java.io.File lastModified()
Description
Where it is required to distinguish an I/O exception from the case where 0L is returned, or where several attributes of the same file are required at the same time, or where the time of last access or the creation time are required, then the Files.readAttributes method may be used.
Throws:
SecurityException – If a security manager exists and its SecurityManager.checkRead(java.lang.String) method denies read access to the file.
Method Syntax
public long lastModified()
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method Returns
This method returns a long, representing the time the file was last modified, measured in milliseconds since the epoch (00:00:00 GMT, January 1, 1970), or 0L if the file does not exist or if an I/O.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.0 and up
Java File lastModified() Example
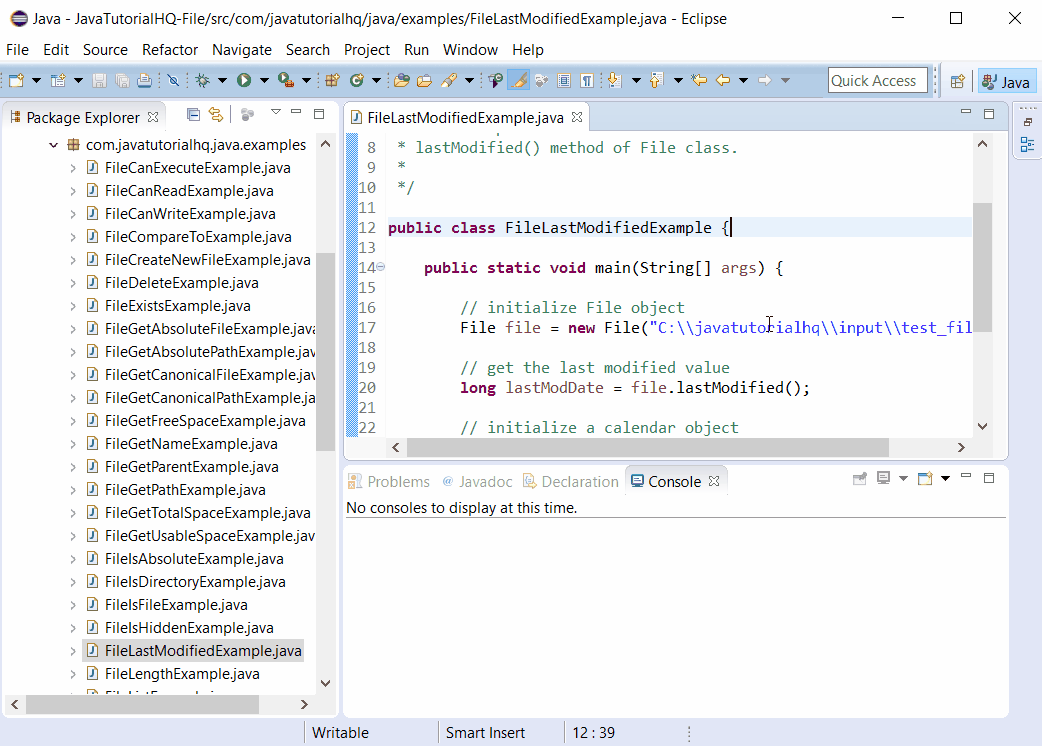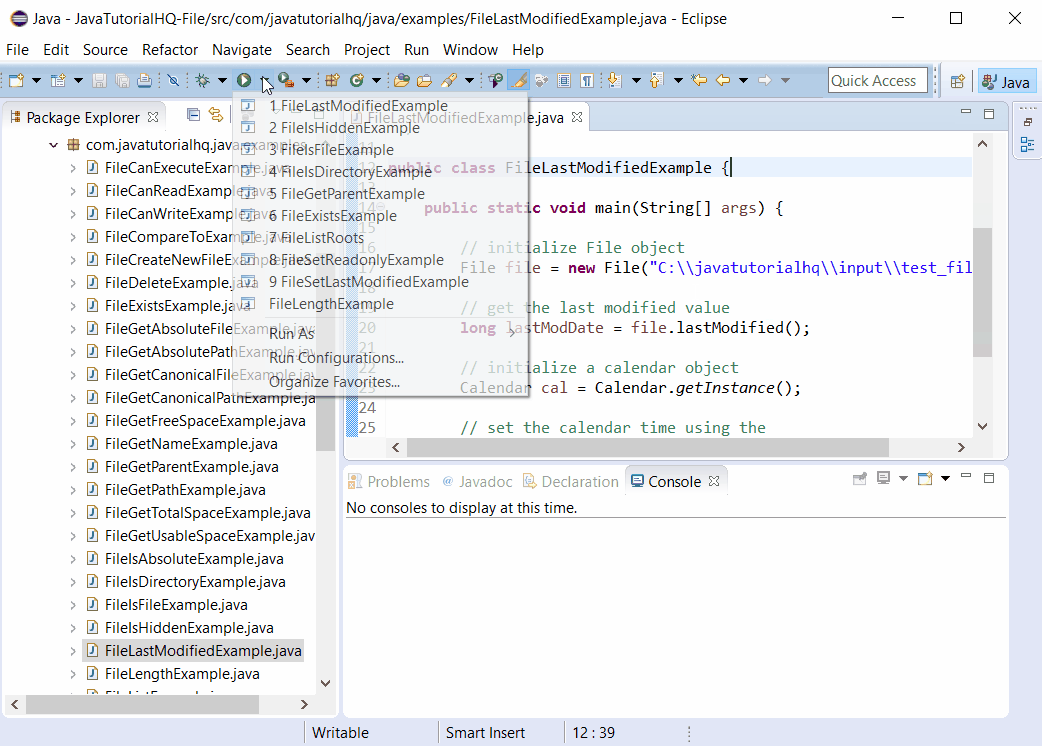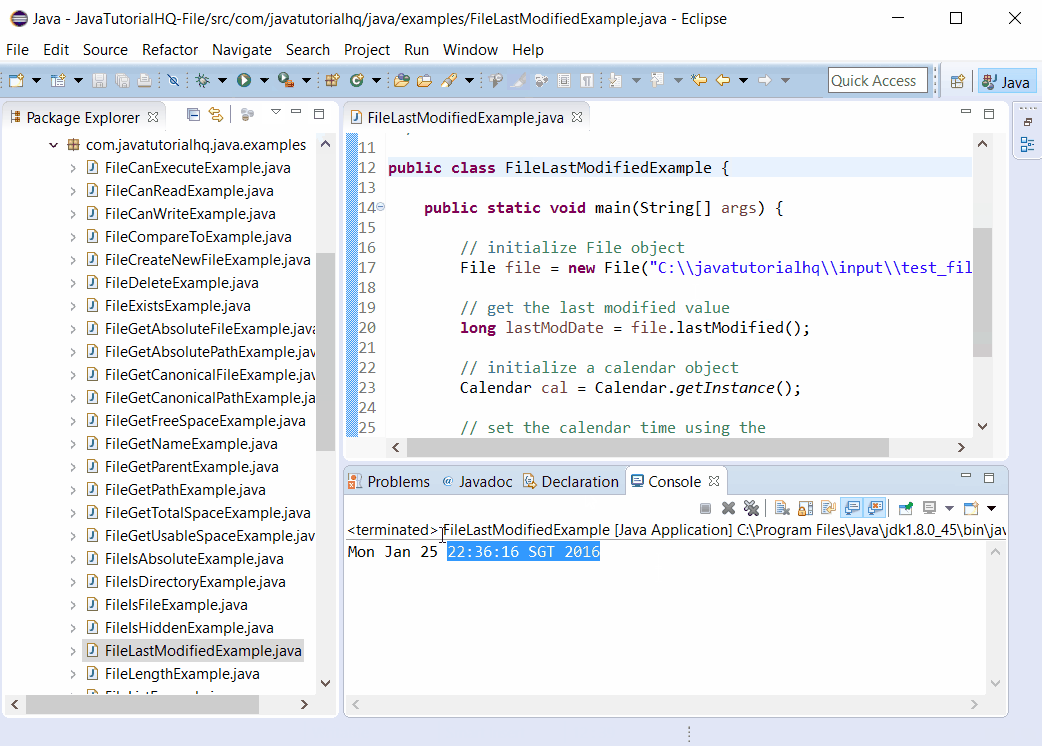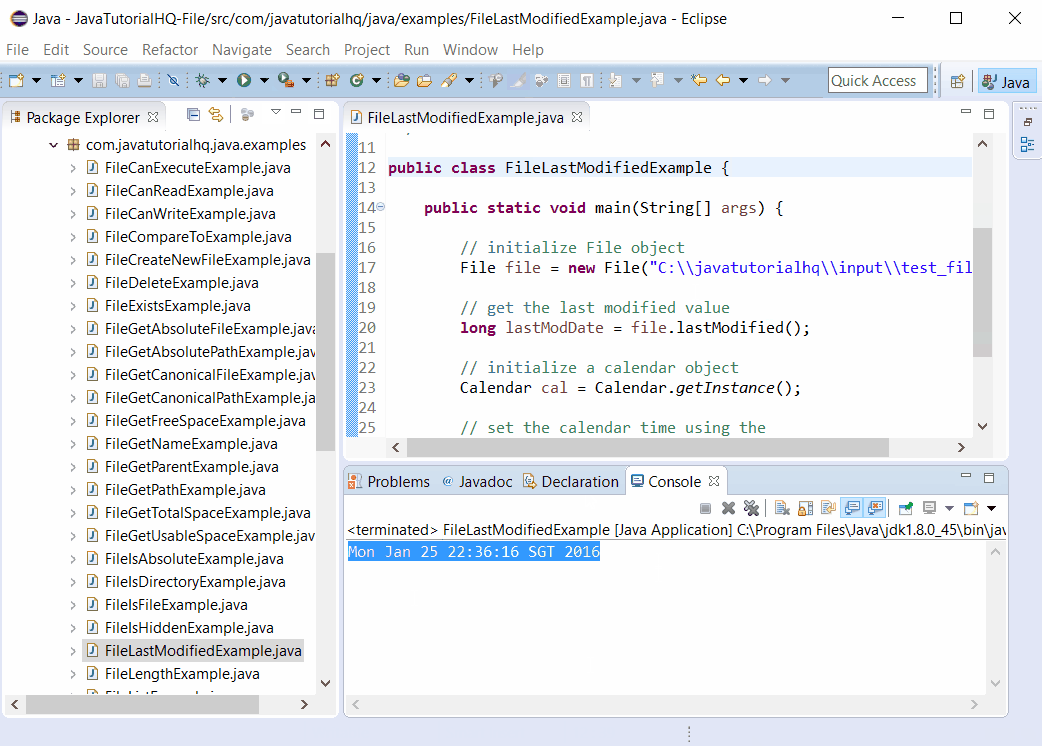
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of lastModified() method of File class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behaviour of the lastModified() method of File class. The return value of lastModified() method is a long which doesn’t make sense on it’s raw format, thus we have used methods of Calendar class to convert it into more meaningful format.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Calendar;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* lastModified() method of File class.
*
*/
public class FileLastModifiedExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize File object
File file = new File("C:javatutorialhqinputtest_file.txt");
// get the last modified value
long lastModDate = file.lastModified();
// initialize a calendar object
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
// set the calendar time using the
// last modified date of the file
cal.setTimeInMillis(lastModDate);
System.out.println(cal.getTime());
}
}