java.io.BufferedWriter.flush()
Description
On this document we will be showing a java example on how to use the flush() method of BufferedWriter Class.The flush() primary usage is to flush the stream. Take note that an IOException will be thrown if an I/O error occurs.
Method Syntax
public void flush()
throws IOException
specified by:
flush in class Writer
Method Returns
This method returns void.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.1 and up
Java BufferedWriter flush() Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of flush() method of BufferedWriter class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behaviour of the flush() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of flush() method of BufferedWriter class
*/
public class BufferedWriterWriterFlushExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//initialize a FileWriter
FileWriter fw;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("C:/javatutorialhq/test.txt");
// initialize our BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
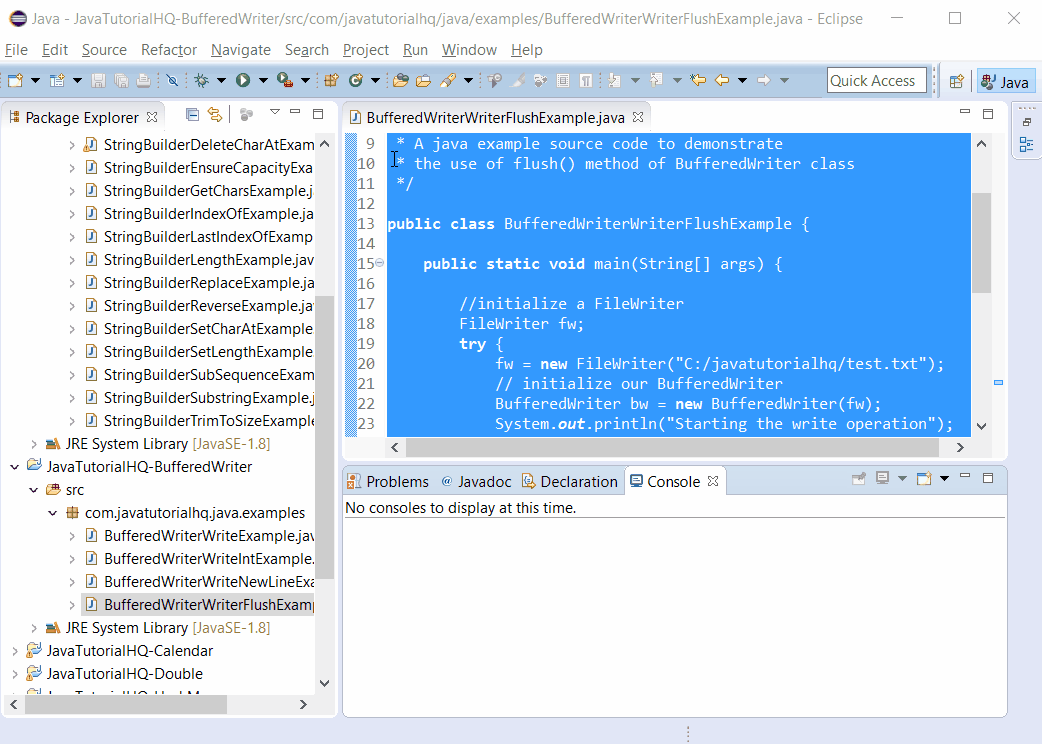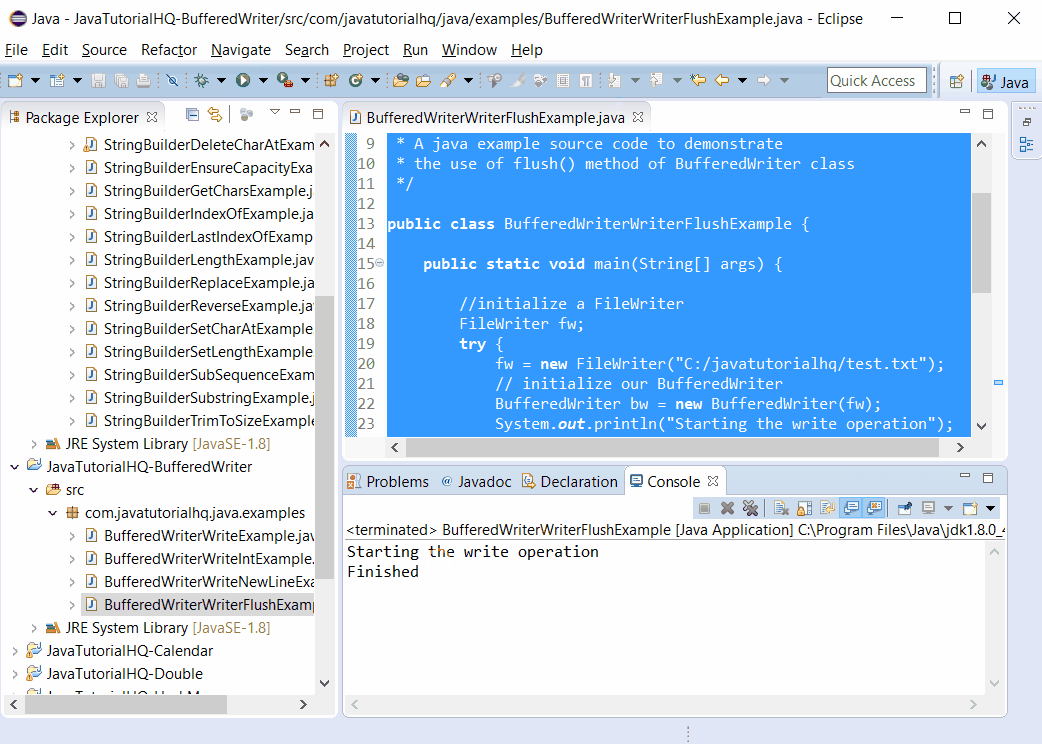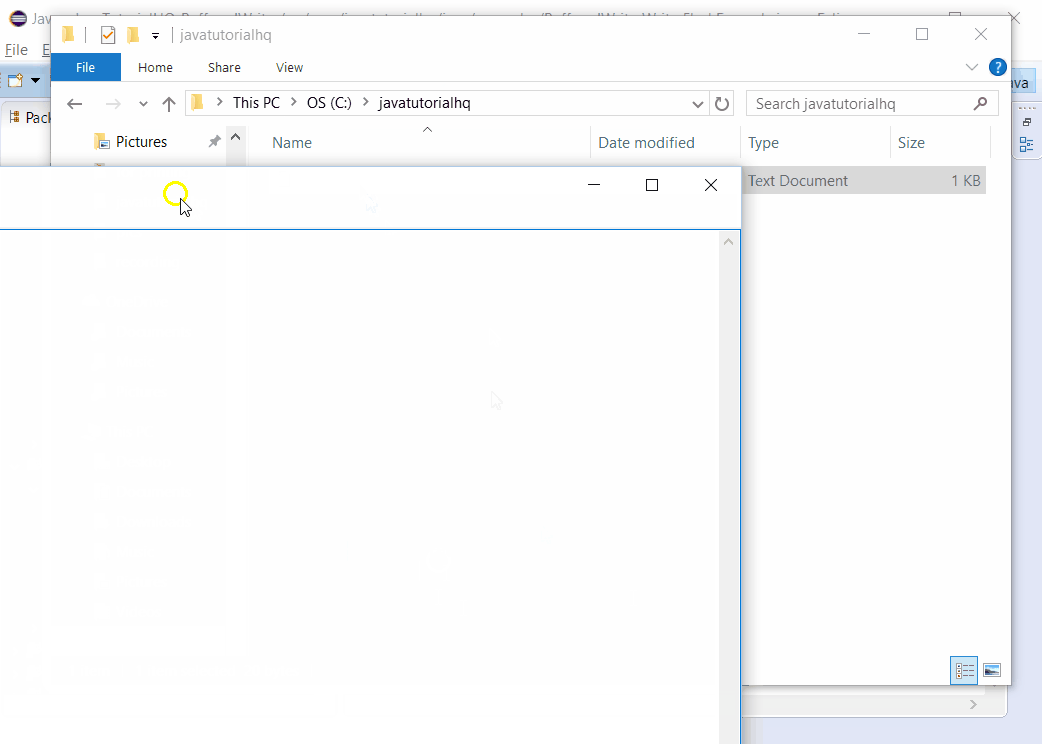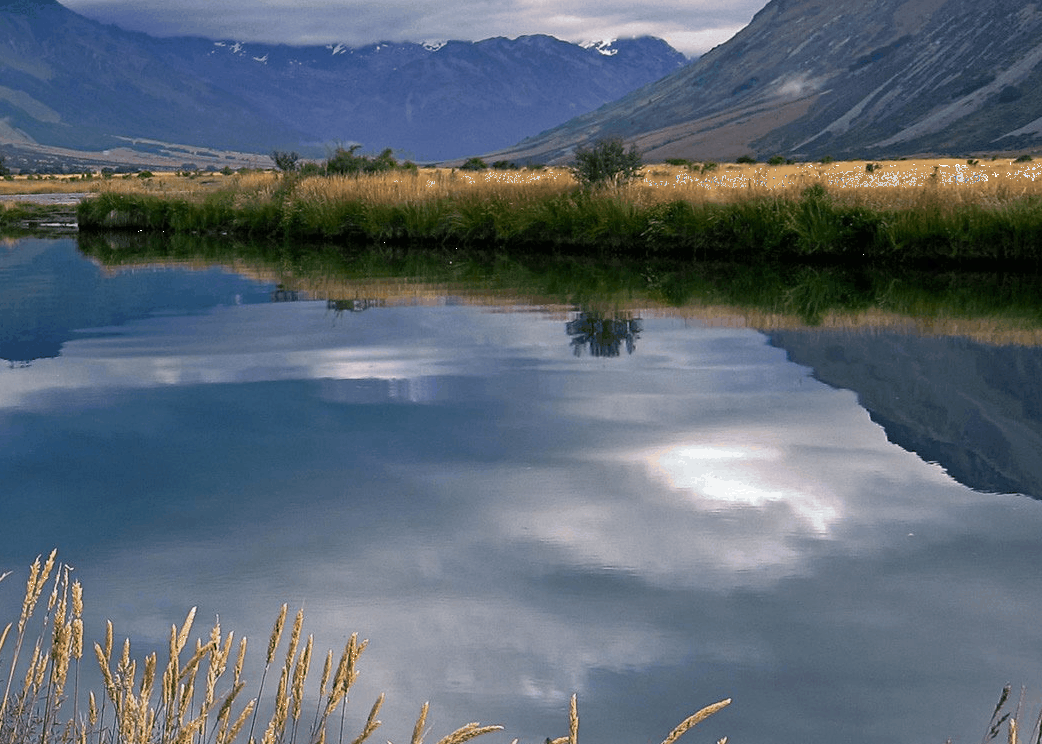
System.out.println("Starting the write operation");
// write values
bw.write("Ryan");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("Vince");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("William");
// flush the stream
bw.flush();
// close the BufferedWriter object to finish operation
bw.close();
System.out.println("Finished");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}