java.util.Arrays asList(T… a)
Description
Notes:
- The returned list is serializable and implements RandomAccess.
Method Syntax
@SafeVarargs
public static <T> List<T> asList(T… a)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| T | a | T – the class of the objects in the array a – the array by which the list will be backed |
Method Returns
The asList() method returns a list view of the specified array.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.2 and up
Java Arrays asList() Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of asList() method of Arrays class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the asList() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of asList() method of Arrays class
*/
public class ArraysAsListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize a new String array
String[] studentDatabase = new String[]{"Ryan","Alfred","Beth"};
// convert the student database into list
List alist = Arrays.asList(studentDatabase);
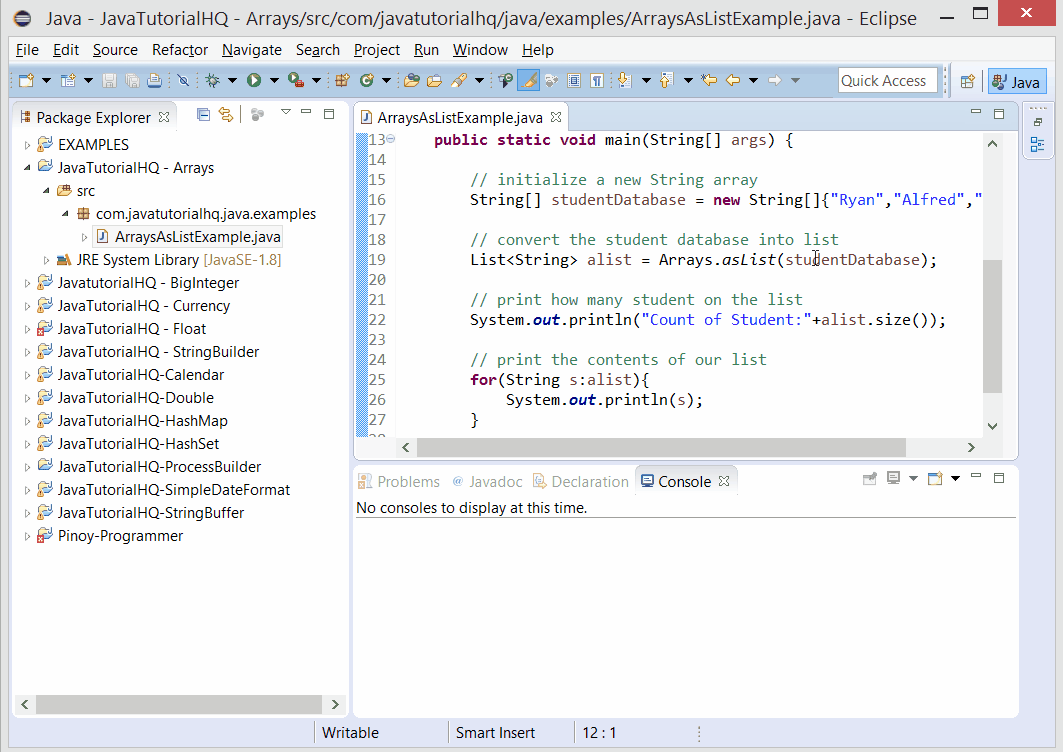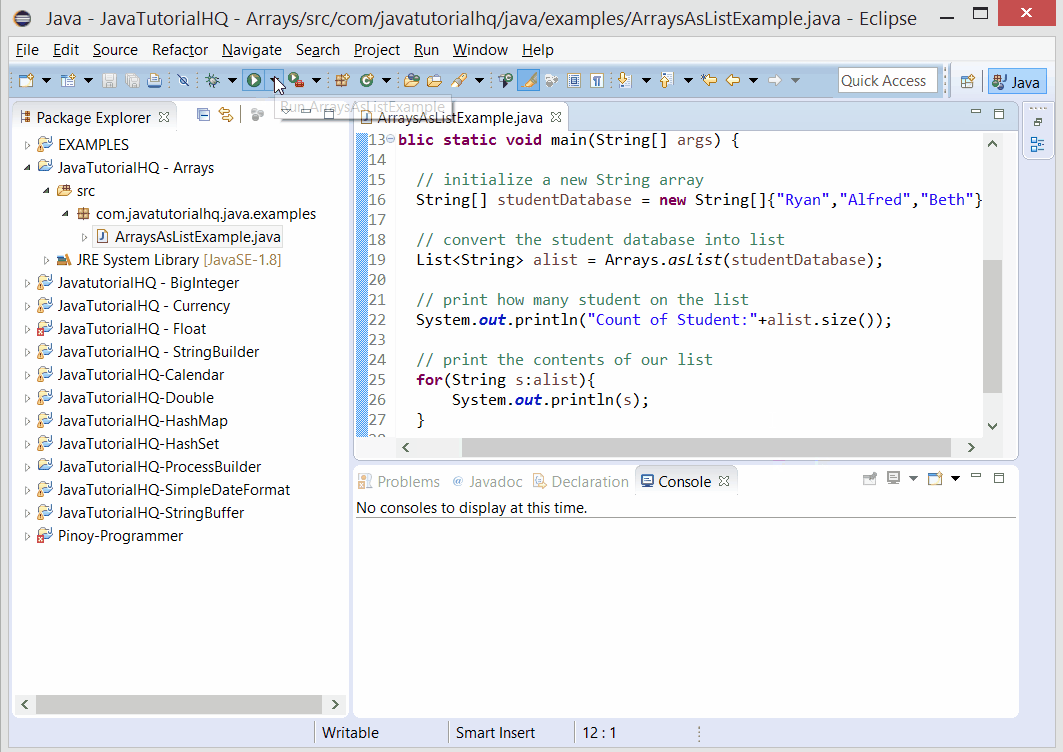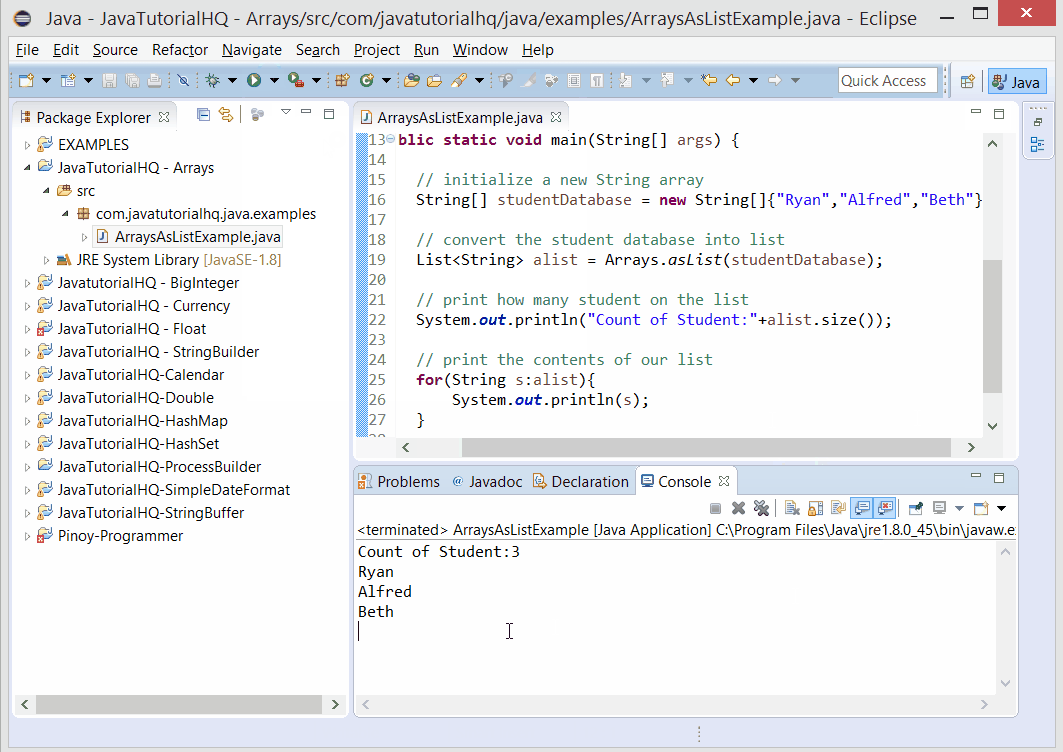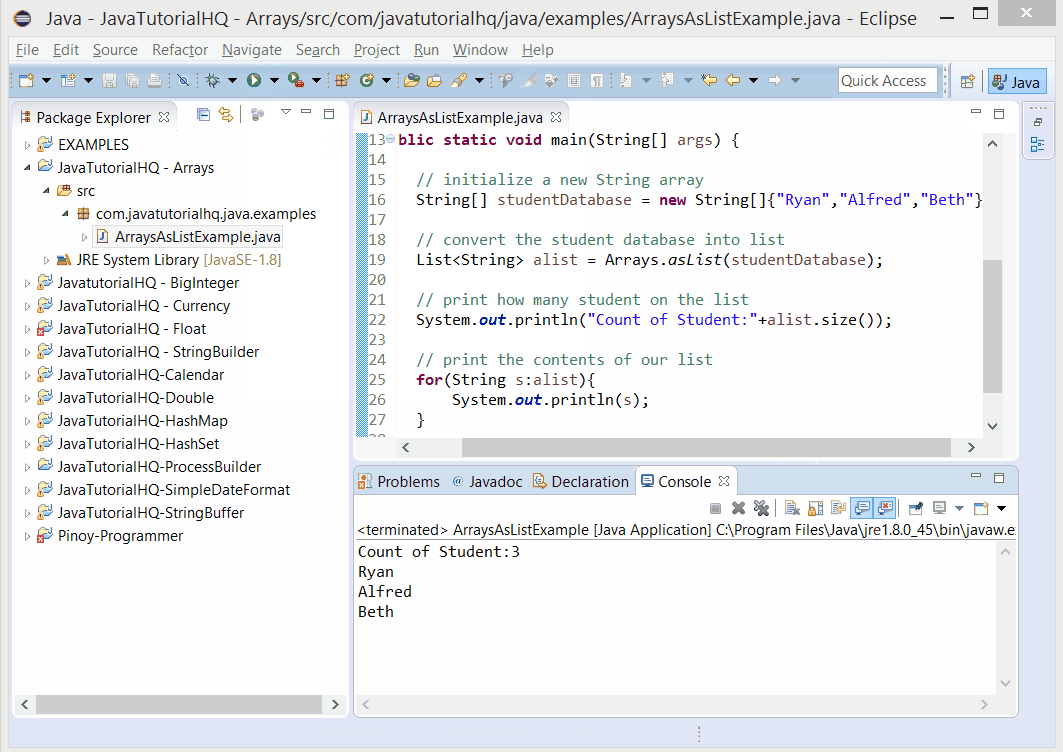
// print how many student on the list
System.out.println("Count of Student:"+alist.size());
// print the contents of our list
for(String s:alist){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
The above java example source code demonstrates the use of asList() method of Arrays class.We simply declare a new String Array that correspond to student names. Then we use the static method asList() of Arrays class. This method basically just converts our arrays of String into List. This gives a lot more versatility in our handling of our student database because there’s a lot of methods available in List class.