java.util.Arrays deepToString()
Description
As a reference we can say that both array are deeply equals to each other if both are null or they have the same number of elements and all corresponding pairs of elements in the two arrays are deeply equal.
Method Syntax
public static String deepToString(Object[] a)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Object[] | a | the array whose string representation to return |
Method Returns
The deepToString() method returns a string representation of a.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.5 and up
Java Arrays deepToString(Object[] a) Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of deepToString() method of Arrays class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behaviour of the deepToString() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Arrays;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of deepToString() method of Arrays class
*/
public class ArraysDeepToStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize a new String array
String[] names = new String[]{
"Alfred","Beth","Stan"
};
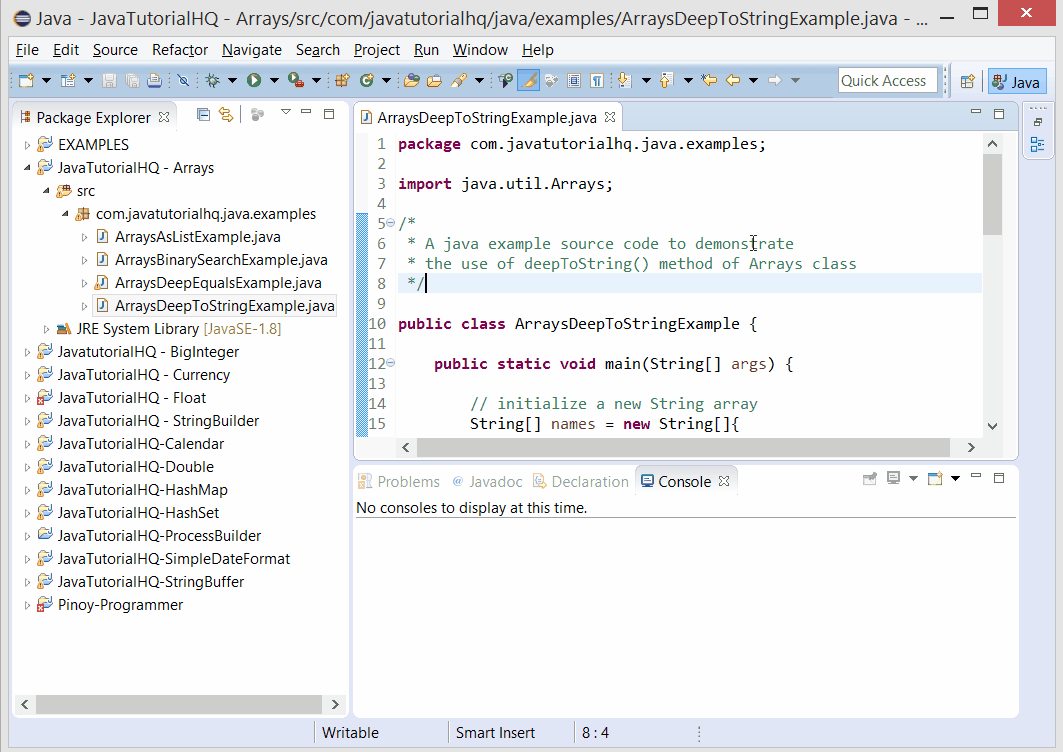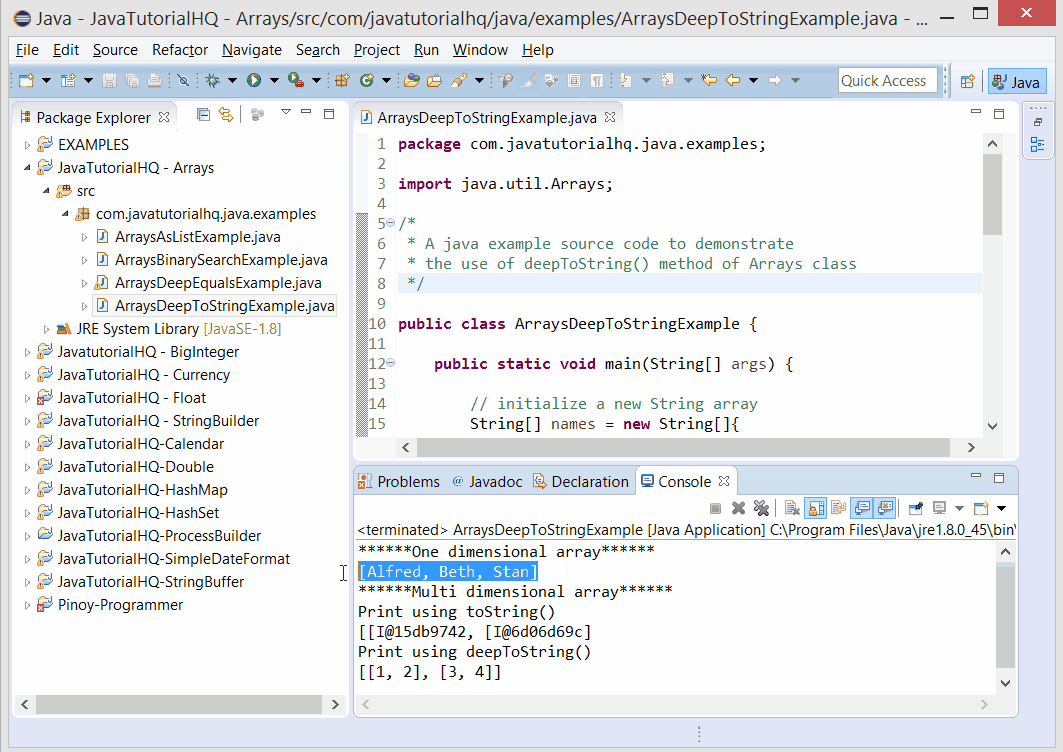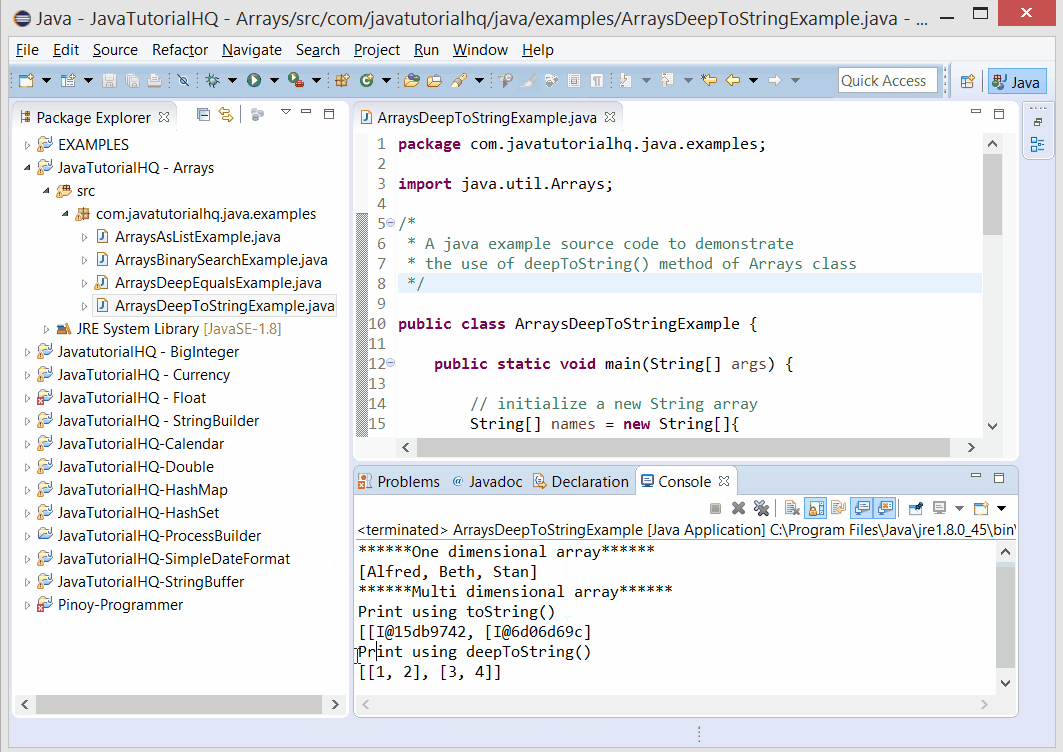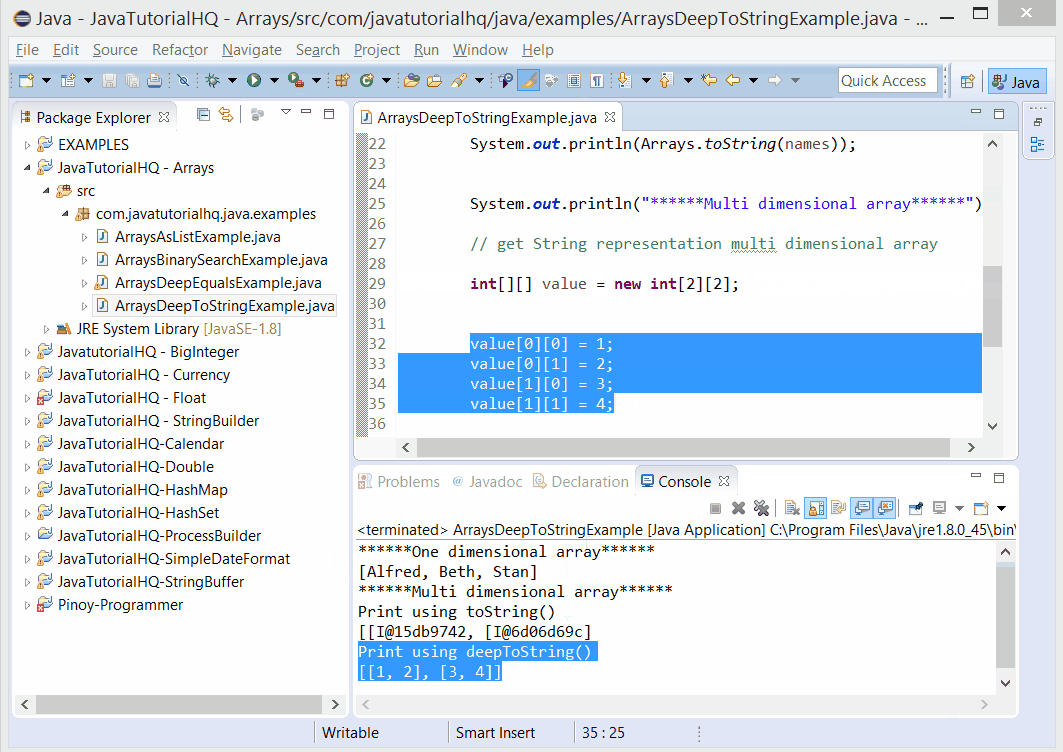
System.out.println("******One dimensional array******");
// get the String representation
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names));
System.out.println("******Multi dimensional array******");
// get String representation multi dimensional array
int[][] value = new int[2][2];
value[0][0] = 1;
value[0][1] = 2;
value[1][0] = 3;
value[1][1] = 4;
// print using toString() method
System.out.println("Print using toString()");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(value));
// print using deepToString() method
System.out.println("Print using deepToString()");
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(value));
}
}
Basically we initialize a one dimensional array and prints out the Array representation of this array using toString(). At this point the toString() method will work. However on the later part of our example we have initialize another array value and then we printed out the string equivalent of it using the toString() method. At this stage you would have noticed that the printed string is the hashcode of the objects inside the first layer of array which we would not be interested with. Then we use the deepToString() method to print out the values of our array, and this will give a more readable print out.