java.lang.Byte valueOf(String s, int radix)
Description
In other words, this method returns a Byte object equal to the value of:
new Byte(Byte.parseByte(s, radix))
Important Notes:
- The method
valueOf(String s, int radix)throwsNumberFormatException, if the String does not contain a parsable byte.
Method Syntax
public static Byte valueOf(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| String | s | the string to be parsed |
| int | radix | the radix to be used in interpreting s |
Method Returns
The valueOf(String s, int radix) method of Byte class returns a Byte object holding the value represented by the string argument in the specified radix.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.1 and up
Java Byte valueOf(String s, int radix) Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of valueOf(String s, int radix) method of Byte class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* valueOf(byte b) method of Byte class.
*/
public class ByteValueOfStringRadixExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ask for user input
System.out.print("Enter a octal number:");
// read the user input
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
String value = s.nextLine();
s.close();
// convert the user input (octal) into Byte
Byte result = Byte.valueOf(value, 8);
// print the result
System.out.print(value + " octal is equal to " + result);
}
}
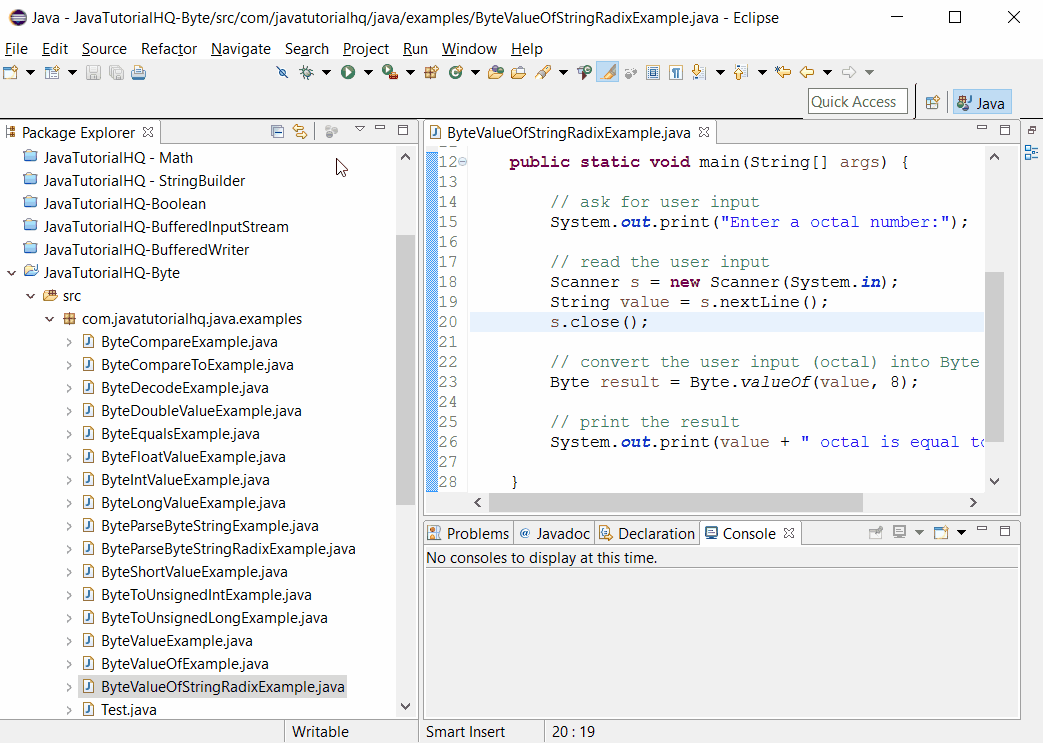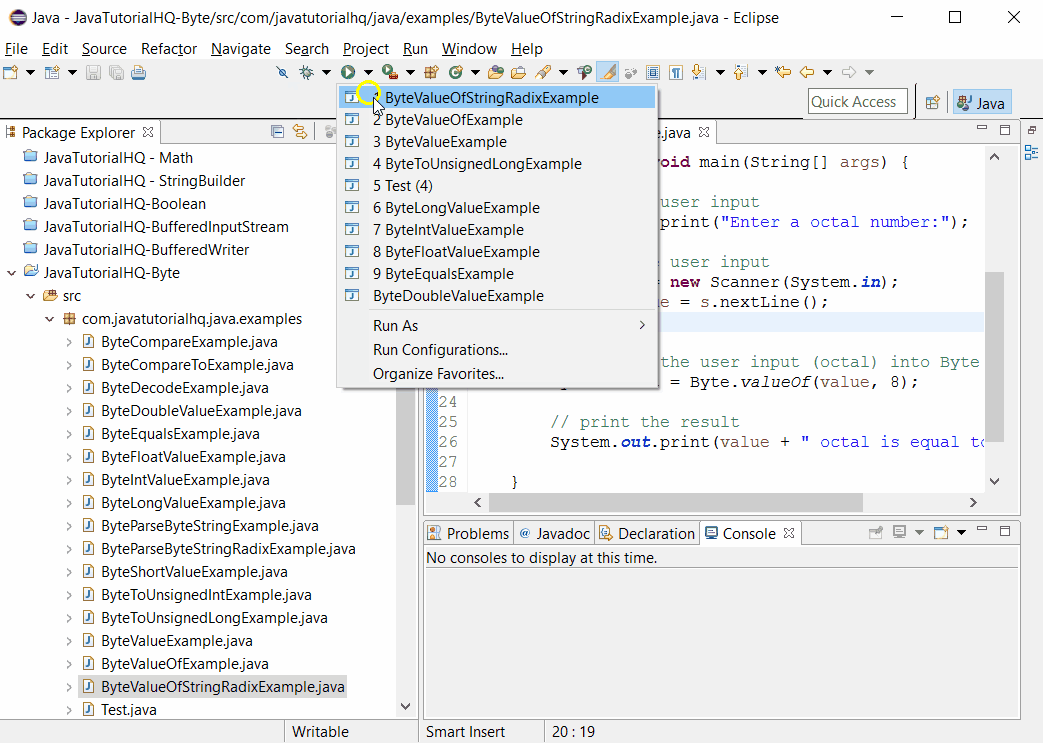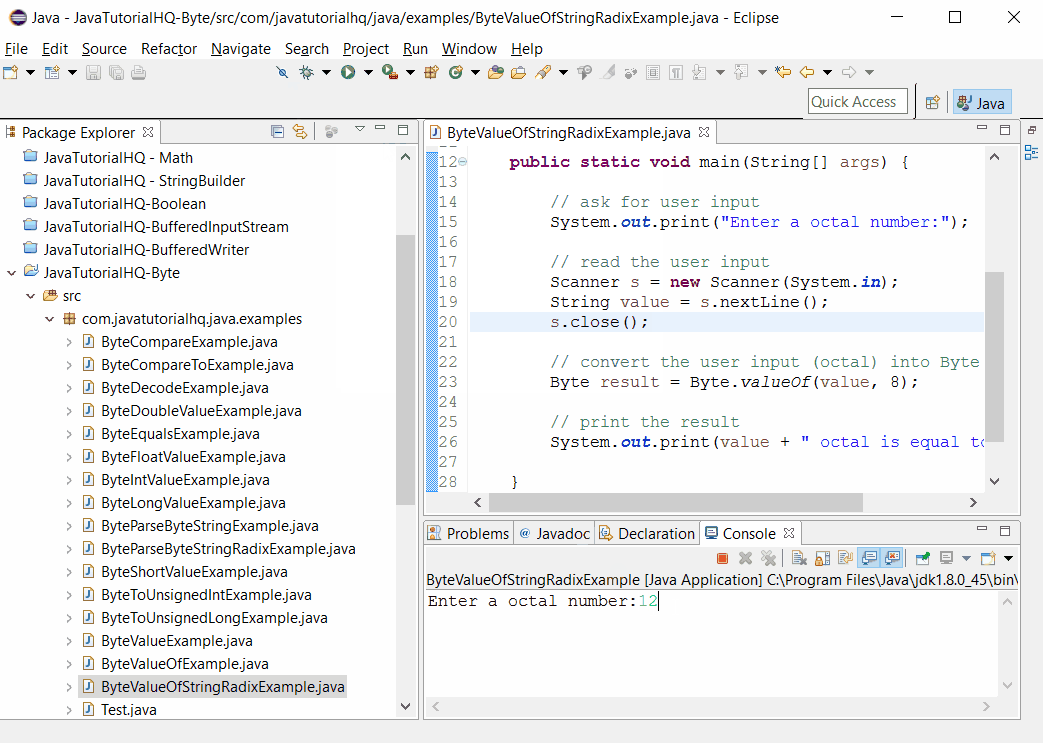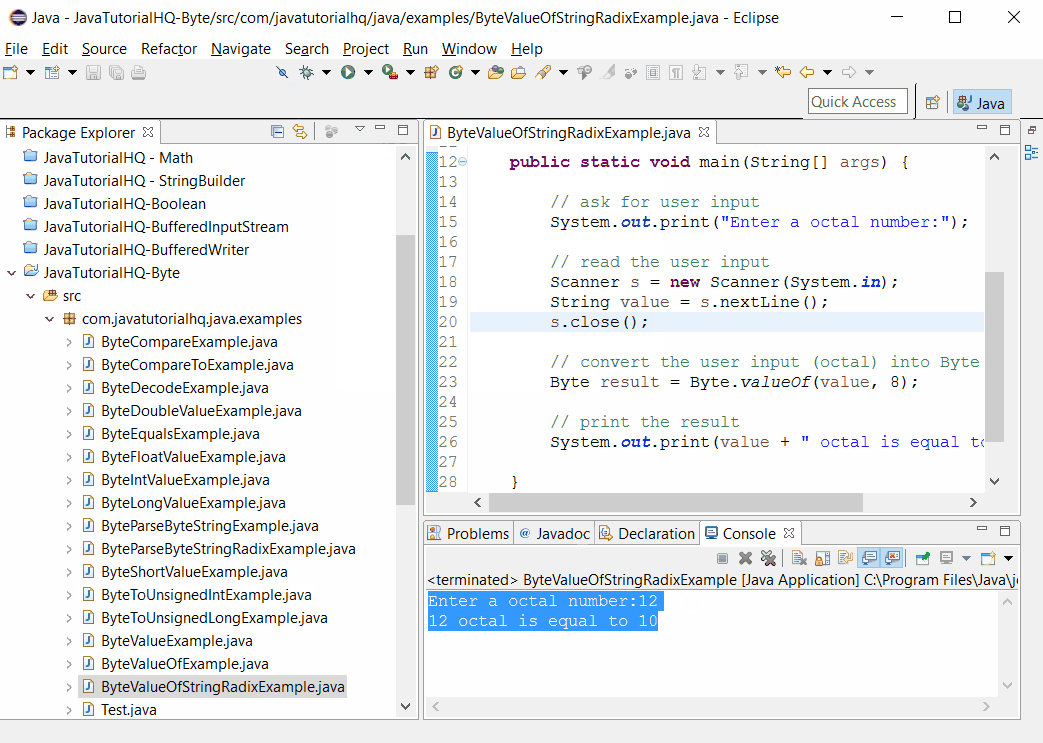
Sample Output
Below is the sample output when you run the above example.