java.lang.Character isHighSurrogate(char ch)
Description
Such values do not represent characters by themselves, but are used in the representation of supplementary characters in the UTF-16 encoding.
The isHighSurrogate(char ch) method of Character class is static thus it should be accessed statically which means the we would be calling this method in this format:
Character.isHighSurrogate(char ch)
Non static method is usually called by just declaring method_name(argument) however in this case since the method is static, it should be called by appending the class name as suffix. We will be encountering a compilation problem if we call the java isHighSurrogate() method non statically.
Method Syntax
public static boolean isHighSurrogate(char ch)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| char | ch | the char value to be tested. |
Method Returns
The isHighSurrogate(char ch) method of Character class returns true if the char value is between MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE and MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE inclusive; false otherwise.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.5 and up
Java Character isHighSurrogate(char ch) Example
Below is a simple java example on the usage of isHighSurrogate(char ch) method of Character class.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* isHighSurrogate(char ch) method of Character class.
*/
public class CharacterIsHighSurrogateExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* Editors Note
* Range is ud800 to udbff
*/
// initialize characters to be tested
char c1 = 'ud800';
char c2 = 'uc71f';
// check the characters if it is a Unicode high-surrogate code unit
boolean result1 = Character.isHighSurrogate(c1);
boolean result2 = Character.isHighSurrogate(c2);
// print the result
System.out.println("is c1 a Unicode high-surrogate code unit?"+result1);
System.out.println("is c2 a Unicode high-surrogate code unit?"+result2);
}
}
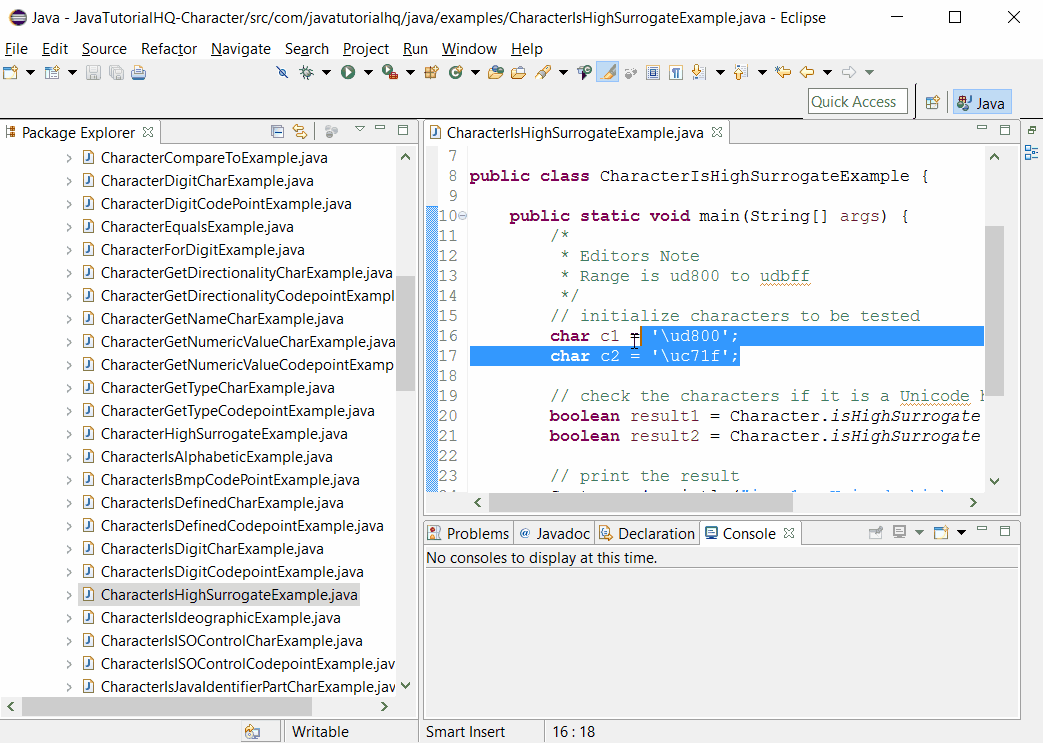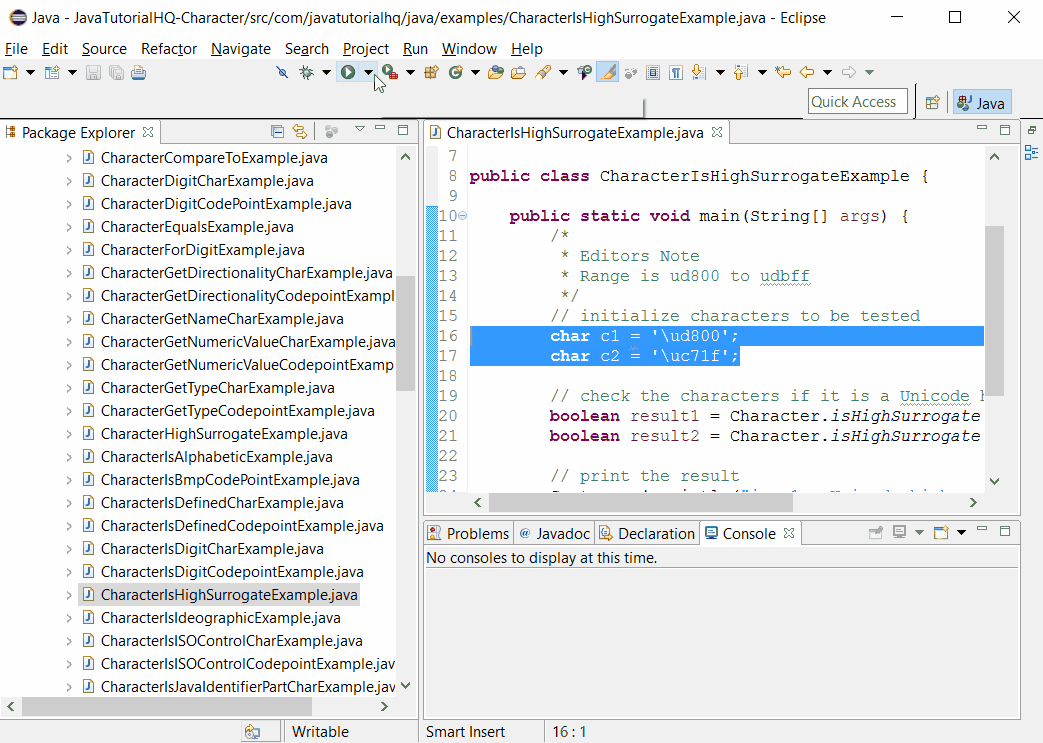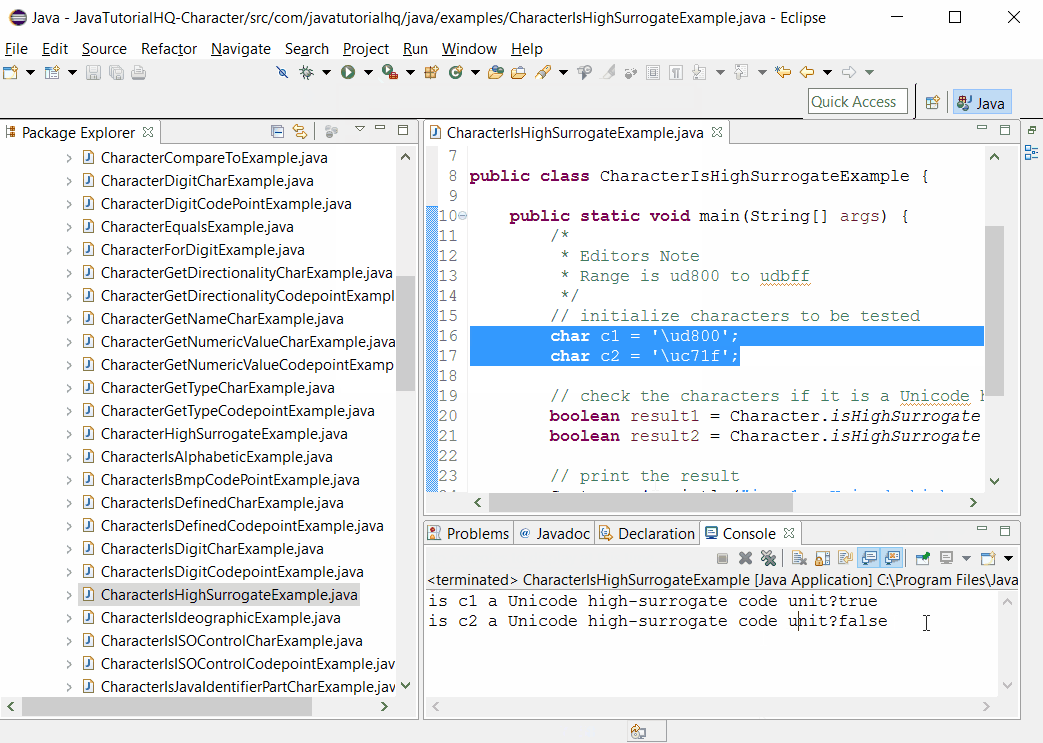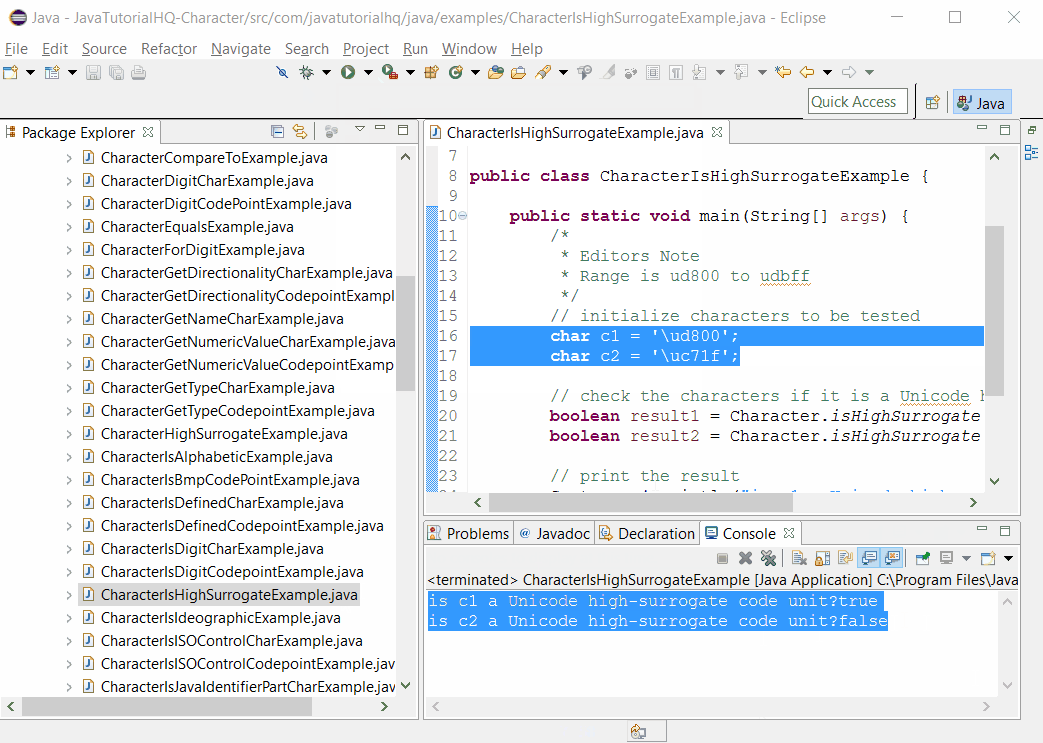
Sample Output
Below is the sample output when you run the above example.