java.util.Arrays deepEquals()
Description
As a reference we can say that both array are deeply equals to each other if both are null or they have the same number of elements and all corresponding pairs of elements in the two arrays are deeply equal.
Method Syntax
public static boolean deepEquals(Object[] a1, Object[] a2)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Object | a1 | one array to be tested for equality |
| Object | a2 | the other array to be tested for equality |
Method Returns
The deepEquals() method returns true if the two arrays are equal otherwise false.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.5 and up
Java Arrays deepEquals(Object[] a1, Object[] a2) Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of deepEquals(Object[] a1, Object[] a2) method of Arrays class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behaviour of the deepEquals() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of deepEquals() method of Arrays class
*/
public class ArraysDeepEqualsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize a new String array
String[] names = new String[]{
"Alfred","Beth","Stan"
};
Object[] data = new Object[3];
data[0] = "Alfred";
data[1] = "Beth";
data[2] = "Stan";
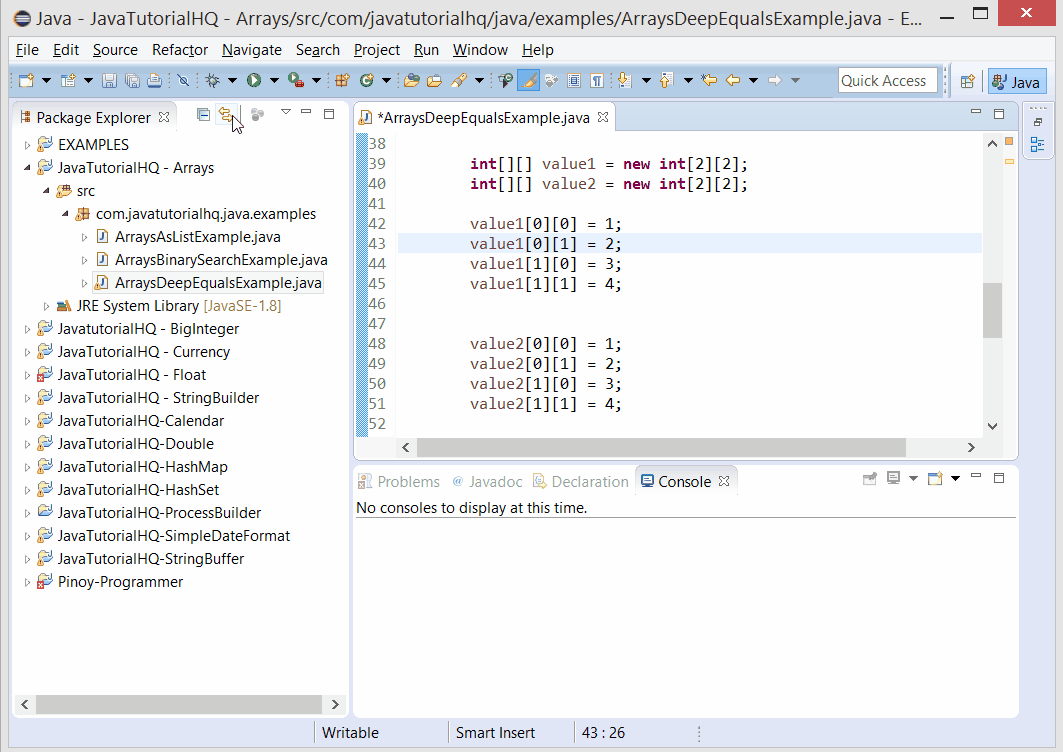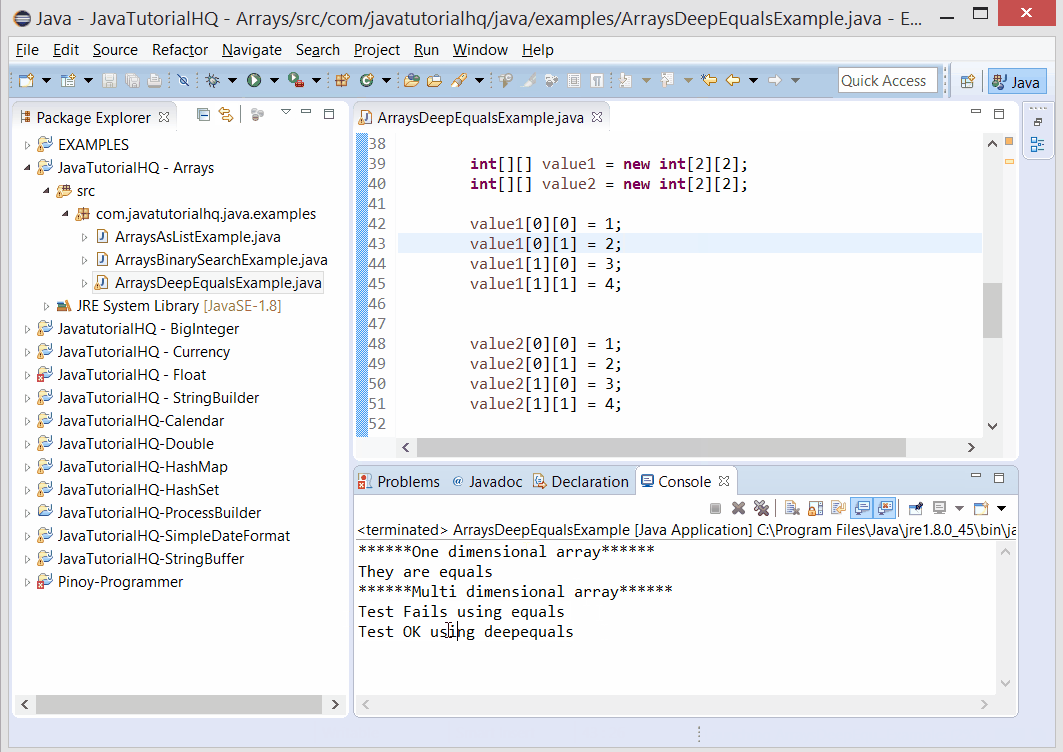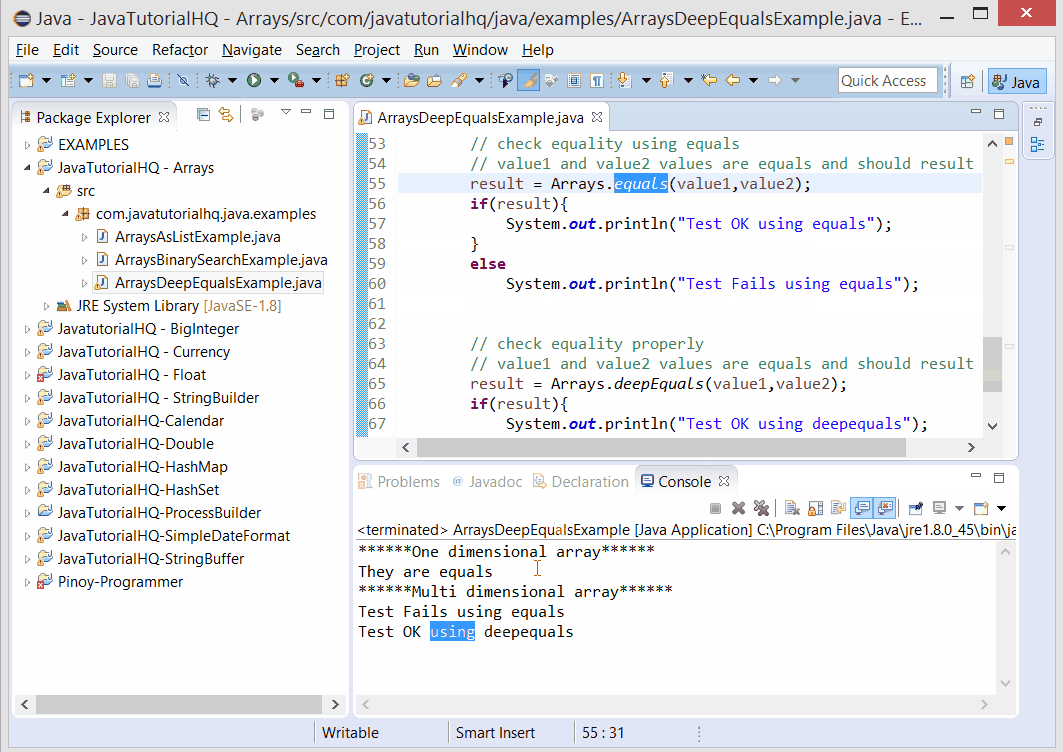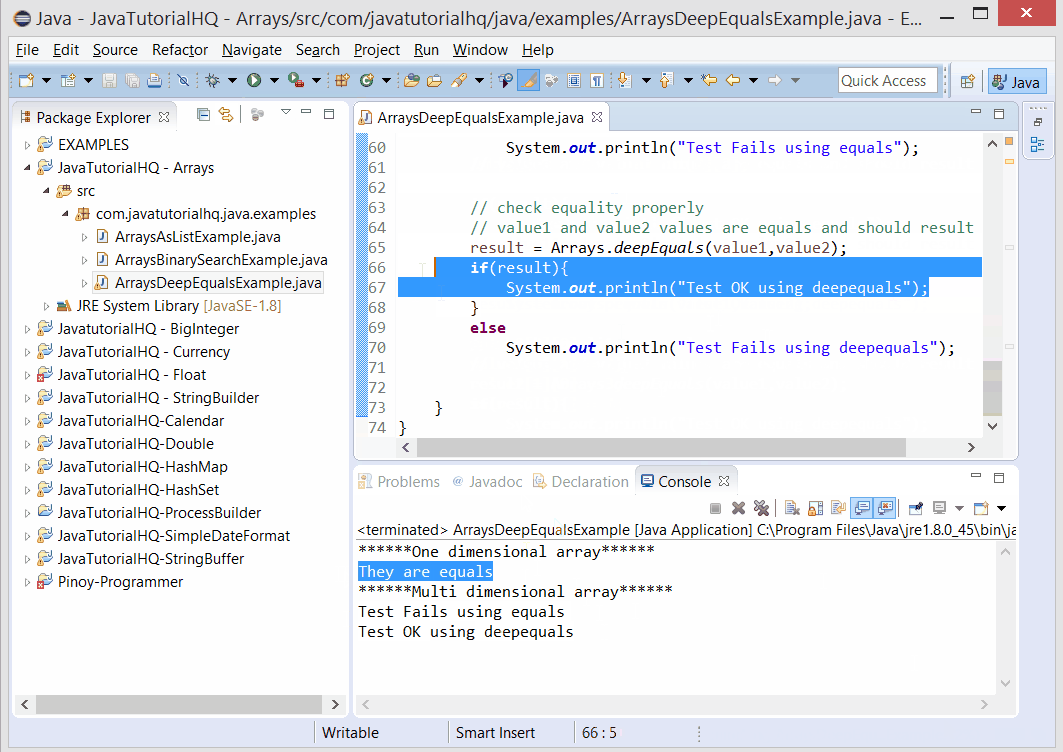
System.out.println("******One dimensional array******");
// test for equality
boolean result = Arrays.equals(names, data);
if(result){
System.out.println("They are equals");
}
else{
System.out.println("They are not equals");
}
System.out.println("******Multi dimensional array******");
// test multi dimensional array
int[][] value1 = new int[2][2];
int[][] value2 = new int[2][2];
value1[0][0] = 1;
value1[0][1] = 2;
value1[1][0] = 3;
value1[1][1] = 4;
value2[0][0] = 1;
value2[0][1] = 2;
value2[1][0] = 3;
value2[1][1] = 4;
// check equality using equals
// value1 and value2 values are equals and should result to true
result = Arrays.equals(value1,value2);
if(result){
System.out.println("Test OK using equals");
}
else
System.out.println("Test Fails using equals");
// check equality properly
// value1 and value2 values are equals and should result to true
result = Arrays.deepEquals(value1,value2);
if(result){
System.out.println("Test OK using deepequals");
}
else
System.out.println("Test Fails using deepequals");
}
}
The above java example source code demonstrates the use of deepEquals() method of Arrays class. Example above show the difference in using equals and deepEquals. As you can see using equals works fine in single dimensional array but it will fail if we are testing multi dimensional array. To properly handle the equality test of multi dimensional array, the deepEquals method works like a charm.