java.util.StringTokenizer.nextElement()
Description
This method is actively being used hand in hand with hasMoreElement() method. When this two method are combined together, we will have a way to effectively traverse throughout the tokens. Same as that of the combination hasNextToken and nextToken, these two method works well. You might be wondering if it’s ok to use hasMoreToken and then nextElement(), that would be Yes. It will work, but as a matter of consistency you must consider it thoroughly.
Method Syntax
public Object nextElement()
throws
NoSuchElementException – if there are no more tokens in this tokenizer’s string.
Method Returns
The nextElement() method returns the next token in the string.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.0 and up
Java STringTokenizer nextElement() Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of nextElement() method of StringTokenizer class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behaviour of the nextToken() method. Basically we have a string declared initially and as you can see it’s actually a group of string delimited by “|” pipe. And we used StringTokenizer to break it down into tokens. This will transform the String into a more meaningful information on this case, we presented the first token as string, then the second as age, etc. If you have noticed, the example below is very similar with our nextToken() method example, but since the nextElement() returns an Object rather than a String, we have to cast the return value.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* nextElement() method of StringTokenizer class.
*
*/
public class StringTokenizerNextElementExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//declare a new String with tokens delimited by |
String str = "Vince|2|Male|Paya Lebar, Singapore";
/*
* initialize our StringTokenizer using input
* as source String and | as the delimiter
*/
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(str,"|");
String name = (String) st.nextElement();
String age = (String) st.nextElement();
String gender = (String) st.nextElement();
String address = (String) st.nextElement();
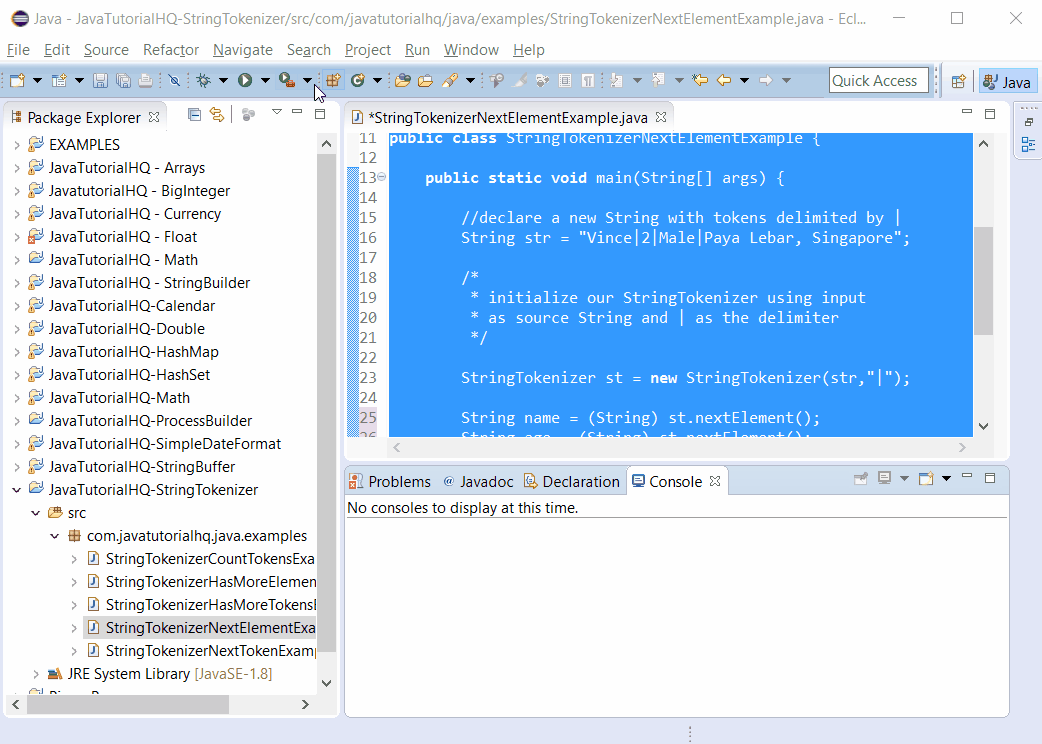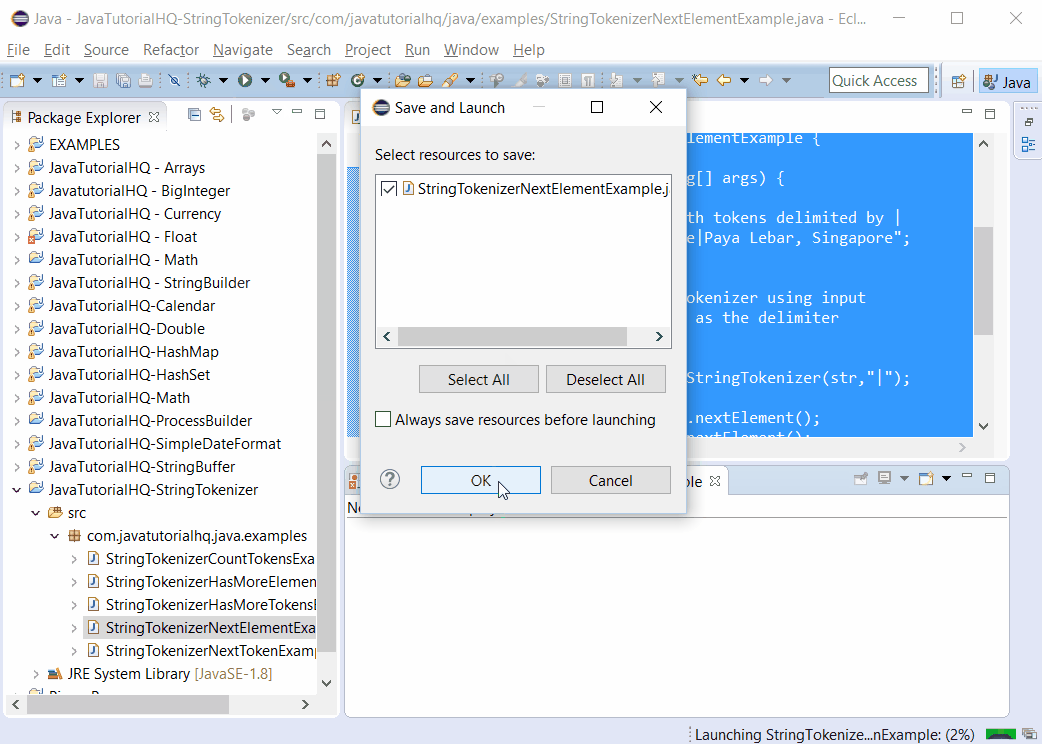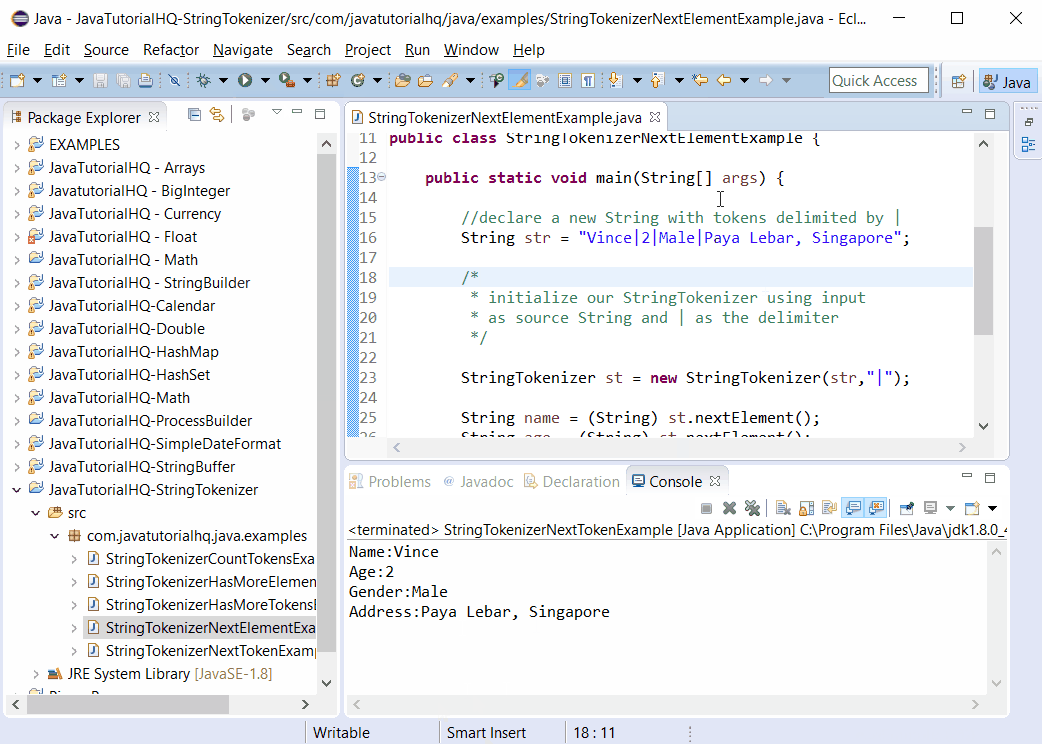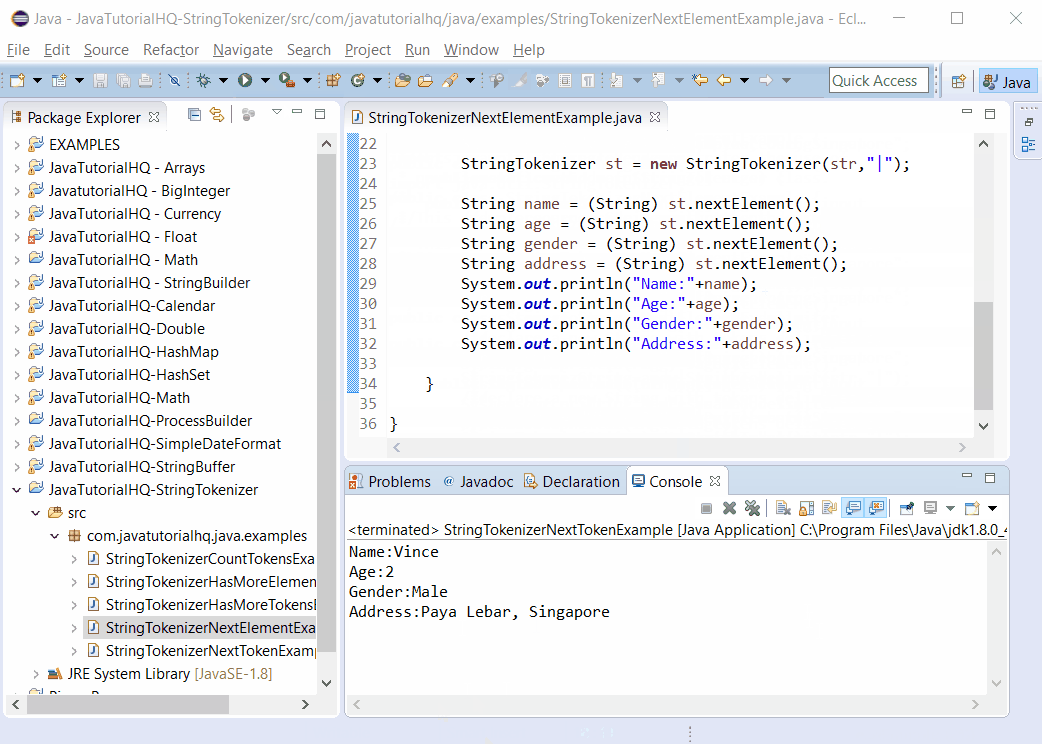
System.out.println("Name:"+name);
System.out.println("Age:"+age);
System.out.println("Gender:"+gender);
System.out.println("Address:"+address);
}
}