java.lang.Byte compareTo(Byte anotherByte)
Description
Important Notes:
- The method
compareTo(Byte anotherByte)is specified by compareTo in interface Comparable<Byte>
Method Syntax
public int compareTo(Byte anotherByte)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Byte | anotherByte | the Byte to be compared. |
Method Returns
The compareTo() method of Byte class returns the value 0 if this Byte is equal to the argument Byte; a value less than 0 if this Byte is numerically less than the argument Byte; and a value greater than 0 if this Byte is numerically greater than the argument Byte (signed comparison).
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.2 and up
Discussion
The compareTo() method and compare() method yield the same result. The only difference is that if you want to just compare two primitive byte datatype without having to convert to Byte object, compare() method is already enough. However if you opt to compare two Byte object, the compareTo() method will do the job better.
Java Byte compareTo(Byte anotherByte) Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of compareTo() method of Byte class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* compareTo(Byte anotherByte) method of Byte class.
*/
public class ByteCompareToExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize 3 Byte object
Byte firstValue = new Byte("12");
Byte secondValue = 12;
Byte thirdValue = 15;
// compare the first byte to the second
int compareOneTwo = firstValue.compareTo(secondValue);
// compare the first byte to the third
int compareOneThree = firstValue.compareTo(thirdValue);
// display the comparison result of first
// and second value
if (compareOneTwo == 0) {
System.out.println("First and second value are equal");
}else if(compareOneTwo > 0){
System.out.println("First value is greater than second value");
}else{
System.out.println("First value is less than second value");
}
// display the comparison result of first
// and third value
if (compareOneThree == 0) {
System.out.println("First and third value are equal");
}else if(compareOneTwo > 0){
System.out.println("First value is greater than third value");
}else{
System.out.println("First value is less than third value");
}
}
}
Basically on the above example, we have declared three Byte values. We then use the compareTo method to do comparison of these three values. Based on the result of this method, we have devised a logic to display specific messages.
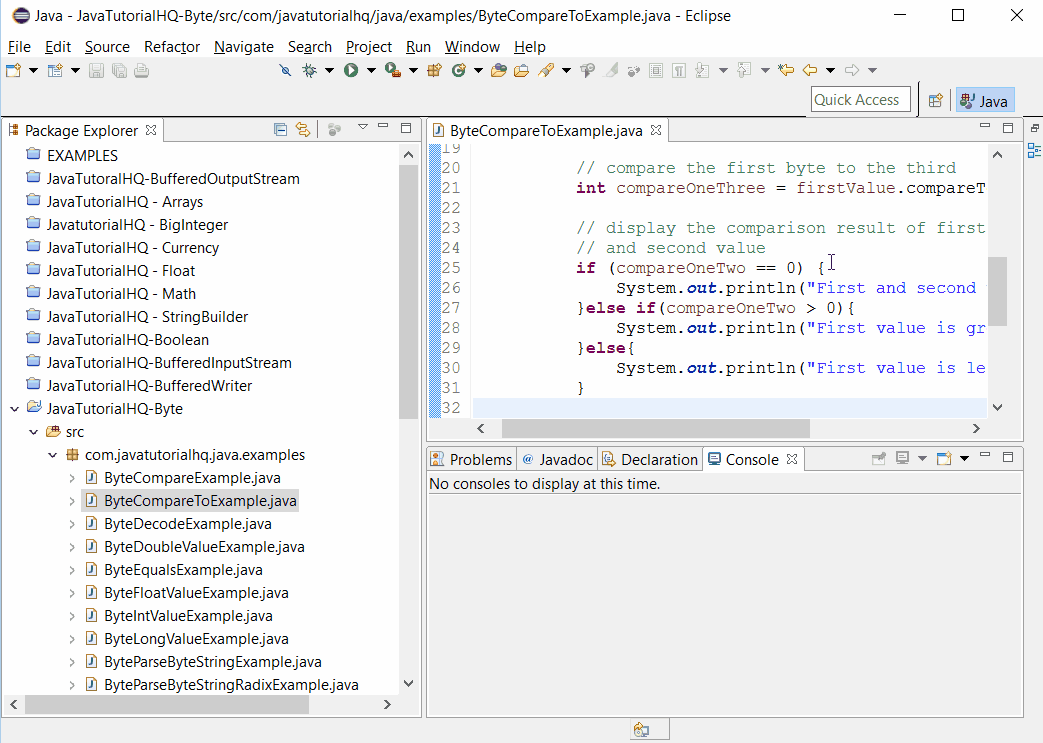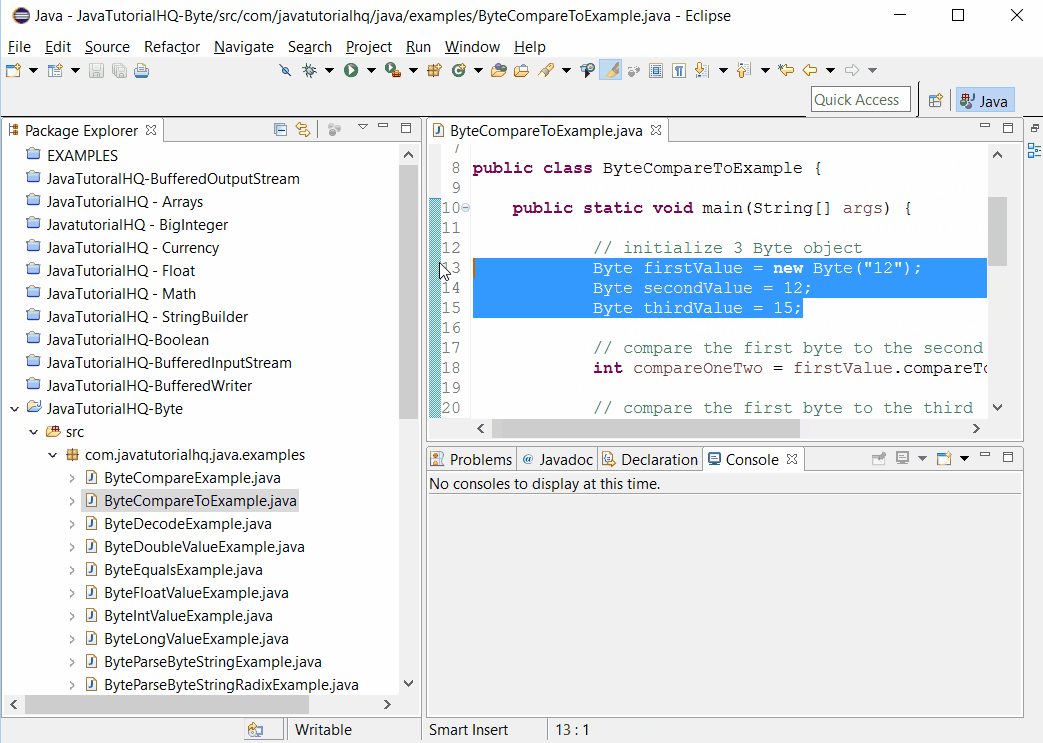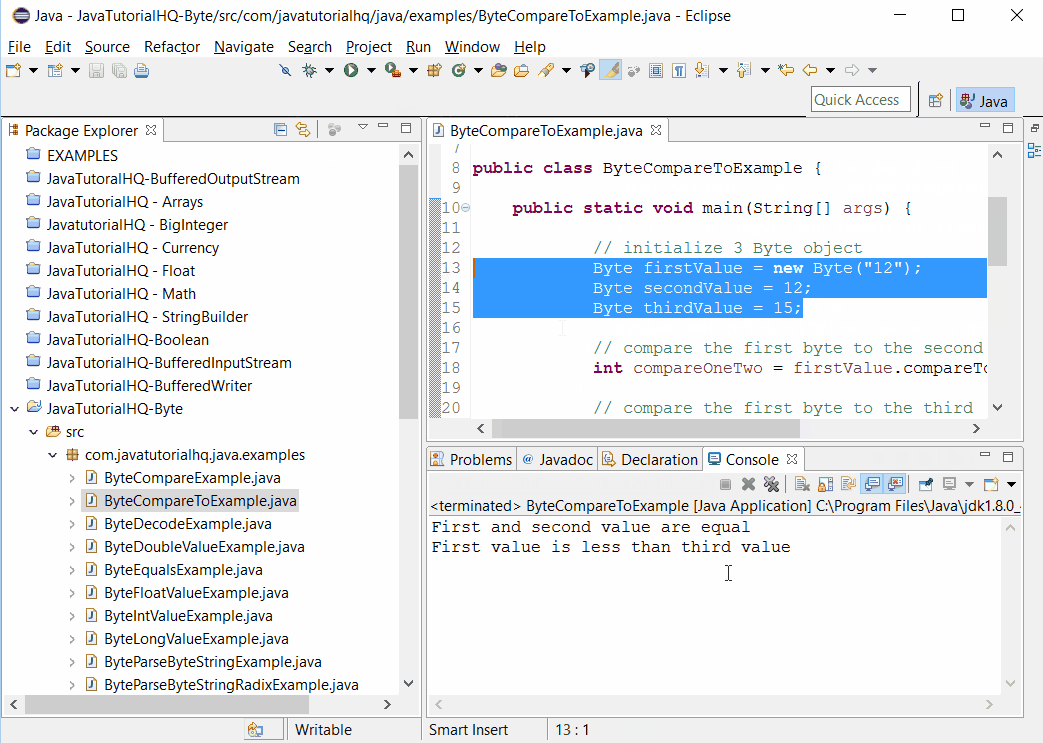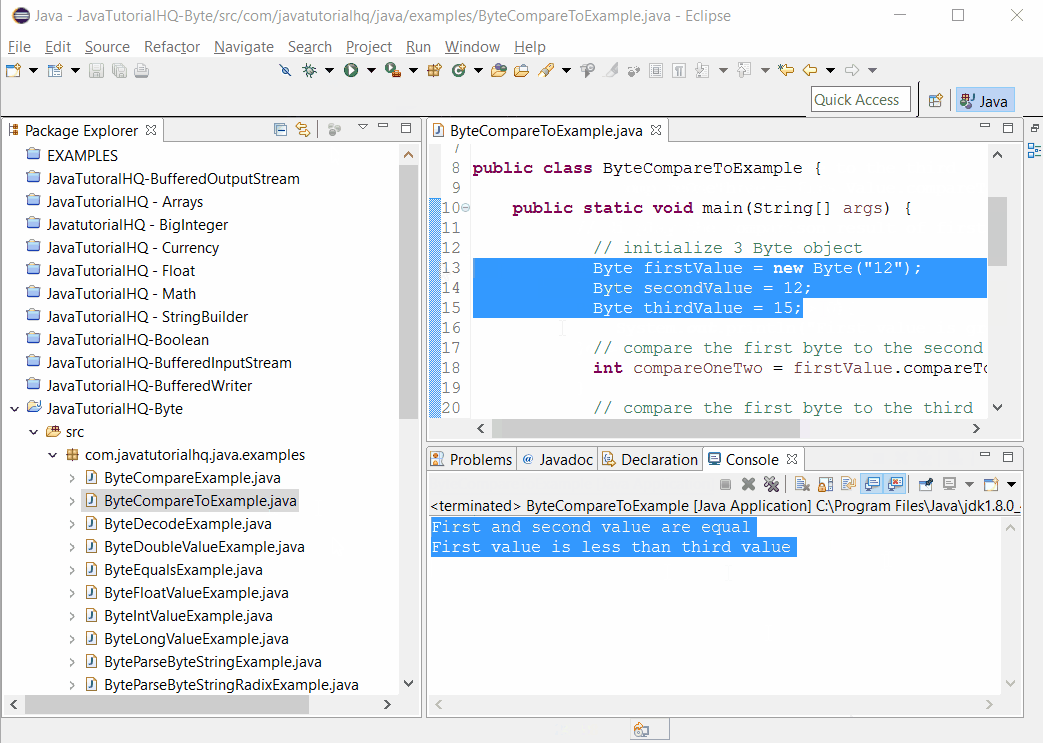
Sample Output
Below is the sample output when you run the above example.