java.lang.Float equals(Object obj)
Description
Important Notes:
- overrides equals in class Object
Method Syntax
public boolean equals(Object obj)
Method Returns
The equals(Object obj) method of Float class returns true if the objects are the same; false otherwise.
Compatibility
Java 1.0
Discussion
Float f1 = 3.12f; Float f2 = 3.12f; System.out.println(f1==f2);
Normally if the above code declaration uses float primitive type, the result would be true however since the float value 3.12f is assigned to wrapper class Float, it would print out false. If we wanted to use the == operator instead of equals, then we need to convert the Float values using the floatValue() method of Float class.
f1.floatValue() == f2.floatValue()
The above code snippet would result to true.
Java Float equals(Object obj) Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of equals(Object obj) method of Float class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Scanner;
import static java.lang.System.*;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* equals(Object obj) method of Float class.
*/
public class FloatEqualsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Ask user input for first number
System.out.print("Enter First Number:");
// declare the scanner object
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// use scanner to get value from user console
Float f1 = scan.nextFloat();
// Ask user input for second number
System.out.print("Enter Second Number:");
Float f2 = scan.nextFloat();
// close the scanner object
scan.close();
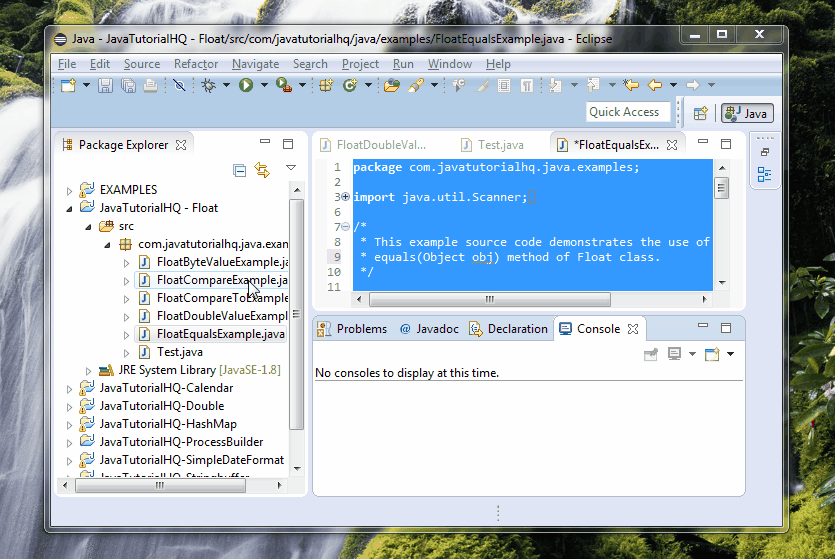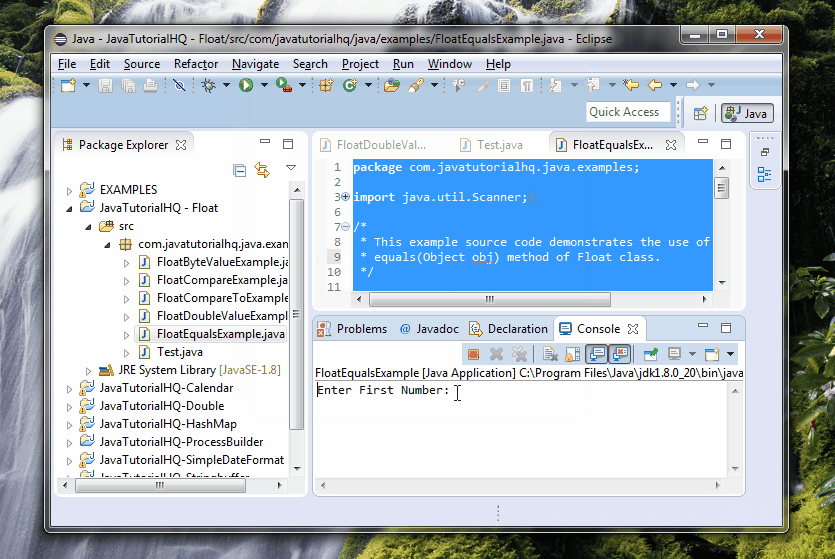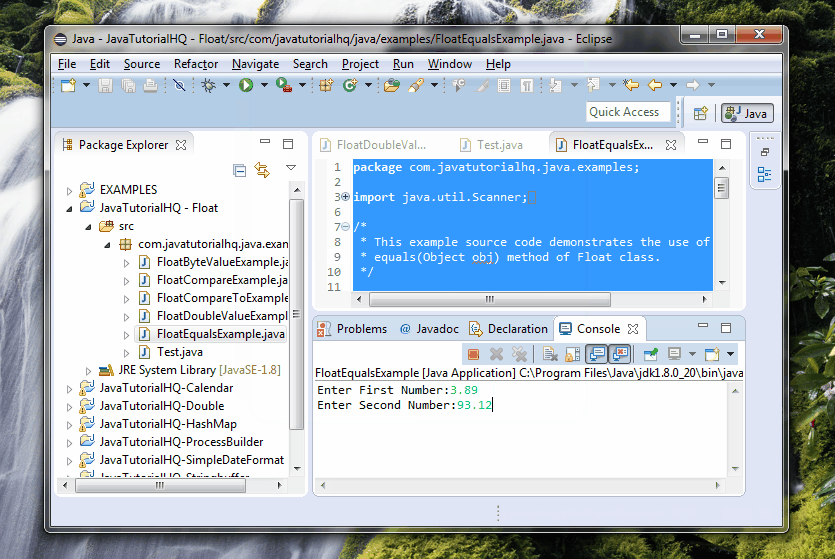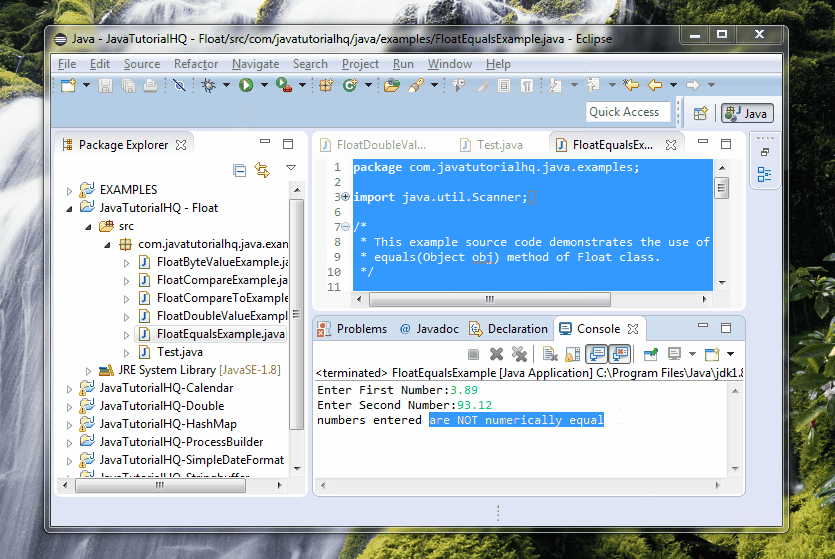
if (f1.equals(f2)) {
out.println("numbers entered are numerically equal");
} else {
out.println("numbers entered are NOT numerically equal");
}
}
}
Basically on the above example, we just ask for two values from user using the console. We then use Scanner class to assign the values entered to Float objects. These two object were tested for equality using the equals method of Float class. As a result of the test, we then printed out corresponding message to the console.