java.lang.Float floatValue()
Description
Float value = 1.32f then both of the following statement will yield the same result
float primitiveVal = value.floatValue()
and
float primitiveVal = value
The unboxing feature of java will take care of the conversion of Float object to its primitive data type.
Method Syntax
public float floatValue()
Method Returns
The floatValue() method of Float class returns the float value represented by this object.
Compatibility
Java 1.0
Java Float floatValue() Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of floatValue() method of Float class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Scanner;
import static java.lang.System.*;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* floatValue() method of Float class.
*/
public class FloatValueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Ask user input
System.out.print("Enter Desired Value:");
// declare the scanner object
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// use scanner to get value from user console
Float userInput = scan.nextFloat();
// close the scanner object
scan.close();
// convert the Float input to primitive float
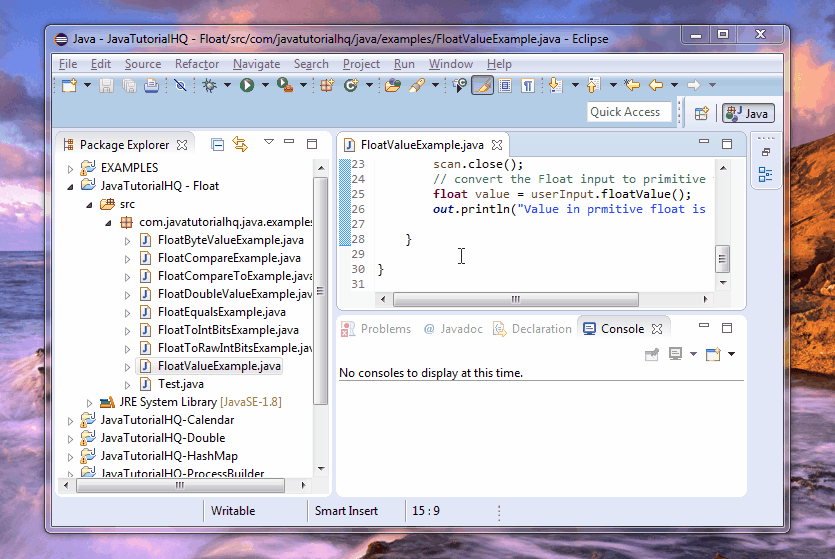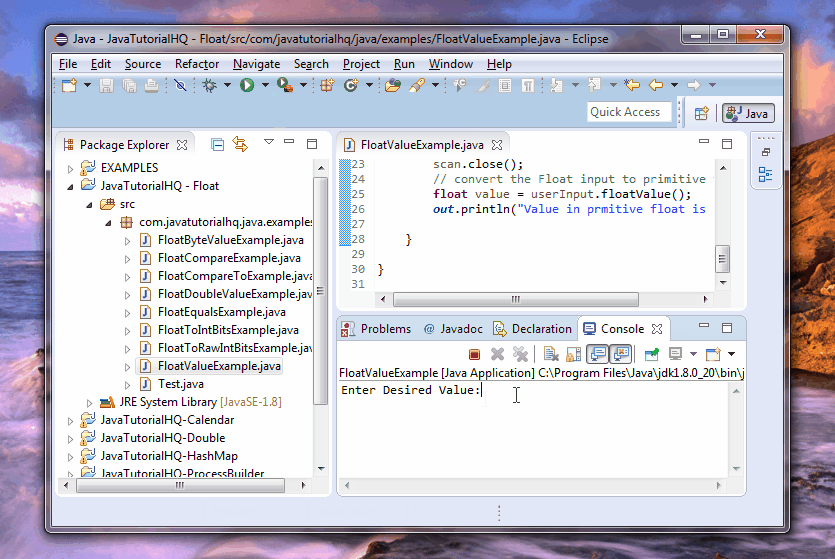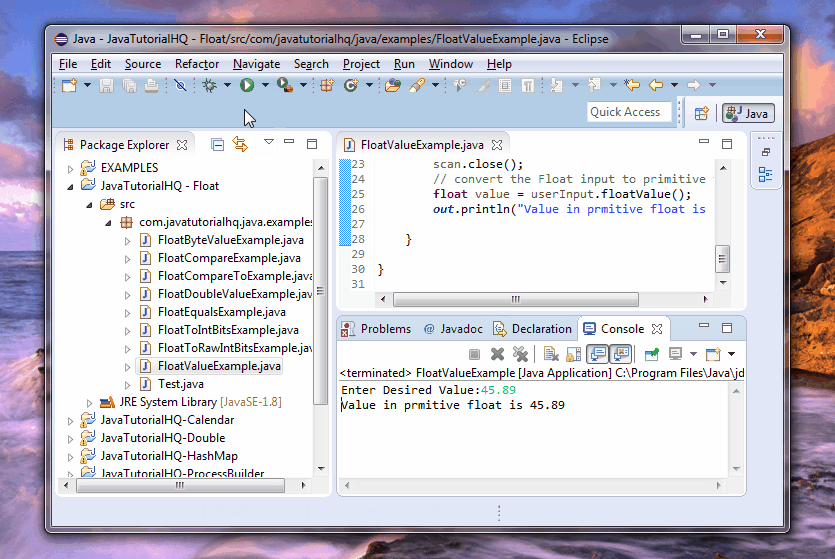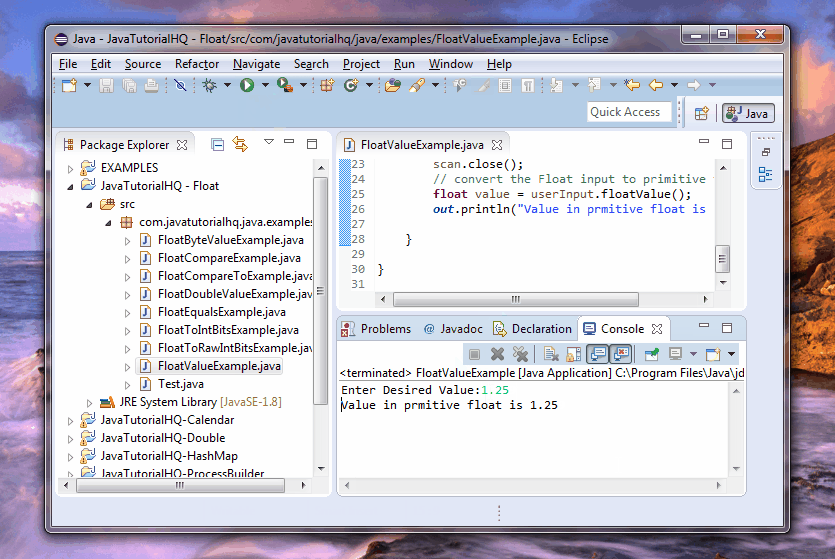
float value = userInput.floatValue();
out.println("Value in prmitive float is " + value);
}
}
Basically on the above example, we just ask for user input on the console and then we use the scanner object to get the float input. After that we assign the value to an Float wrapper class and we then get the primitive equivalent of the Float object. Notice that the example above is quite repetitive. Repetitive in the sense that we already have the primitive data type from the start since we use the autoboxing features on this example. Let’s do a little review, the method nextFloat() of Scanner class returns primitive float however we assign the value to object data type Float. Autoboxing feature comes into play on this conversion.