java.math.BigInteger bitLength()
Description
Basics:
Let’s say we have a decimal number of -24 then in order to get the 2’s complement of this number, write it first in binary.
| 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
and then since this is a sign integer we will be appending a 1 at the beginning so it becomes
11000
Then we invert the values
00111
Counting all the bits of the above result will give you the bitLength.
Method Syntax
public int bitLength()
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method Returns
The bitLength() method returns an int value which corresponds to the number of bits in the minimal two’s-complement representation of this BigInteger, excluding a sign bit.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.1 and up
Java BigInteger BitLength() Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of bitCount() method of BigInteger class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the bitCount() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of bitLength() method of BigInteger class
*/
public class BigIntegerBitLengthExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// get user input
System.out.print("Enter the first value:");
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
String firstInput = s.nextLine();
s.close();
// convert the first String Input to BigInteger
BigInteger val1 = new BigInteger(firstInput);
/*
* get the the length of bits of the
* user input
*/
int result = val1.bitLength();
System.out.println("Bit Length of "+val1+" is "+result);
}
}
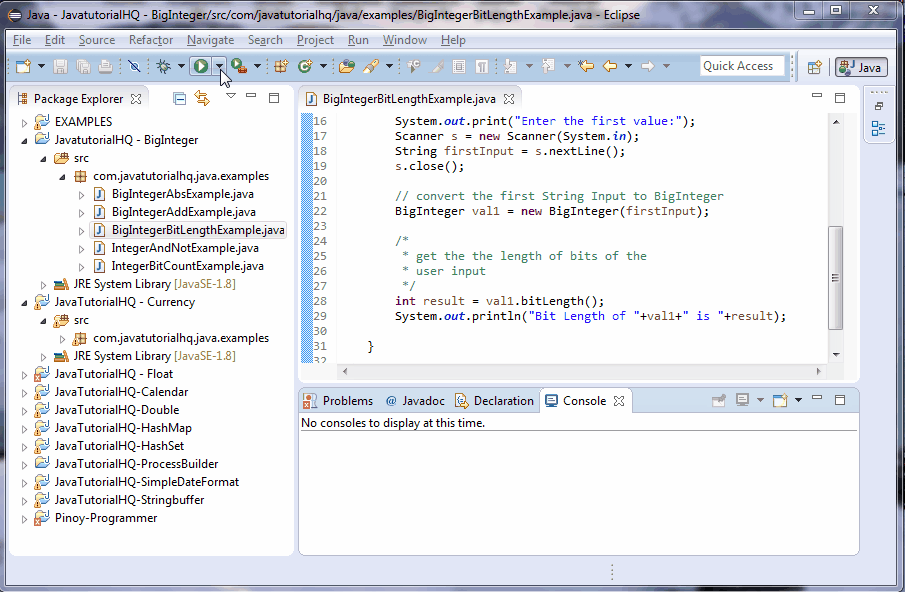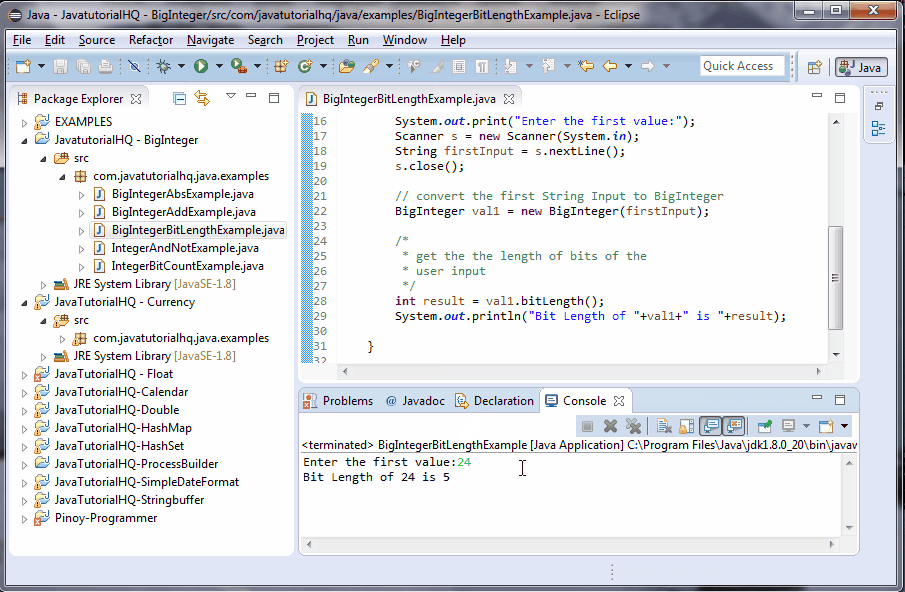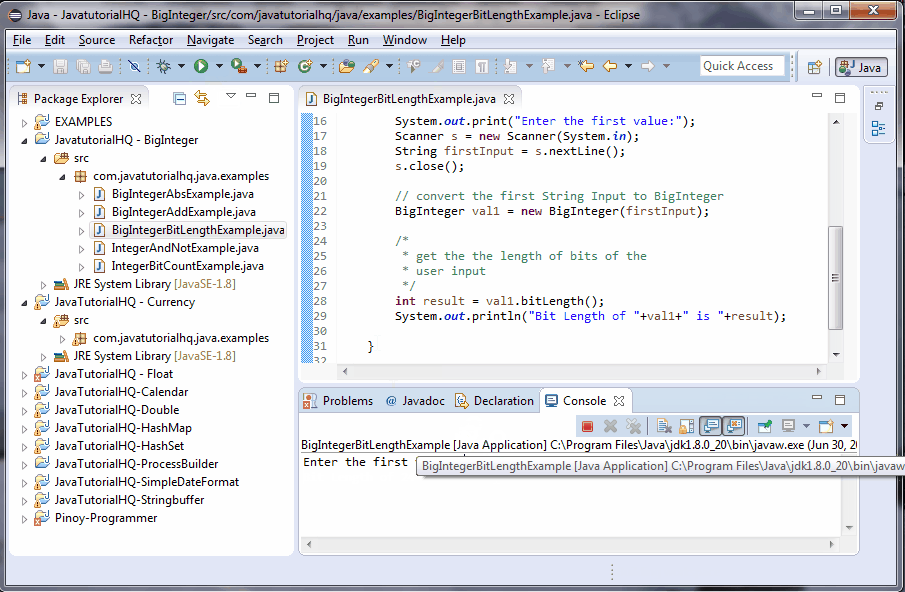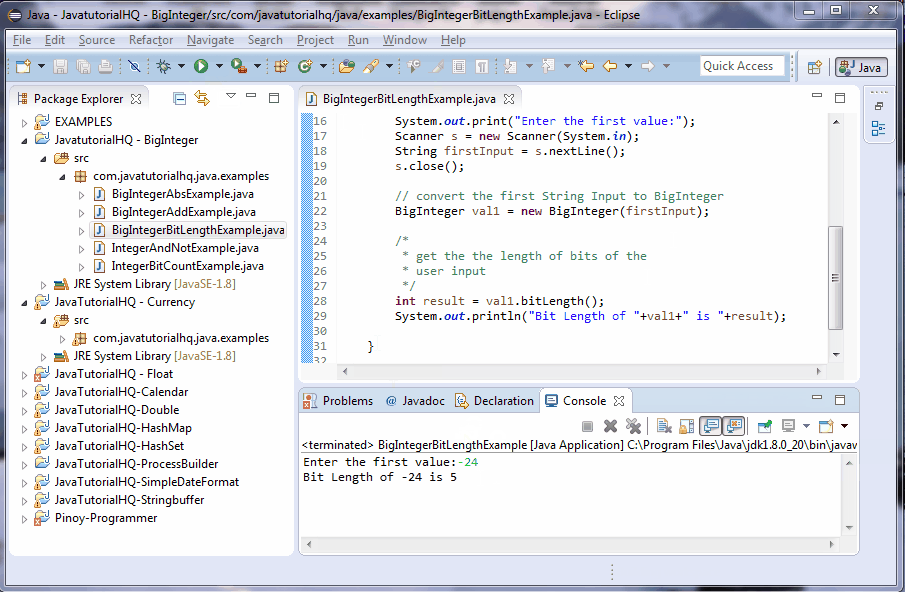
This example is a lot simpler than it looks. Basically we ask for user input and converted this value into BigInteger. We then printed out the results of the bitLength() operation.