java.lang.Byte toUnsignedLong(byte x)
Description
Make a note that the toUnsignedLong method of Byte class is static thus it should be accessed statically which means the we would be calling this method in this format:
Byte.toUnsignedLong(method args)
Non static method is usually called by just declaring method_name(argument) however in this case since the method is static, it should be called by appending the class name as suffix. We will be encountering a compilation problem if we call the java toUnsignedLong method non statically.
Method Syntax
public static long toUnsignedLong(byte x)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| byte | x | the value to convert to an unsigned long |
Method Returns
The toUnsignedLong(byte x) method of Byte class returns the argument converted to long by an unsigned conversion
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.8 and up
Java Byte toUnsignedLong(byte x) Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of toUnsignedLong(byte x) method of Byte class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* toUnsignedLong(byte x) method of Byte class.
*/
public class ByteToUnsignedLongExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ask for user input
System.out.print("Enter a number:");
// read the user input
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
String value = s.nextLine();
s.close();
Byte byteValue = new Byte(value);
// convert byteValue into unsign long
long result = Byte.toUnsignedLong(byteValue);
// print the result
System.out.println("unsigned long value is "+result);
}
}
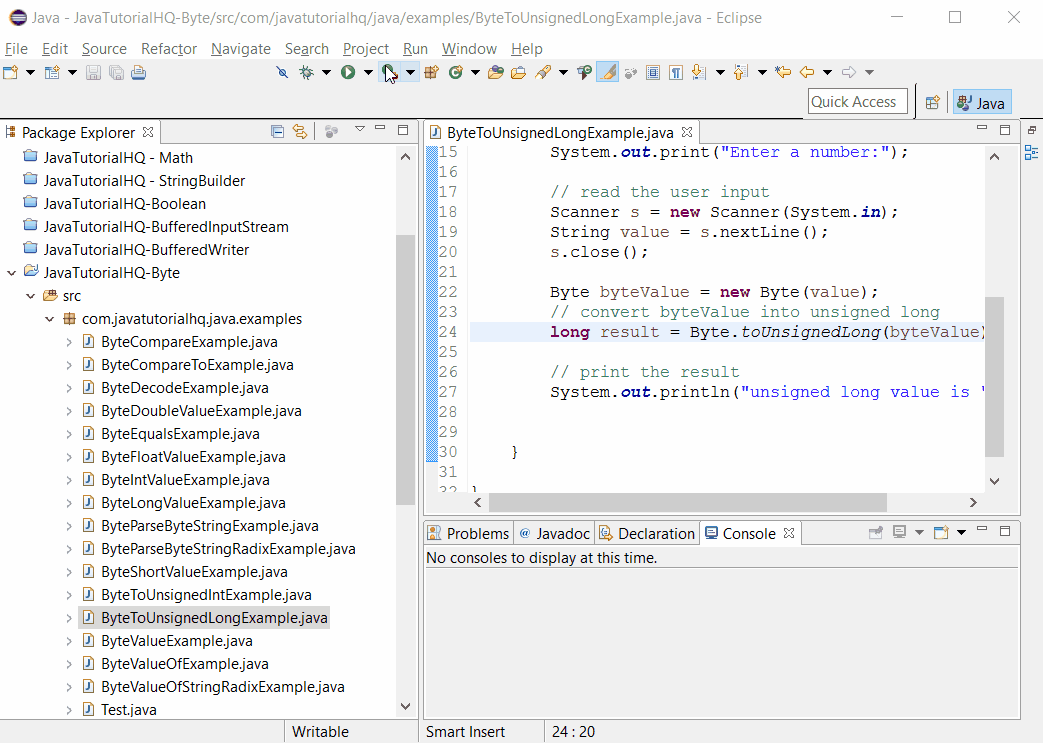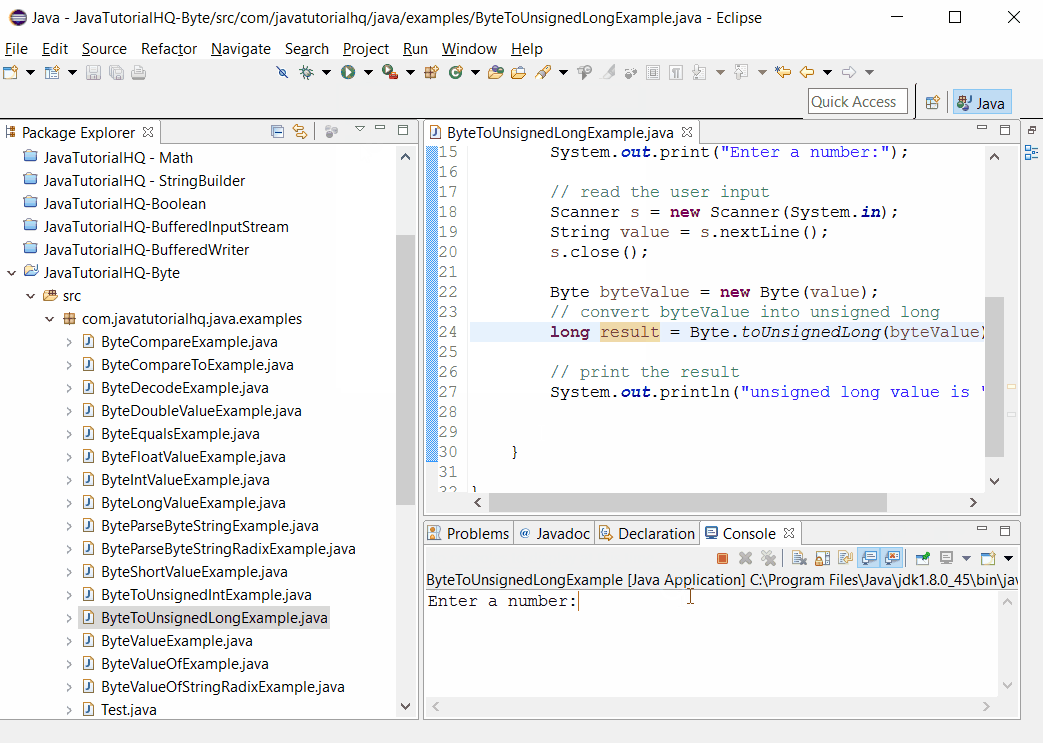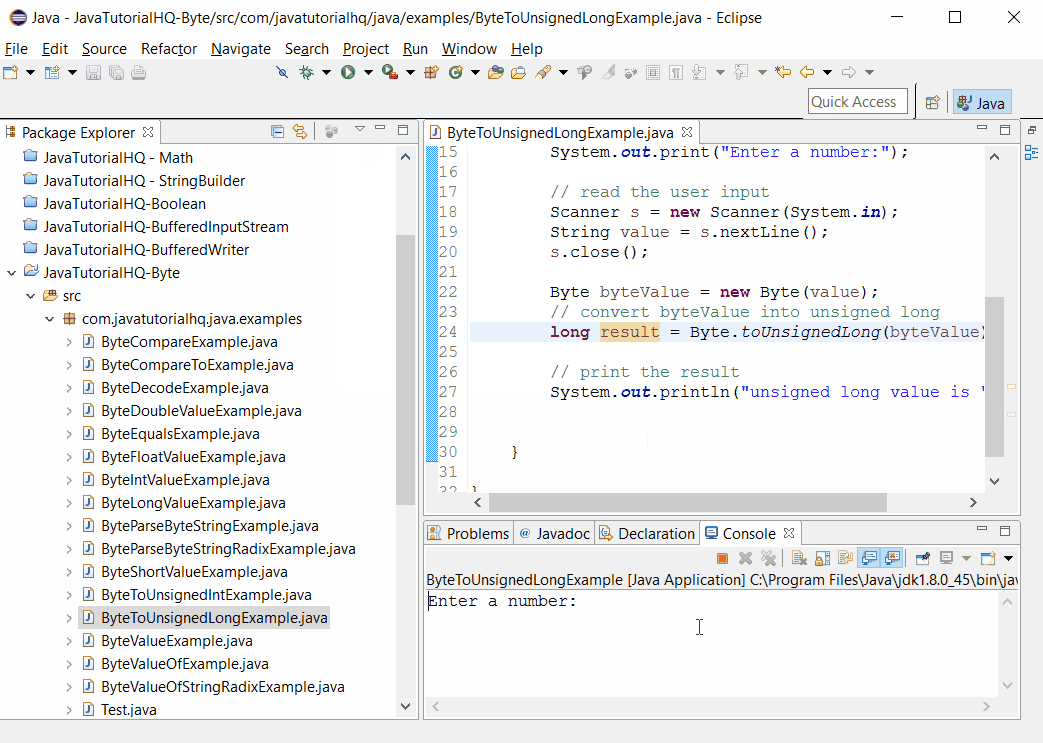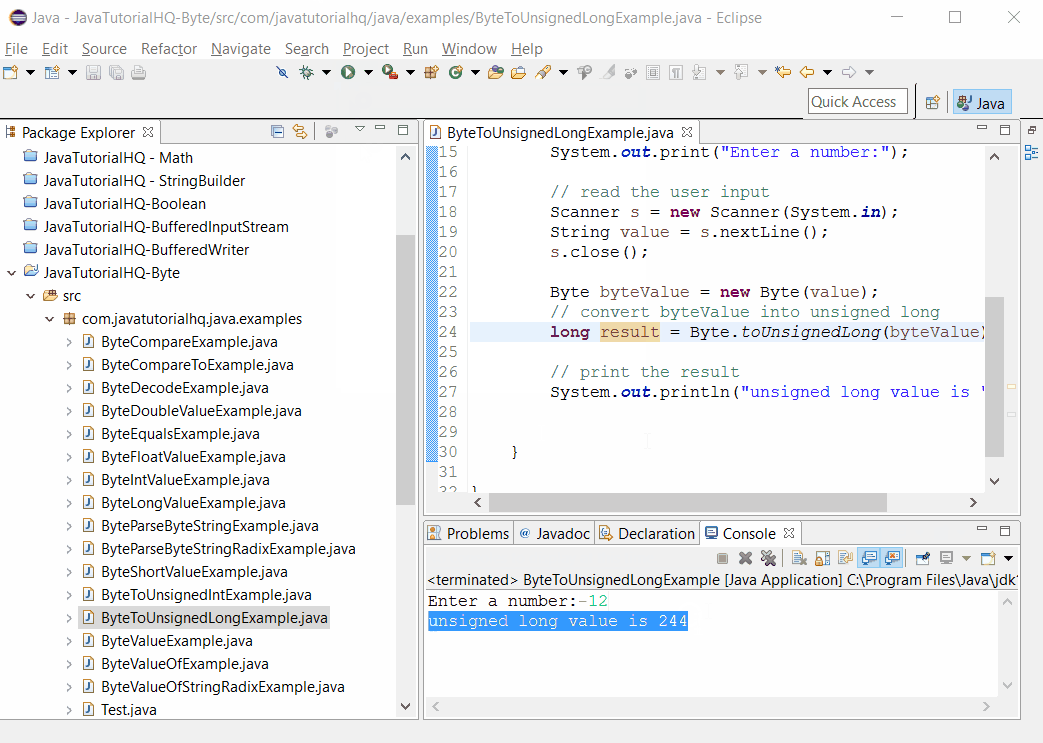
Basically on the above example, we have asked the user to enter a number on the console. Then we printed the result of the toUnsignedInt method. As you would have noticed positive numbers would result to the same number but for negative numbers that’s where we would see the difference in result.
Sample Output
Below is the sample output when you run the above example.