java.lang.Math abs()
Description
- If the argument is positive zero or negative zero, the result is positive zero.
- If the argument is infinite, the result is positive infinity.
- If the argument is NaN, the result is NaN.
Method Syntax
public static datatype abs(datatype a)
As we have noted already the abs() method is overloaded, thus on the method signature above we have mentioned datatype which signifies that this method accepts any data type and will return the absolute value of the method argument reflecting the same data type as the input.
Method Returns
The abs() method returns the absolute value of the argument.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.0 and up
Java Math abs() Example
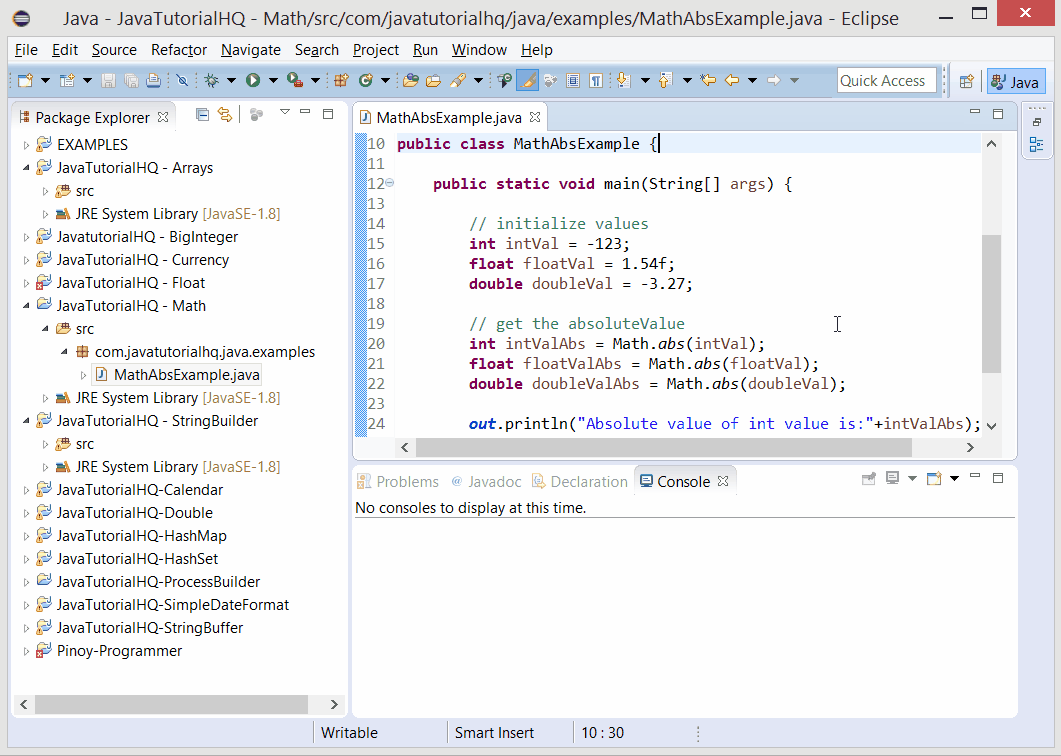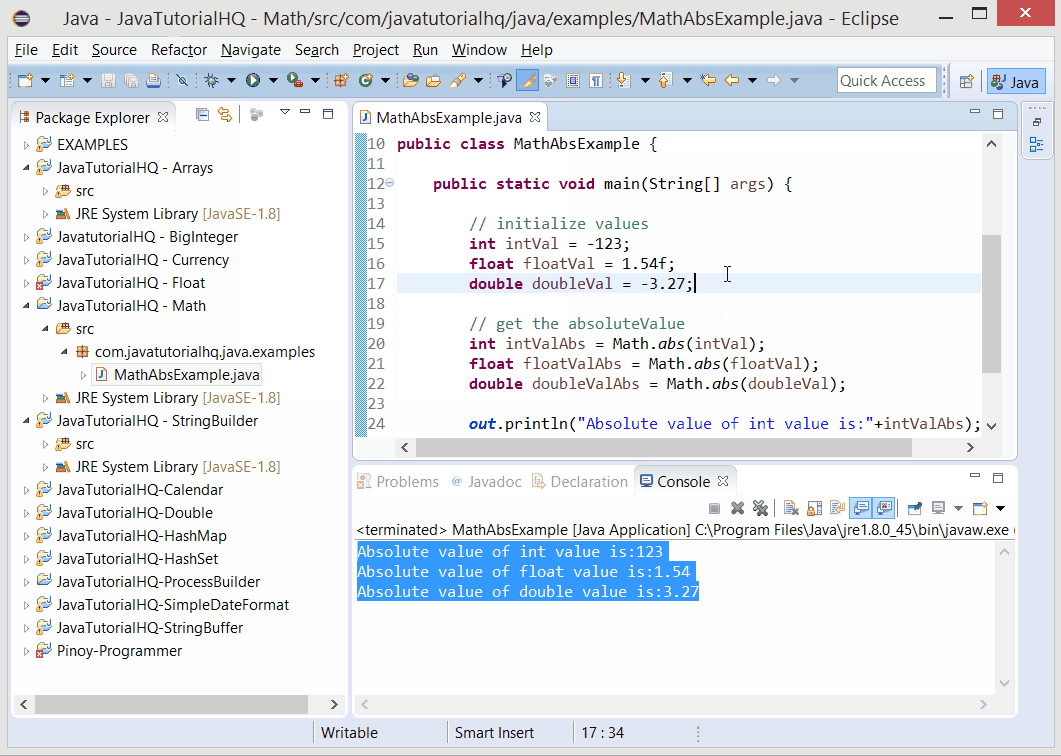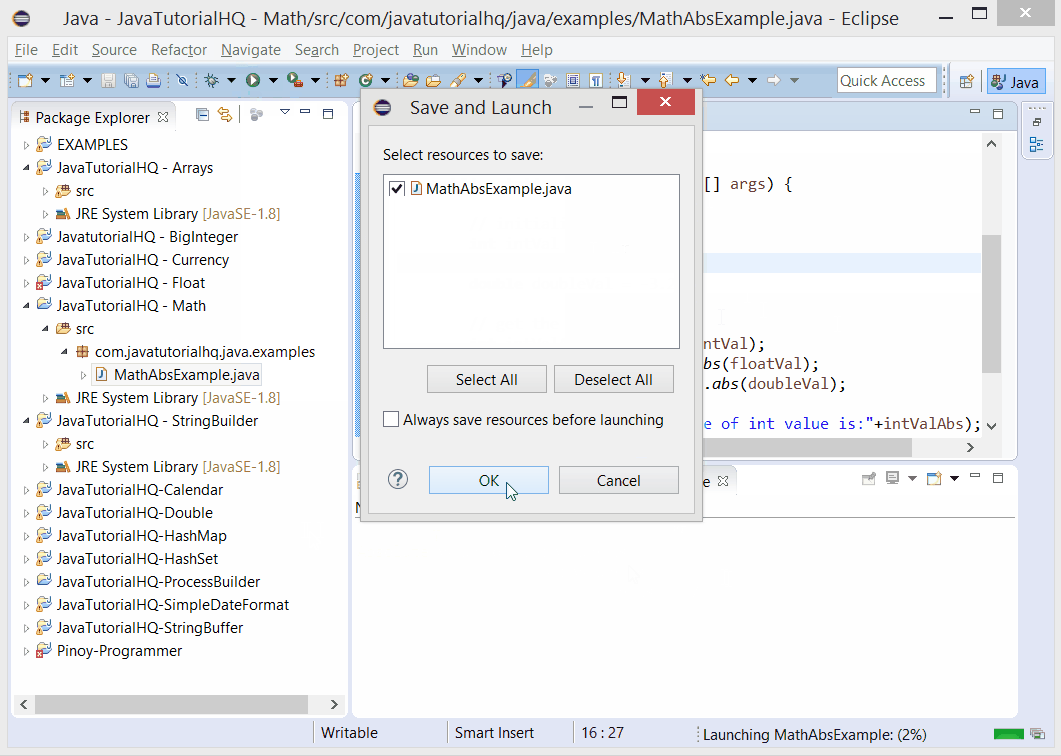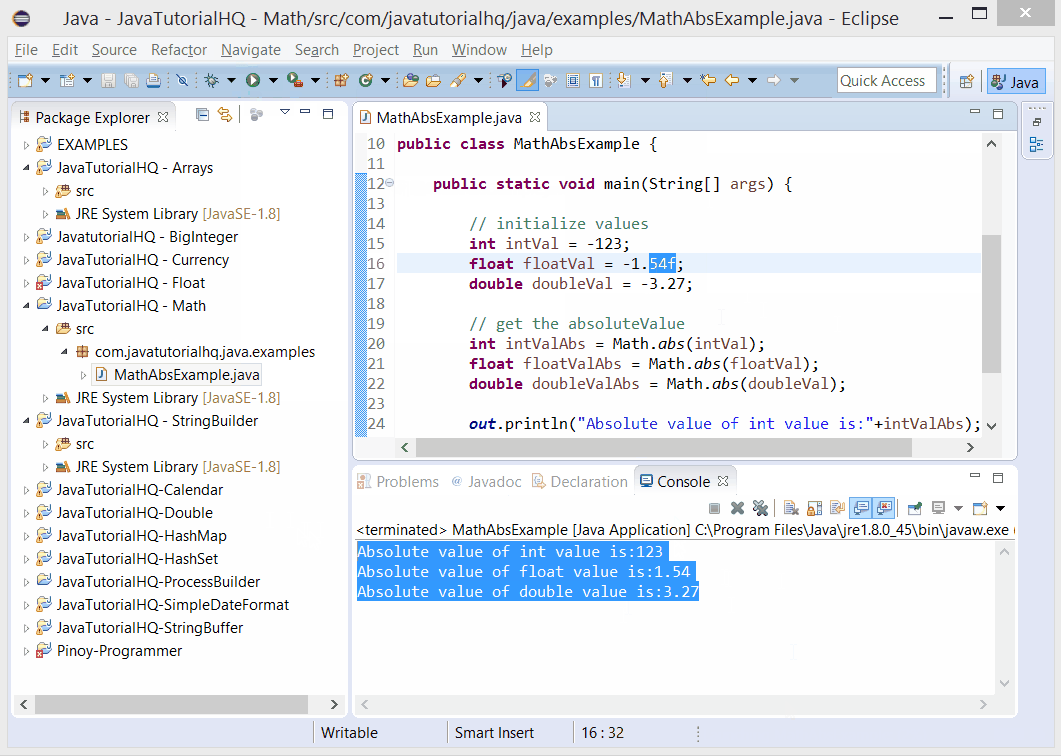
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of abs() method of Math class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the abs() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import static java.lang.System.out;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of abs() method of Math class
*/
public class MathAbsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize values
int intVal = -123;
float floatVal = 1.54f;
double doubleVal = -3.27;
// get the absoluteValue
int intValAbs = Math.abs(intVal);
float floatValAbs = Math.abs(floatVal);
double doubleValAbs = Math.abs(doubleVal);
out.println("Absolute value of int value is:"+intValAbs);
out.println("Absolute value of float value is:"+floatValAbs);
out.println("Absolute value of double value is:"+doubleValAbs);
}
}
The above java example source code demonstrates the use of abs() method of Math class. We simply declare values of different values and we get the absolute value of those. This is to demonstrate on how the abs() method works on different data types.