java.lang.Math.cos()
Description
- If the argument is NaN or an infinity, then the result is NaN.
Most of the methods of the Math class is static and the cos() method is no exception. Thus don’t forget that in order to call this method, you don’t have to create a new object instead call it using Math.cos(a).
Method Syntax
public static double cos(double a)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| double | a | an angle, in radians. |
Method Returns
The Math.cos() method returns the cosine of the argument.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.0 and up
Java Math cos() Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of cos() method of Math class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the cos() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* This example source code demonstrates the use of
* cos() method of Math class
*/
public class MathCosineExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Ask for user input
System.out.print("Enter an angle in degrees:");
// use scanner to read the console input
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// Assign the user to String variable
String s = scan.nextLine();
// close the scanner object
scan.close();
// convert the string input to double
double value = Double.parseDouble(s);
// convert the value to radians
double valueRadians = Math.toRadians(value);
// get the cosine of the angle
double cosValue = Math.cos(valueRadians);
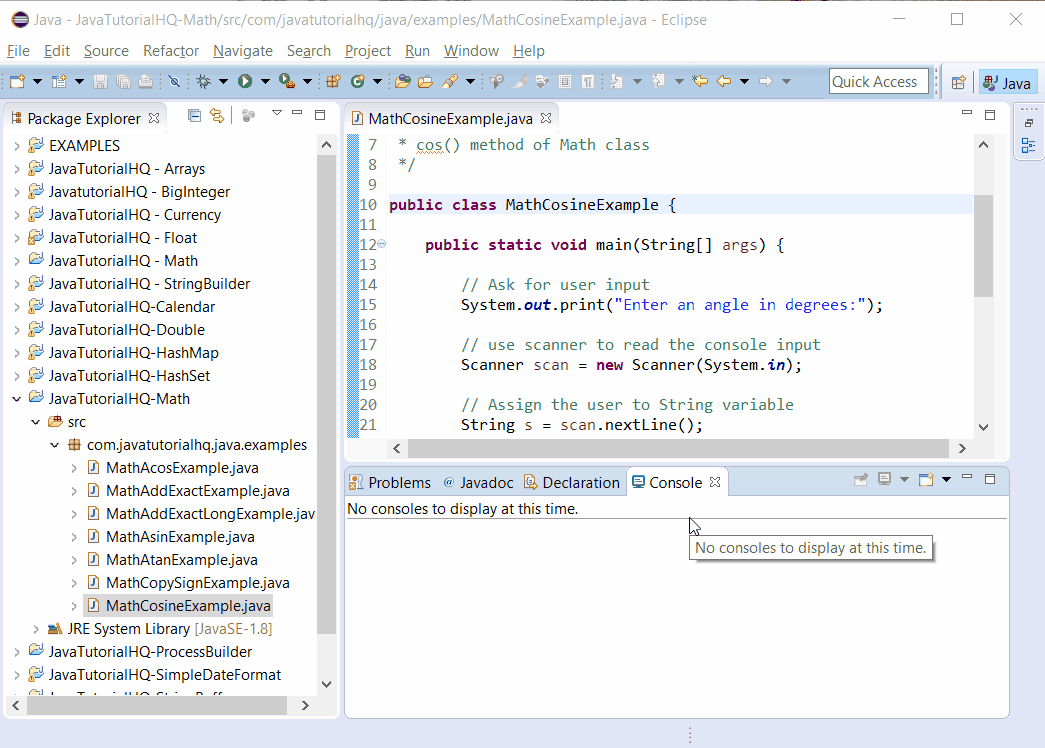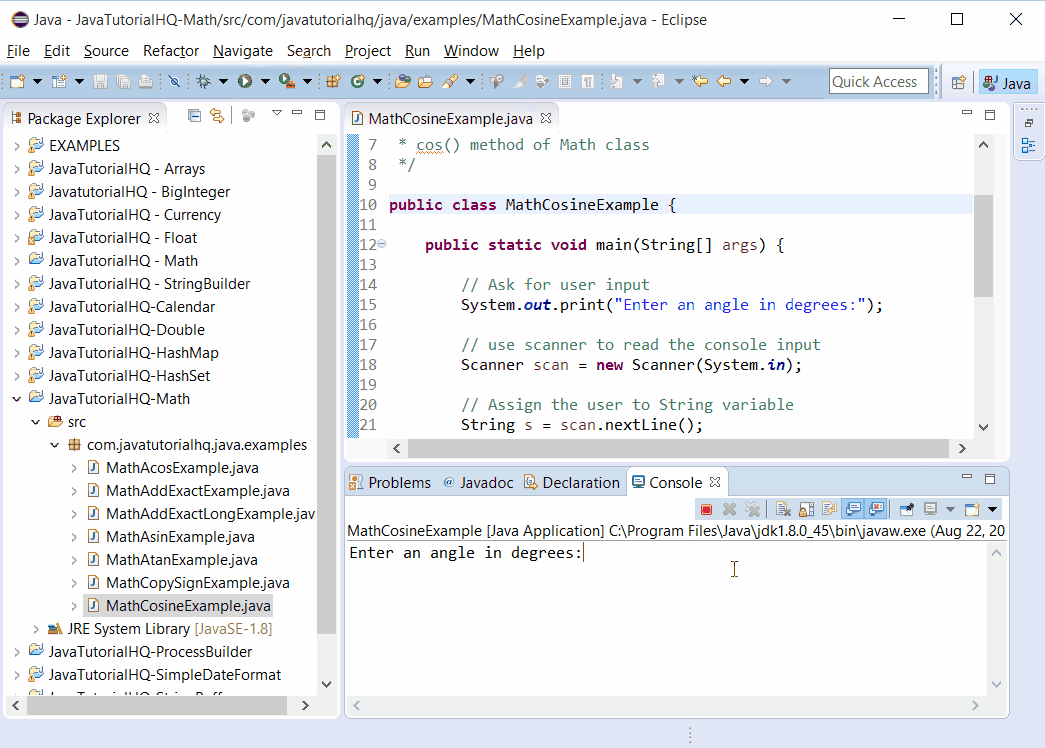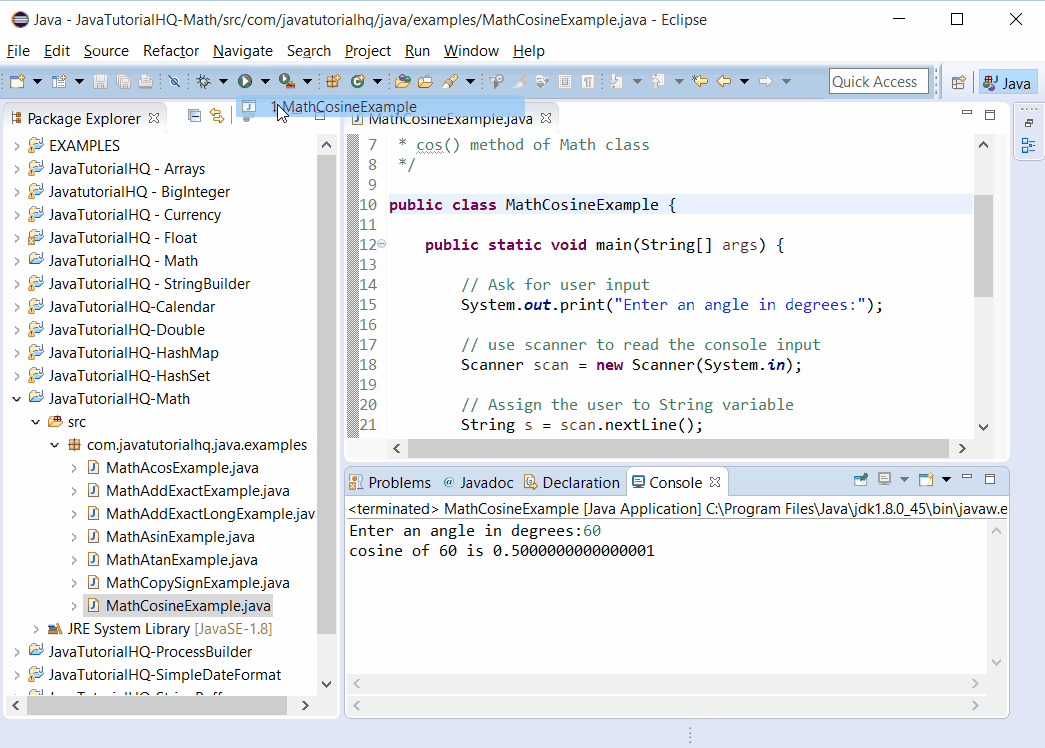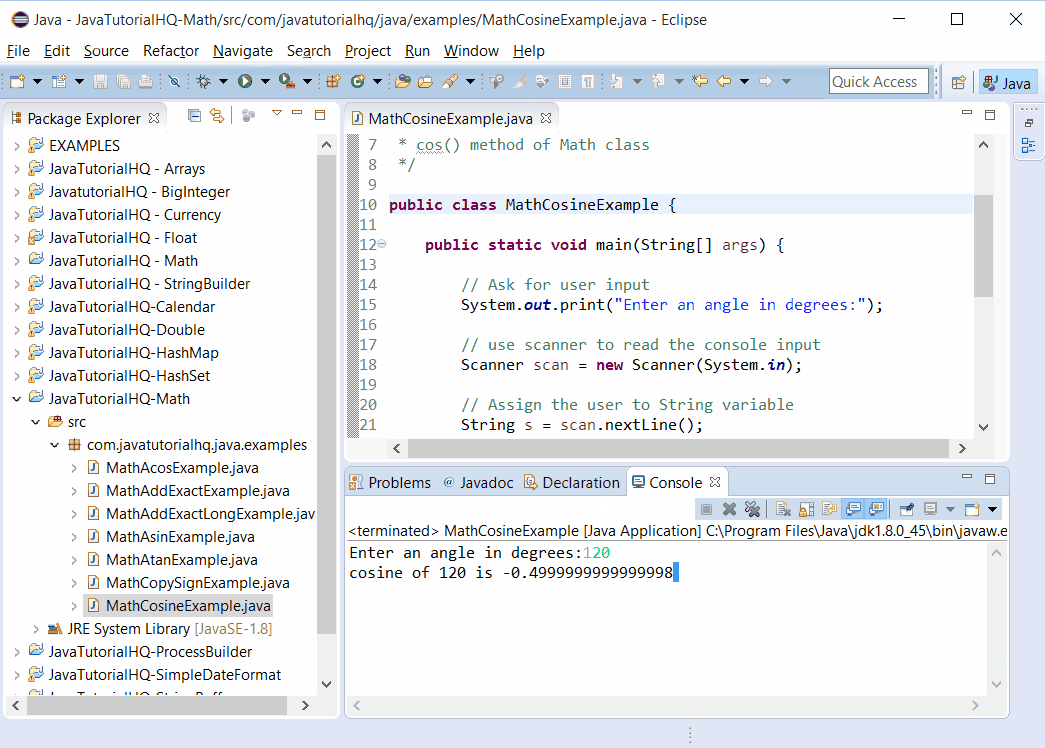
System.out.println("cosine of " + s + " is " + cosValue);
}
}
The above java example source code demonstrates the use of cos() method of Math class. We simply ask for user input and we use the Scanner class to parse it. Since we have used the nextLine() method to get the console value, and the return data type is String thus we have used the Double.parseDouble() to transform it into double. We have to convert it first to double because the asin() method accepts double method argument. After transforming into double we have also used Math.toRadians() to convert the input to radians which is the required method argument.