java.util.Arrays binarySearch()
Description
Method Syntax
public static int binarySearch(datatype[] a, dataype key)
Method Returns
The binarySearch() method returns the index of the search key, if it is contained in the array; otherwise, (-(insertion point) – 1). The insertion point is defined as the point at which the key would be inserted into the array: the index of the first element greater than the key, or a.length if all elements in the array are less than the specified key. Note that this guarantees that the return value will be >= 0 if and only if the key is found.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.2 and up
Java Arrays binarySearch() Example
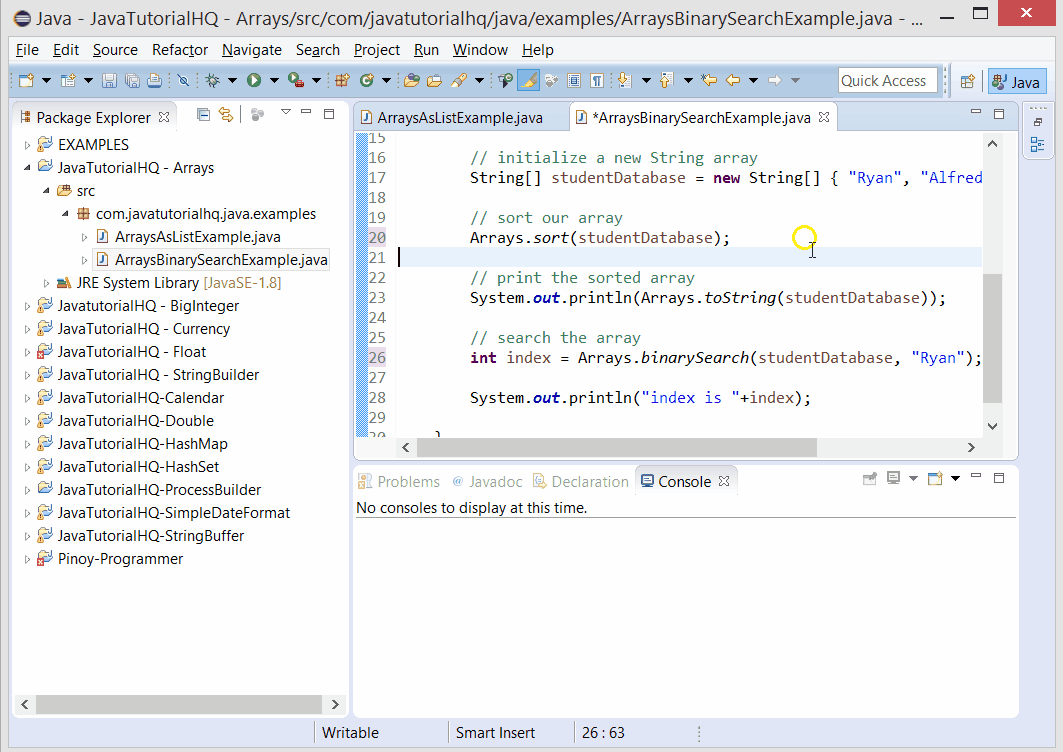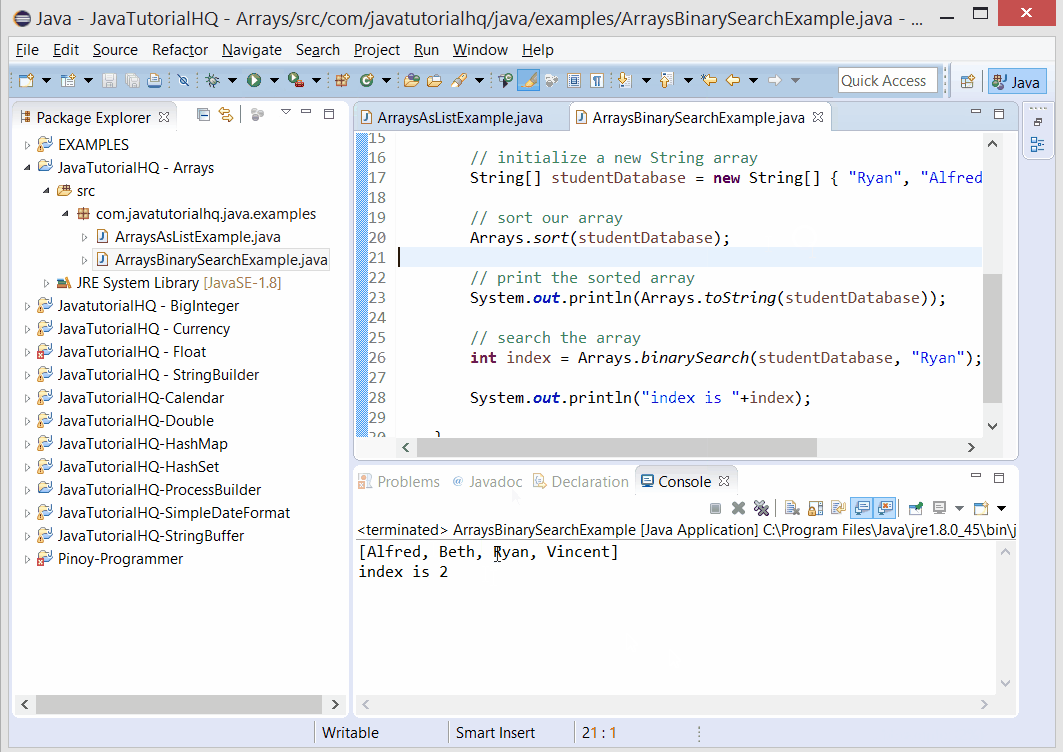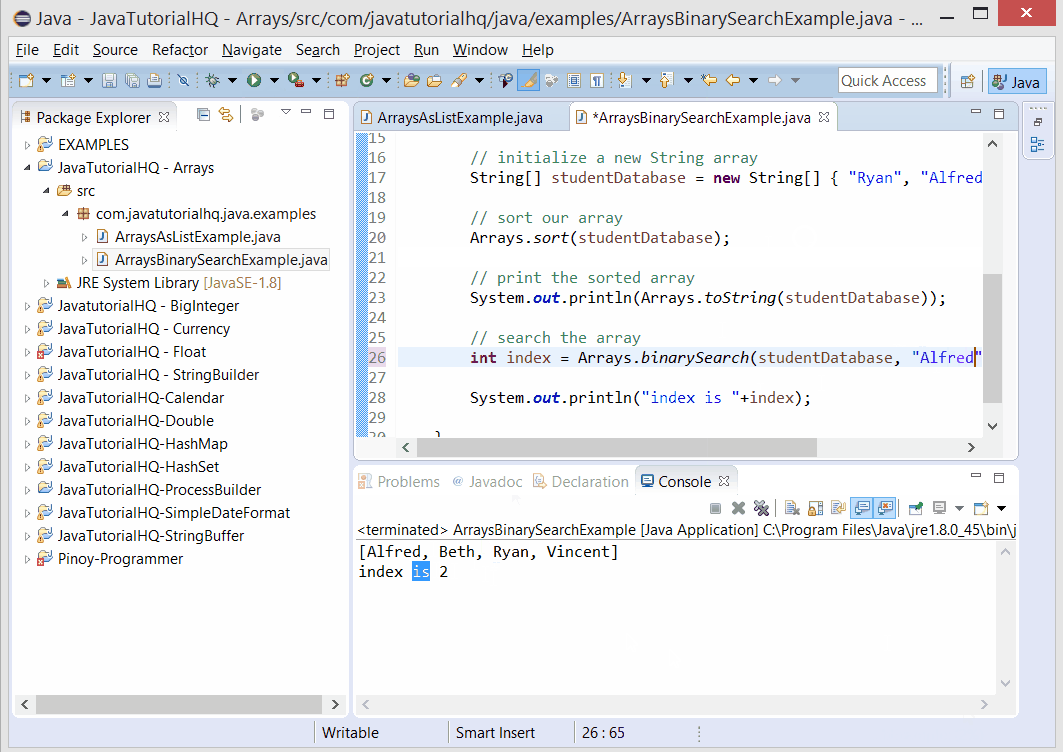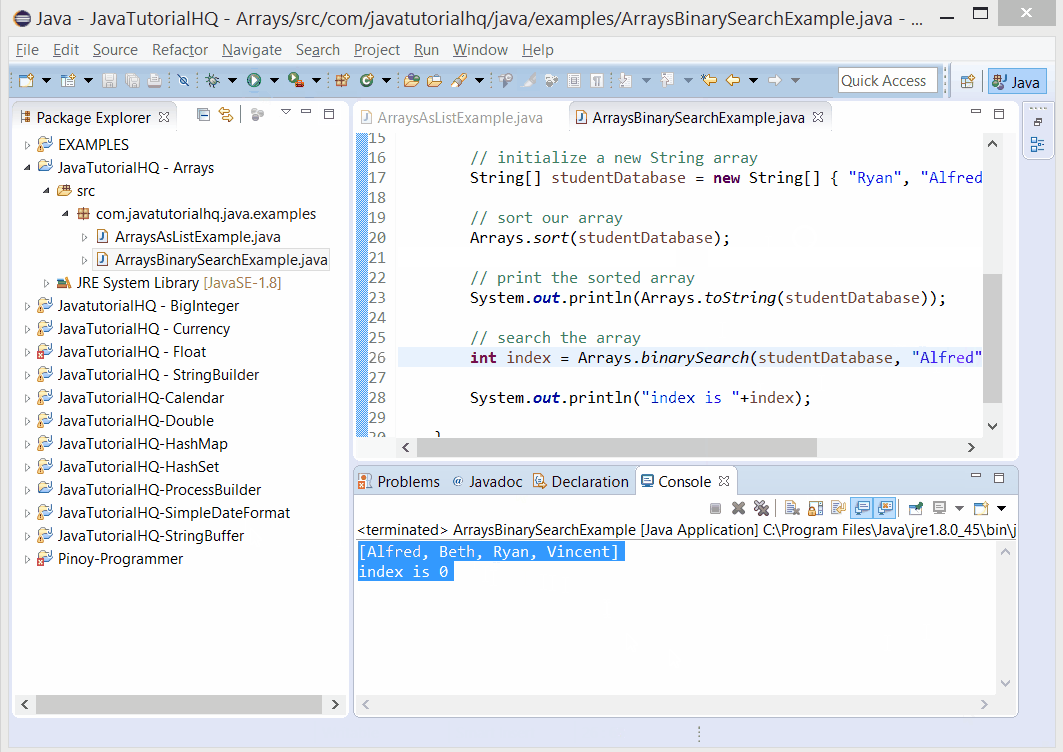
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of binarySearch() method of Arrays class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the binarySearch() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Arrays;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of binarySearch() method of Arrays class
*/
public class ArraysBinarySearchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize a new String array
String[] studentDatabase = new String[] { "Ryan", "Alfred", "Beth", "Vincent" };
// sort our array
Arrays.sort(studentDatabase);
// print the sorted array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(studentDatabase));
// search the array
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(studentDatabase, "Beth");
System.out.println("index is "+index);
}
}
The above java example source code demonstrates the use of binarySearch() method of Arrays class.We simply declare a new String Array that correspond to student names. As a requirement in using the binarySearch the array must be sorted so we use another static method of Arrays class which is the Arrays.sort(). After which we tested the use of binarySearch() by getting the index of one of our student name that we have initially declared.