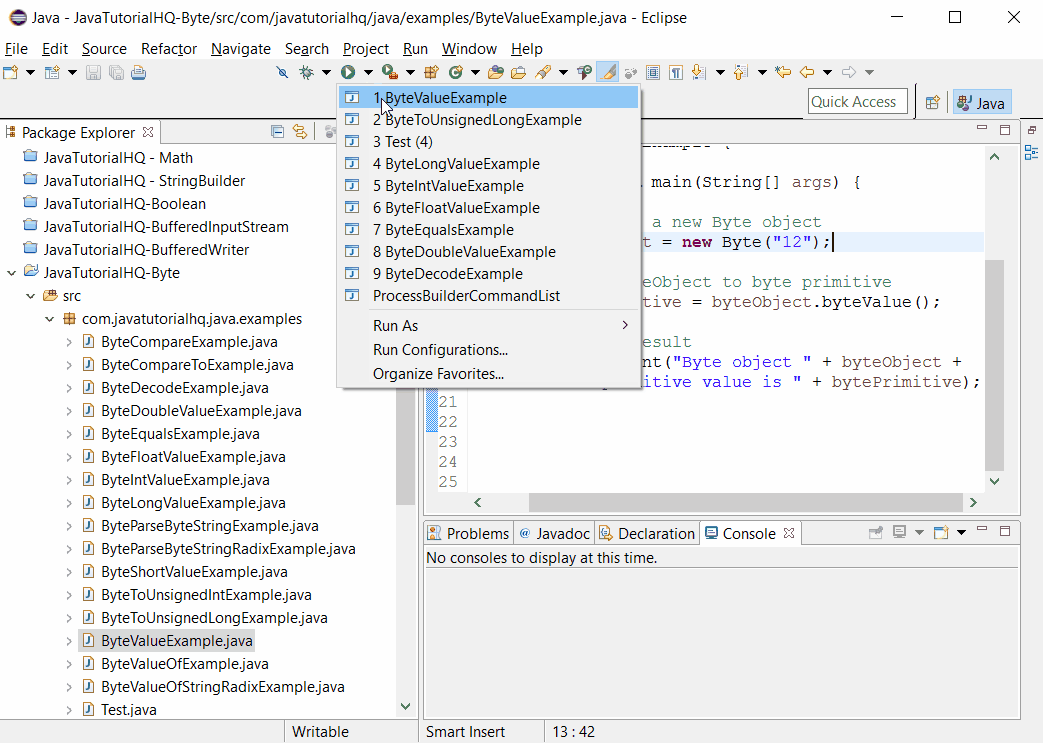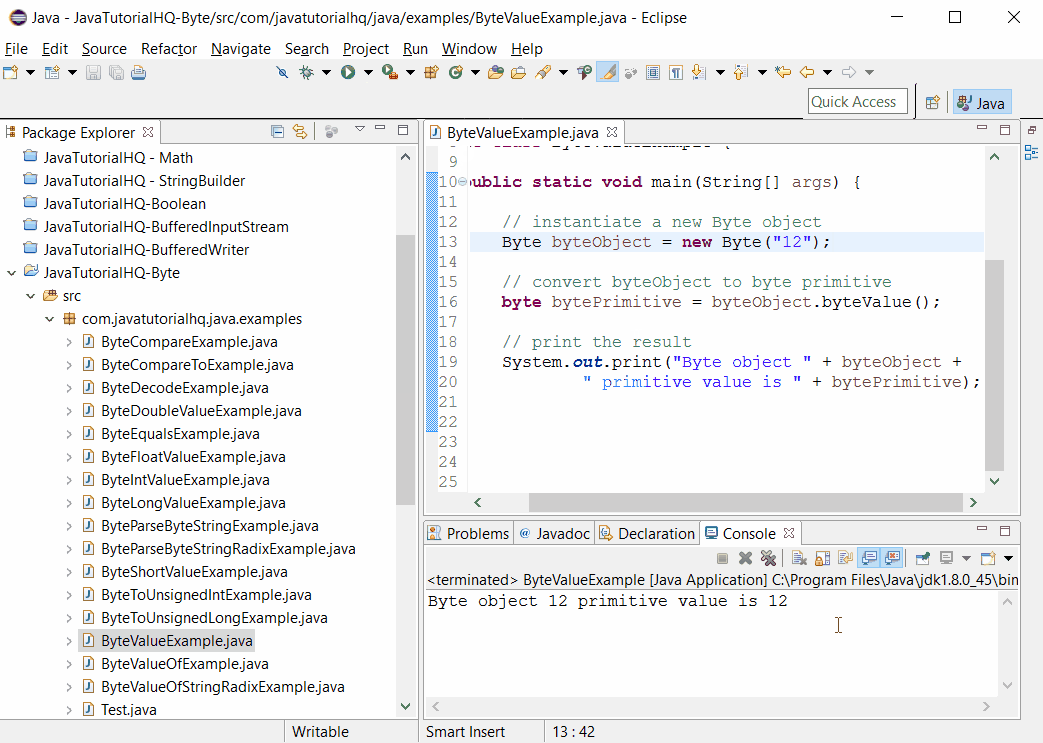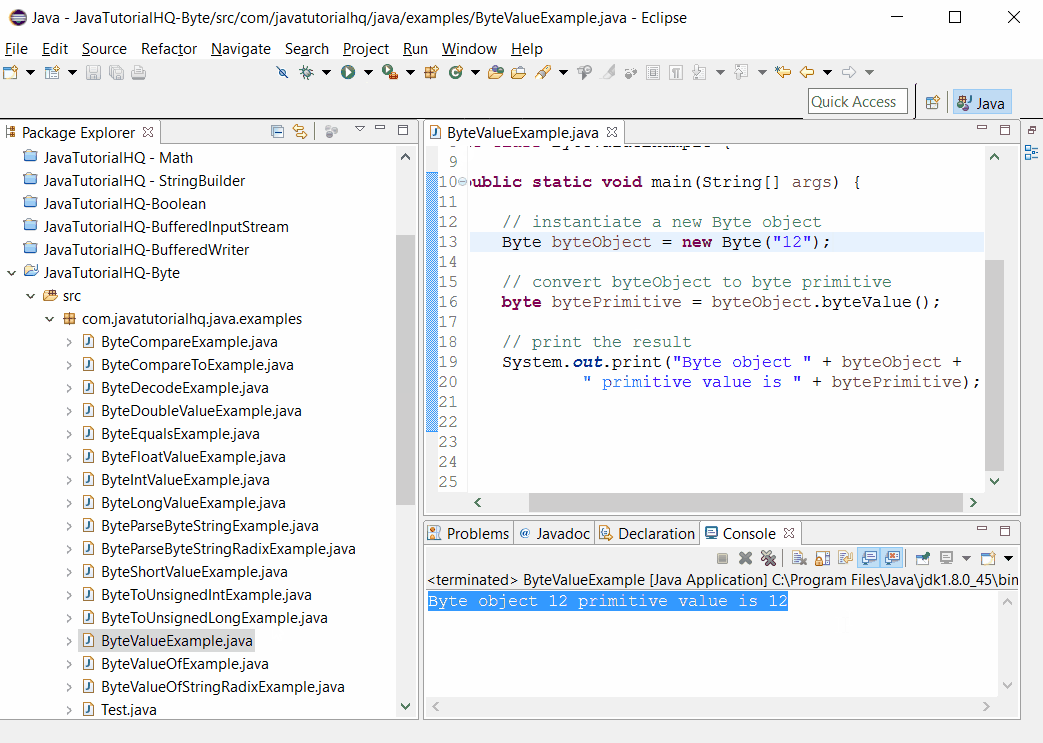
Sample Output
Below is the sample output when you run the above example.