java.lang.Byte equals()
Description
Important Notes:
- The method
equals(Object obj)overrides equals in class Object
Method Syntax
public boolean equals(Object obj)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Object | obj | the object to compare with |
Method Returns
The equals(Object obj) method of Byte class returns true if the objects are the same; false otherwise.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.1 and up
Discussion
Byte b1 = 12; Byte b2 = 12; System.out.println(b1==b2);
Normally if the above code declaration uses byte primitive type, the result would be true however since the byte value 12 is assigned to wrapper class Byte, it would print out false. If we wanted to use the == operator instead of equals, then we need to convert the Byte values using the byteValue() method of Float class so as to convert the wrapper classes to primitive values
b1.byteValue() == b2.byteValue()
The above code snippet would result to true.
Java Byte equals(Object obj) Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of equals() method of Byte class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* equals(Object obj) method of Byte class.
*/
public class ByteEqualsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// instantiate a Boolean
Byte b = new Byte("15");
// instantiate an Object
Object obj = new Byte("15");
// test equality of the two value
if(b.equals(obj)){
System.out.println("they are equal using equals test");
}
else{
System.out.println("they are not equal using equals test");
}
// test equality of the two value using ==
if(b==obj){
System.out.println("they are equal using == test");
}
else{
System.out.println("they are not equal using == test");
}
}
}
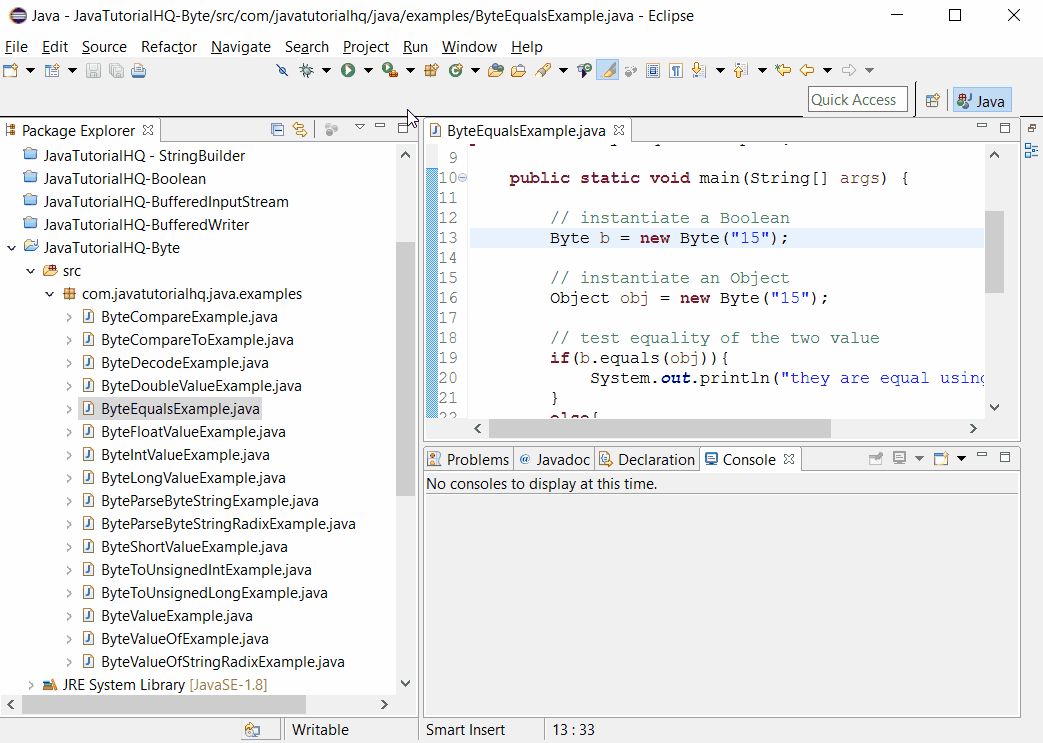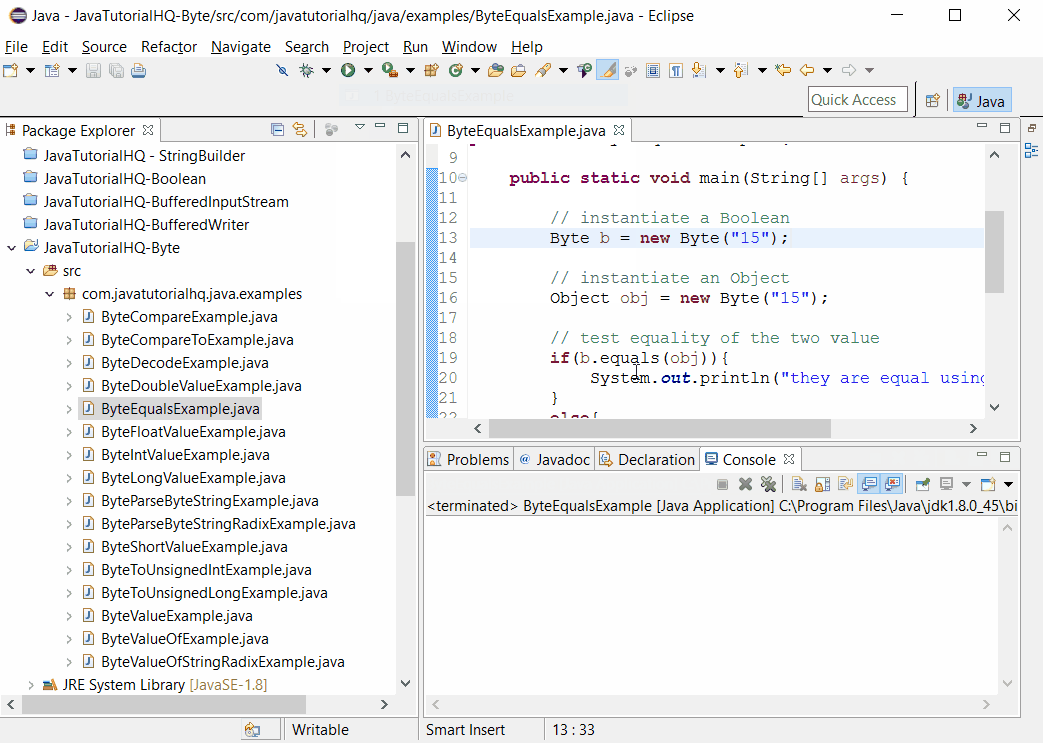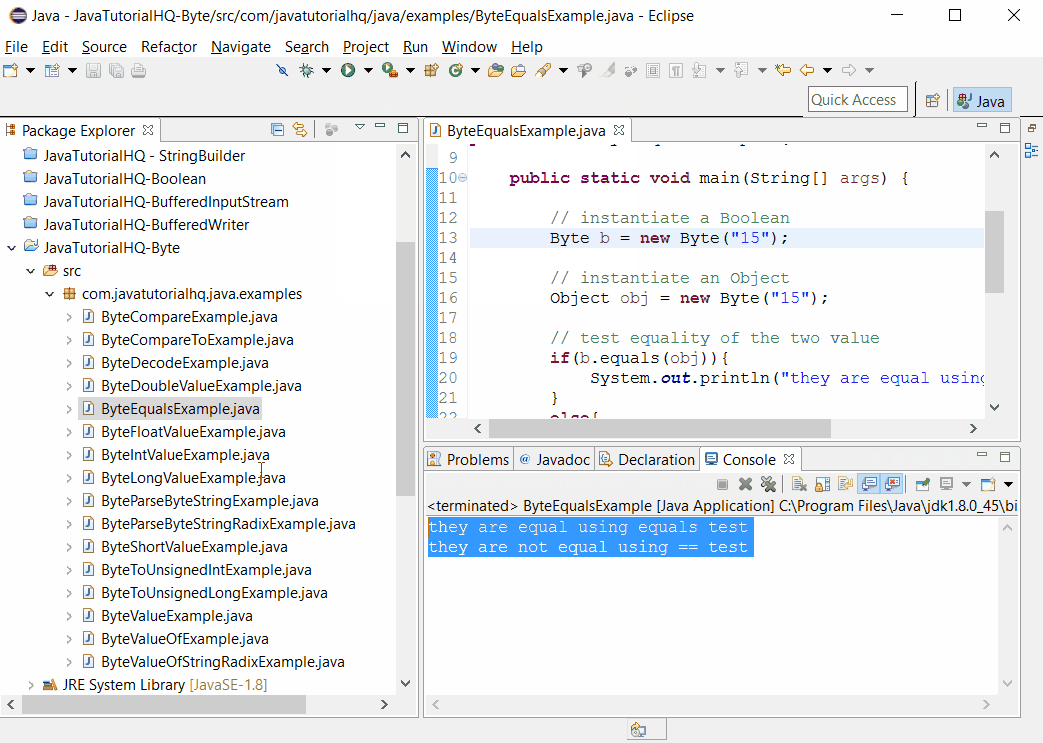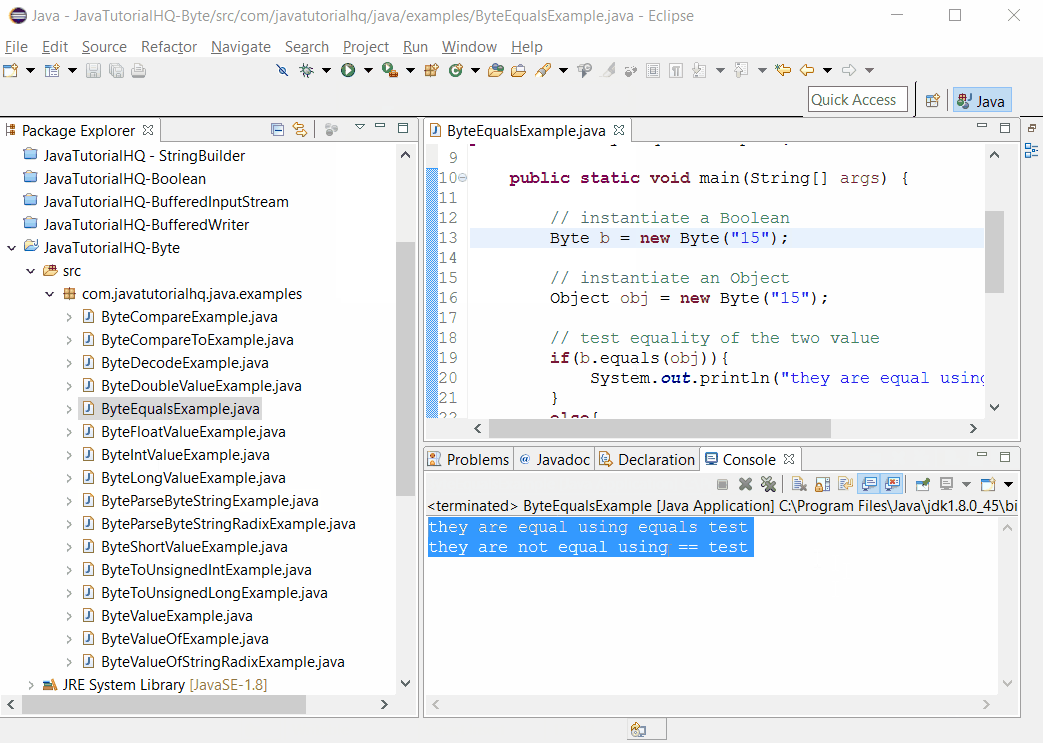
Basically on the above example, we have declared a Byte which has a value 15 and also an object whose type is Byte with a value of 15 as well. To demonstrate the difference in using the operator == and equals() method, we have evaluated both and printed the result. You would notice the == operator will yield to false because both of the objects are two different instances. While the equals() method will yield true because the two Byte have the same numerical value.
Sample Output
Below is the sample output when you run the above example.