java.util.HashSet clear()
Description
The HashSet as majority of the Collection classes make use of Generics such that if we have declared our set like HashSet set = new HashSet() then the elements of inside our set is of type String. And we cannot insert different object type not unless its a subclass of the object declaration, otherwise a runtime error will be thrown.
The HashSet elements are unique, there would be no two identical elements that can exist.
Important notes for clear() method:
- specified by clear in interface Collection<E>
- specified by clear in interface Set<E>
- overrides clear in class AbstractCollection<E>
Method Syntax
public boolean clear()
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method Returns
The clear() method returns void
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.2 and up
Java HashSet clear() Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of clear() method of HashSet class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the clear() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import static java.lang.System.*;
import java.util.HashSet;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* clear() method of HashSet class
*/
public class HashSetRemoveExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// get the HashMap object from the method init()
HashSet studentSet = init();
// check the size of our set
int size = studentSet.size();
out.println("Our set has "+ size +" elements");
// clear the elements of our HashSet
studentSet.clear();
// check again the size of our HashSet
size = studentSet.size();
out.println("Our set has "+ size +" elements");
}
private static HashSet init() {
// declare the HashSet object
HashSet studentSet = new HashSet<>();
// put contents to our HashMap
studentSet.add("Shyra Travis");
studentSet.add("Sharon Wallace");
studentSet.add("Leo Batista");
return studentSet;
}
}
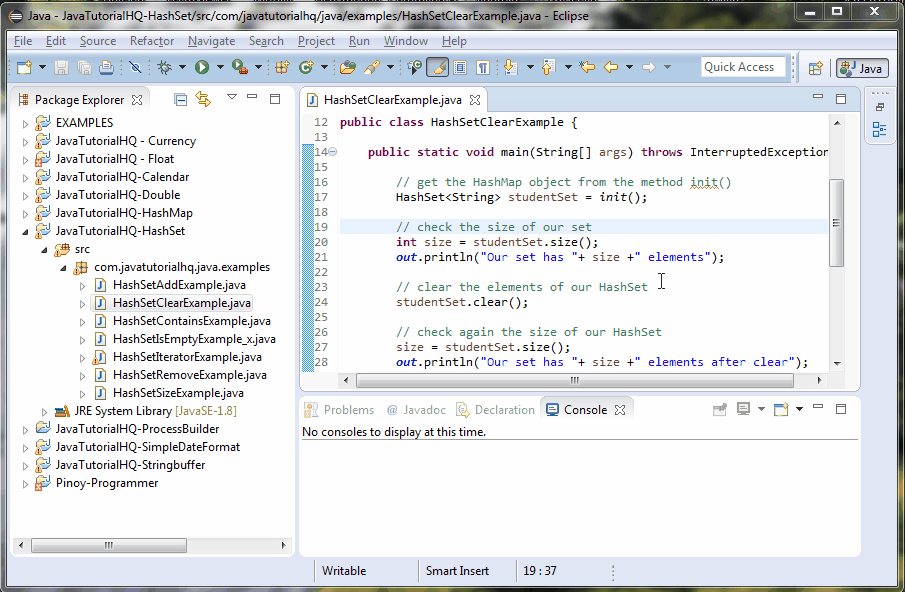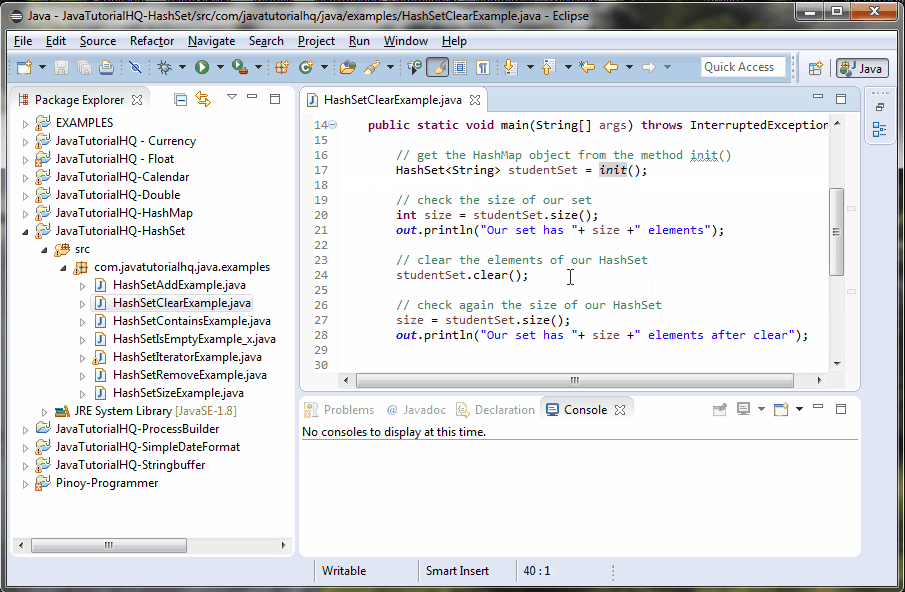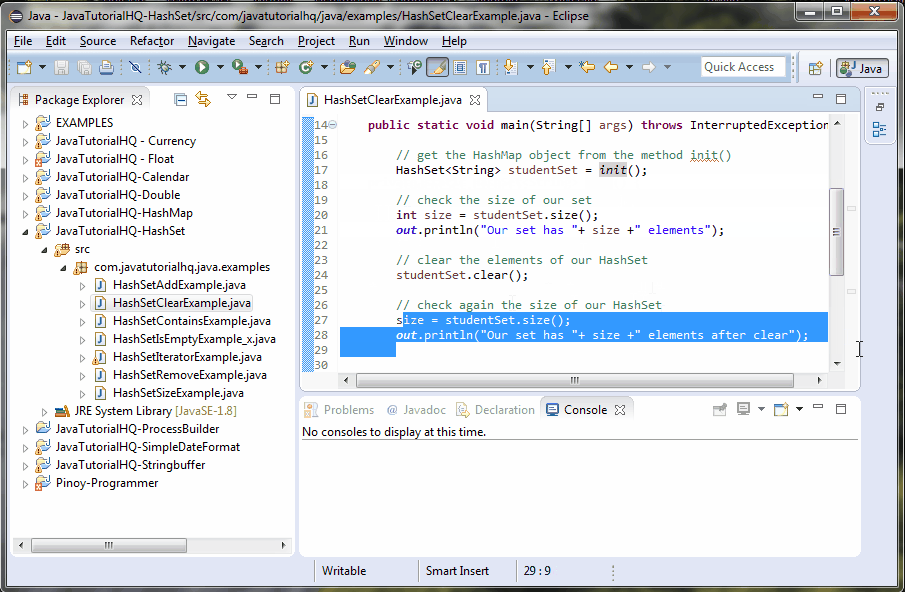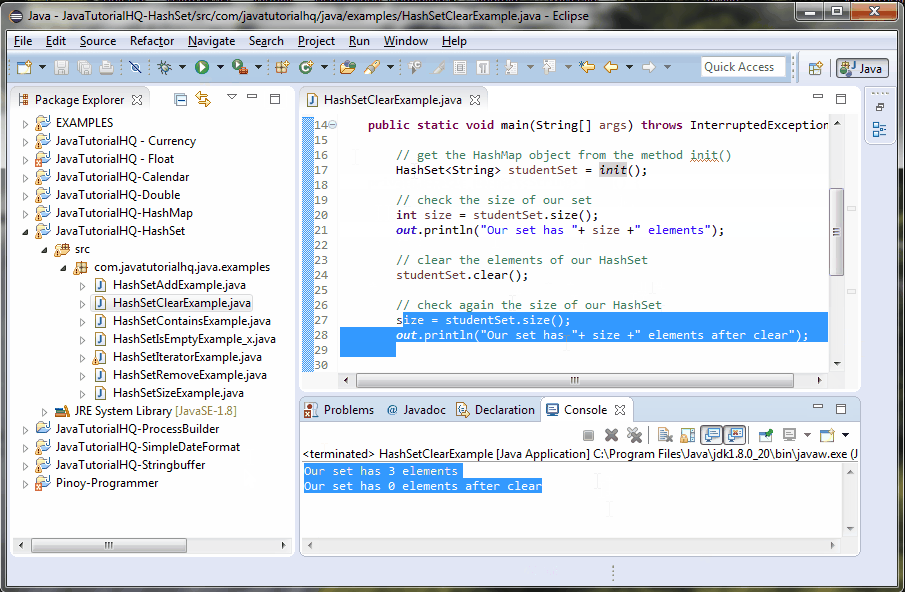
There are two methods created on the above example, main() and init. The main method calls the init() which initializes and assign values to a HashSet object. The main() method assign to a new HashSet object the returned object by the init() method. At this point we know that there are elements contained on the HashSet method and we have verified the same by printing the current size of the set. We called the clear method to remove all the elements of the HashSet and then validate it by getting the size method. Since we have cleared the HashSet, it is expected that the HashSet has zero size.