java.util.HashSet size()
Description
The HashSet as majority of the Collection classes make use of Generics such that if we have declared our set like HashSet set = new HashSet() then the elements of inside our set is of type String. And we cannot insert different object type not unless its a subclass of the object declaration, otherwise a runtime error will be thrown.
The HashSet elements are unique, there would be no two identical elements that can exist.
Important notes for size() method:
- specified by size in interface Collection
- size in interface Set
- size in class AbstractCollection
Method Syntax
public int size()
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method Returns
The size() method returns the number of elements in this set (its cardinality).
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.2 and up
Java HashSet size() Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of size() method of HashSet class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the szie() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import static java.lang.System.*;
import java.util.HashSet;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* size() method of HashSet class
*/
public class HashSetSizeExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// get the HashMap object from the method init()
HashSet studentSet = init();
// get and print the size of the set
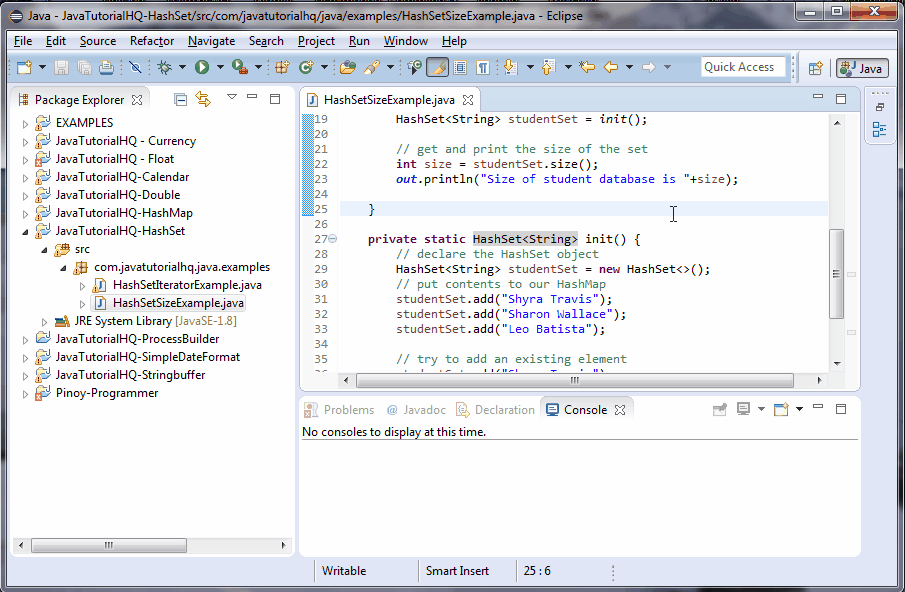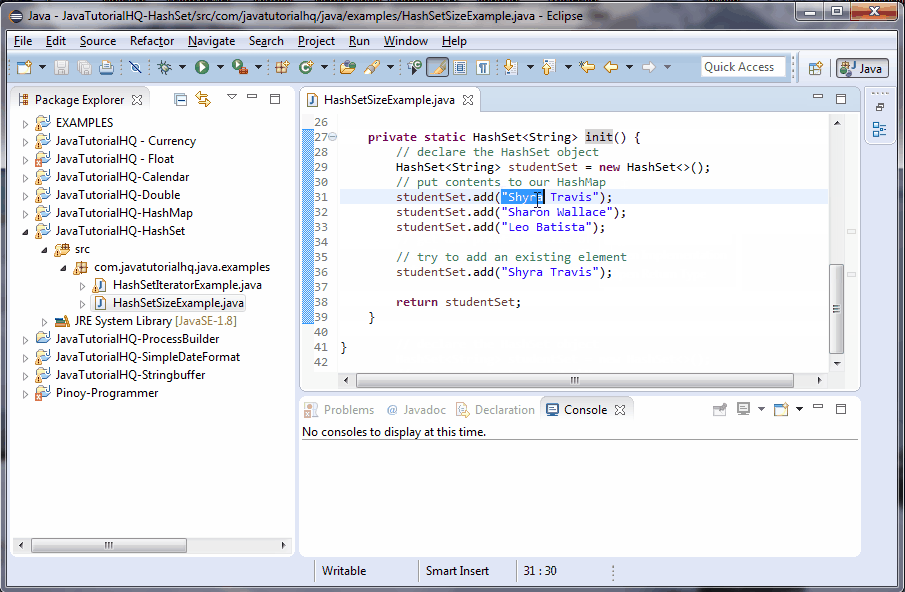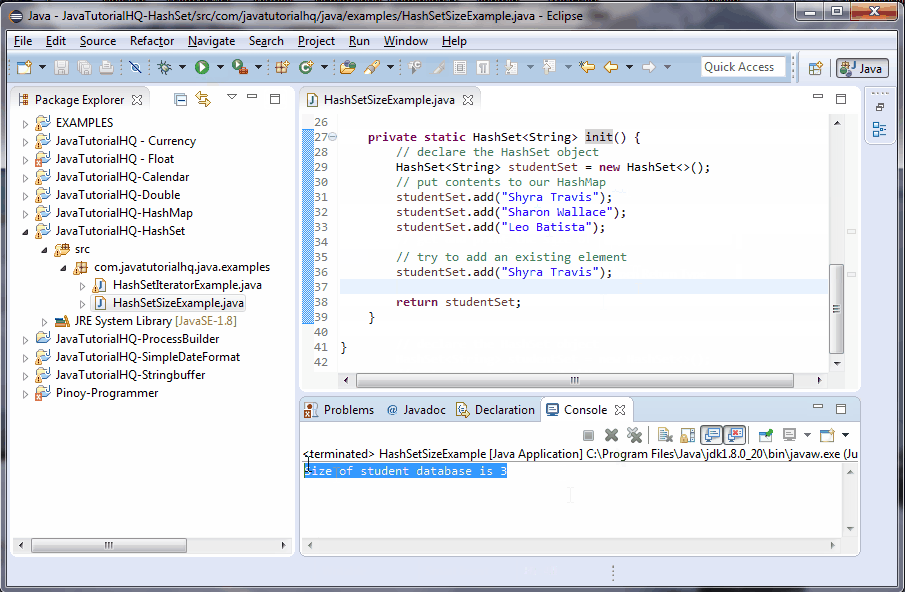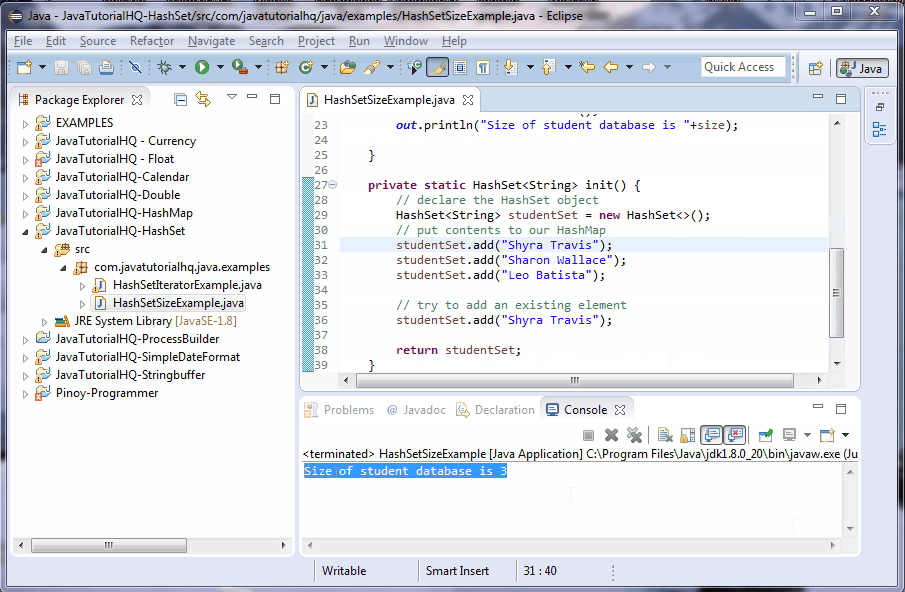
int size = studentSet.size();
out.println("Size of student database is "+size);
}
private static HashSet init() {
// declare the HashSet object
HashSet studentSet = new HashSet<>();
// put contents to our HashMap
studentSet.add("Shyra Travis");
studentSet.add("Sharon Wallace");
studentSet.add("Leo Batista");
studentSet.add("Shyra Travis");
return studentSet;
}
}
There are two methods created on the above example, main() and init. The main method calls the init() which initializes and assign values to a HashSet object. The main() method assign to a new HashSet object the returned object by the init() method. We then print the size of the set.