java.util.Scanner hasNextShort()
Description :
This java tutorial shows how to use the hasNextShort method of Scanner class of java.util package. This method returns boolean, true if the token can be interpreted as short data type with respect to the radix used by the scanner object otherwise false.
Method Syntax :
There are two overloaded method of Scanner hasNextShort() java method
Note: Overloaded methods are those method with same name but with different method signatures
Method 1:
public byte hasNextShort()
Method 2:
public byte hasNextShort(int radix)
Parameter Input :
| DataType | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| int | radix | the base number to scan |
Method Returns :
This method simply returns true if the scanner token is of short data type.
Compatibility Version :
Requires Java 1.5 and up
Exception :
IllegalStateException
– if this scanner is closed and we still invoked the hasNextShort method
Discussion :
The Scanner hasNextShort() method simply return true if the token on the scanner buffer can be interpreter or translated of short data type. There are two overloaded method of hasNextShort method, which accomplishes the same task. The method without a method argument is the same as calling hasNextShort(radix) which is the default radix of the Scanner object. The radix currently set by the Scanner object is defined using the method useRadix(radix) and can be determine using the radix() method. Calling hasNextShort(radix) will override the default radix already defined to the Scanner object.
Make a note that since we are scanning tokens in short data type, there is limit on the maximum and minimum value possible. The Short.MAX_VALUE and Short.MIN_VALUE will show what is the maximum and minimum possible short value than can be evaluated.
Java Code Example :
This java example source code demonstrates the use of hasNextShort method of Scanner class. Basically the code just prints those tokens of short data type on the input string declared on the Scanner constructor. The radix used on the example below is radix 8, means to say we have scanned data type in octal base number and then prints the equivalent in decimal format.
package com.teknoscope.java.tutorial.scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* Example java source code on the usage of
* Scanner hasNextShort() method
* Print short tokens only
*/
public class ScannerNextByte {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize the scanner
Scanner scan = new Scanner("** 12 13 -21 -7 1A **");
// tokenize the string on the constructor input
while(scan.hasNext()){
// check short data type
if(scan.hasNextShort(8)){
// print short tokens
System.out.println("Found a short: "+scan.next());
}
else{
// move to the next token
scan.next();
}
}
scan.close();
}
}
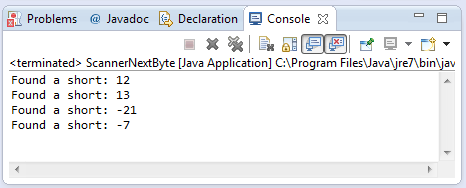
Sample Output :
Running the hasNextShort() method example source code of Scanner class will give you the following output
Exception Scenario :
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Scanner closed at java.util.Scanner.ensureOpen(Unknown Source) at java.util.Scanner.hasNext(Unknown Source) at java.util.Scanner.hasNextShort(Unknown Source) at java.util.Scanner.hasNextShort(Unknown Source) at com.teknoscope.java.tutorial.scanner.ScannerNextByte.main(ScannerNextByte.java:31)
Similar Method :
- N/A
Suggested Reading List :
References :