java.lang.Float floatToRawIntBits
Description
Method Syntax
public static int floatToRawIntBits(float value)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| float | value | a floating-point number. |
Method Returns
The floatToRawIntBits() method example(float value) method of Float class returns the bits that represent the floating-point number.
Compatibility
Java 1.0
Discussion
There are some rules governing the floatToRawIntBits method and here as follows:
- If the argument is positive infinity, the result is 0x7f800000.
- If the argument is negative infinity, the result is 0xff800000.
- If the argument is NaN, the result is the integer representing the actual NaN value. Unlike the floatToIntBits method, floatToRawIntBits does not collapse all the bit patterns encoding a NaN to a single “canonical” NaN value.
Java Float floatToRawIntBits(float value) Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of floatToRawIntBits(float value) method of Float class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Scanner;
import static java.lang.System.*;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* floatToRawIntBits(float value) method of Float class.
*/
public class FloatToRawIntBitsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Ask user input for a number
System.out.print("Enter First Number:");
// declare the scanner object
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// use scanner to get value from user console
Float value = scan.nextFloat();
// close the scanner object
scan.close();
/*
* code block to print the result of
* floatToRawIntBits method
*/
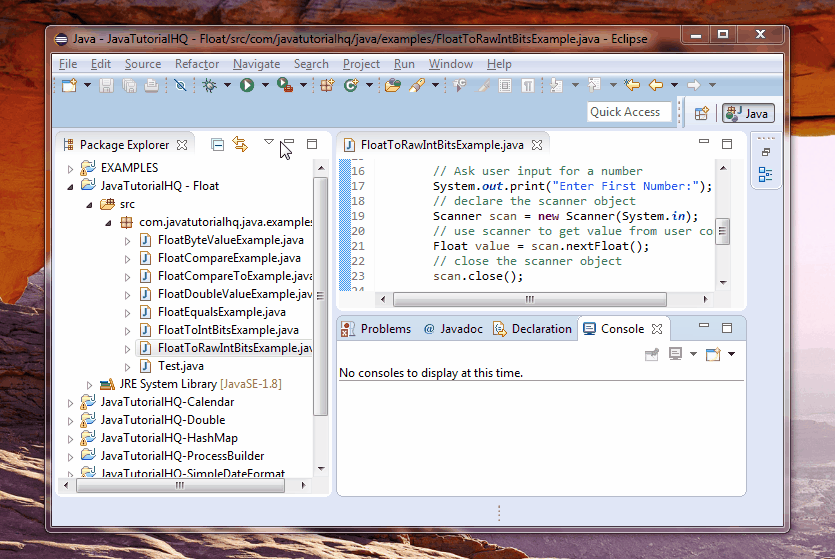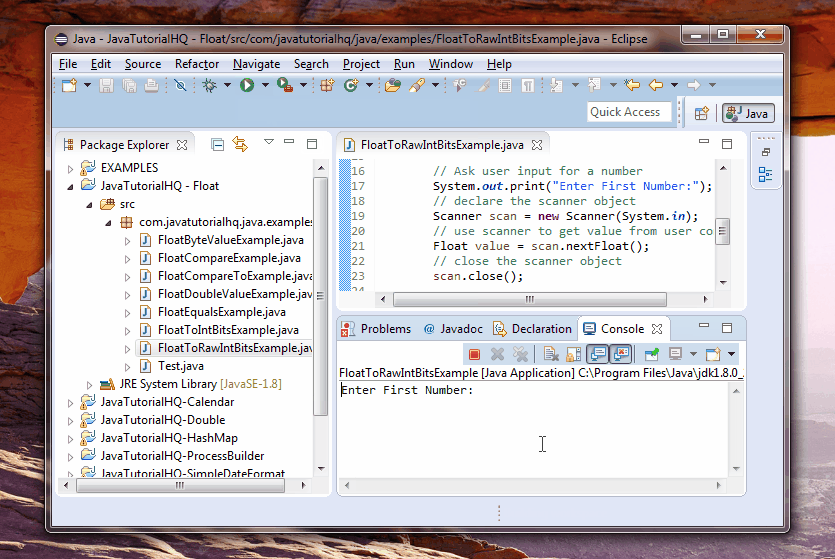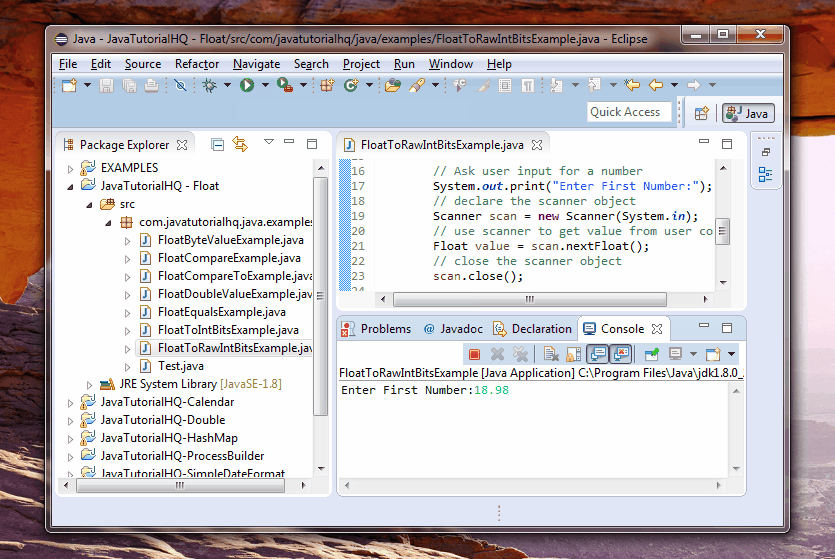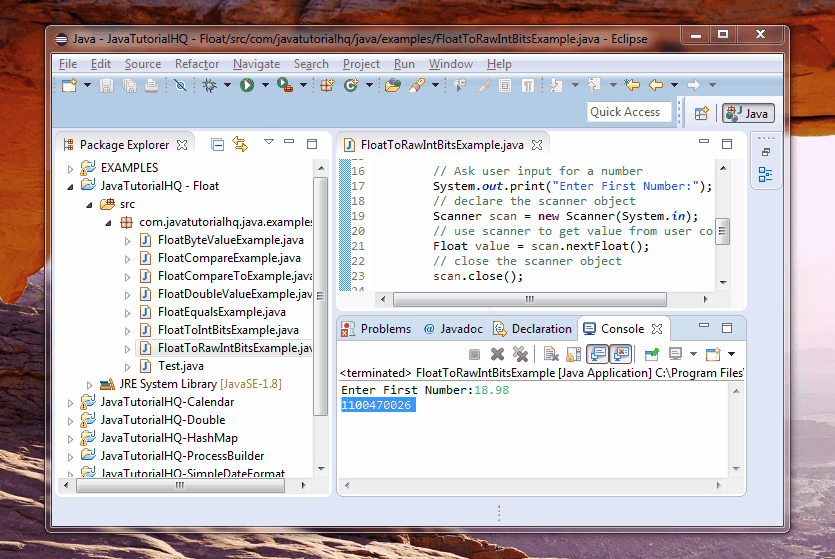
out.println(Float.floatToRawIntBits(value));
}
}
Basically on the above example, we just ask for user input on the console and then we use the scanner object to get the float input. After that we assign the value to an Float wrapper class and we then get the integer bits equivalent using the floatToRawIntBits(float value) method of Float class.