java.math.BigInteger byteValueExact()
Description
For reference the byte range is from -128 to 127 and these information is readily available through the Byte constants Byte.MIN_VALUE and Byte.MAX_VALUE. If the BigInteger is outside of the range defined by these constants, an ArithmeticException will be thrown.
Method Syntax
public byte byteValueExact()
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method Returns
The bitLength() method returns this BigInteger converted to a byte.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.8 and up
Java BigInteger byteValueExact() Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of byteValueExact() method of BigInteger class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the byteValueExact() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of byteValueExact() method of BigInteger class
*/
public class BigIntegerByteValueExactExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare and initialize our BigInteger values
BigInteger val1 = new BigInteger("12");
BigInteger val2 = new BigInteger("3231");
// get the byte value of each BigInteger
byte byteVal1 = val1.byteValueExact();
byte byteVal2 = val2.byteValueExact();
// print the operation
System.out.println("val1 in byte is "+byteVal1);
System.out.println("val2 in byte is "+byteVal2);
}
}
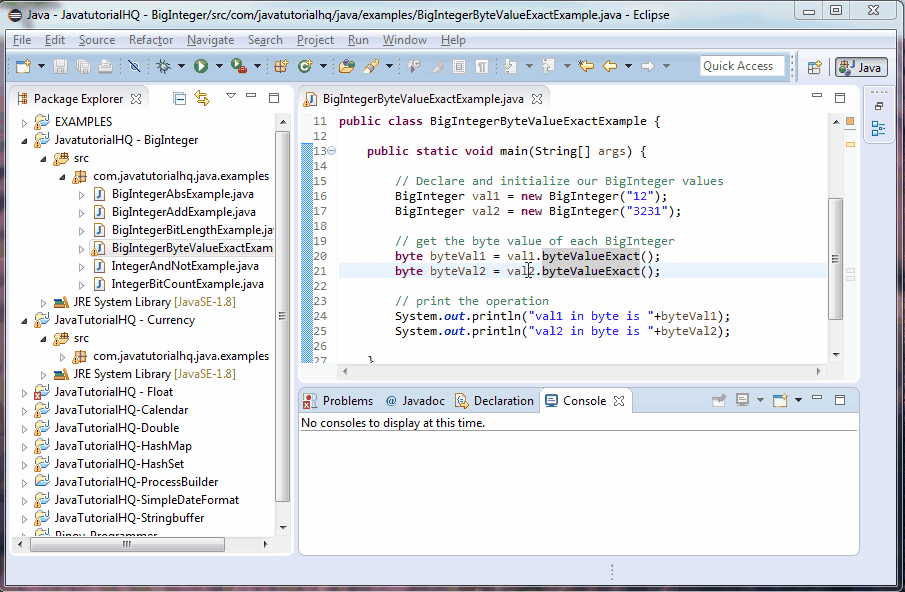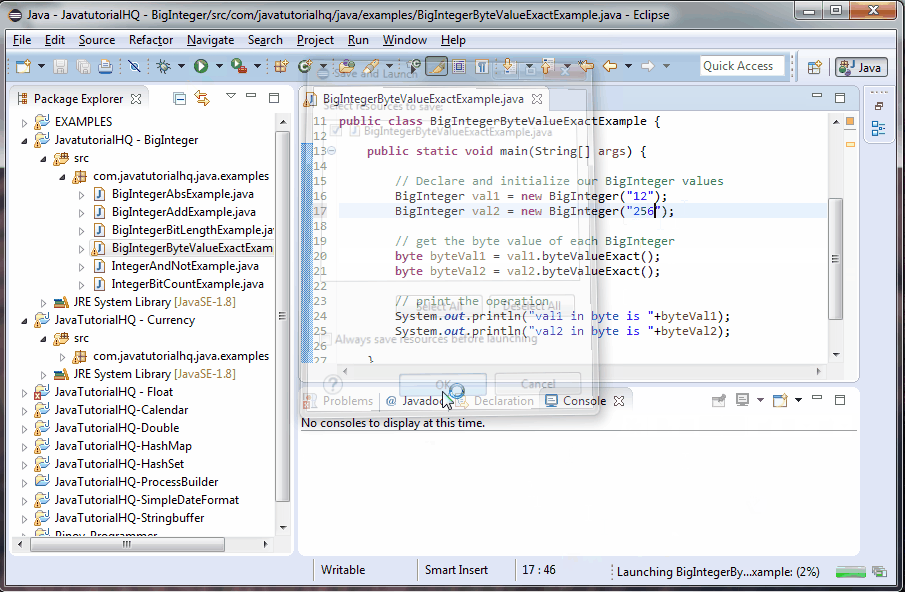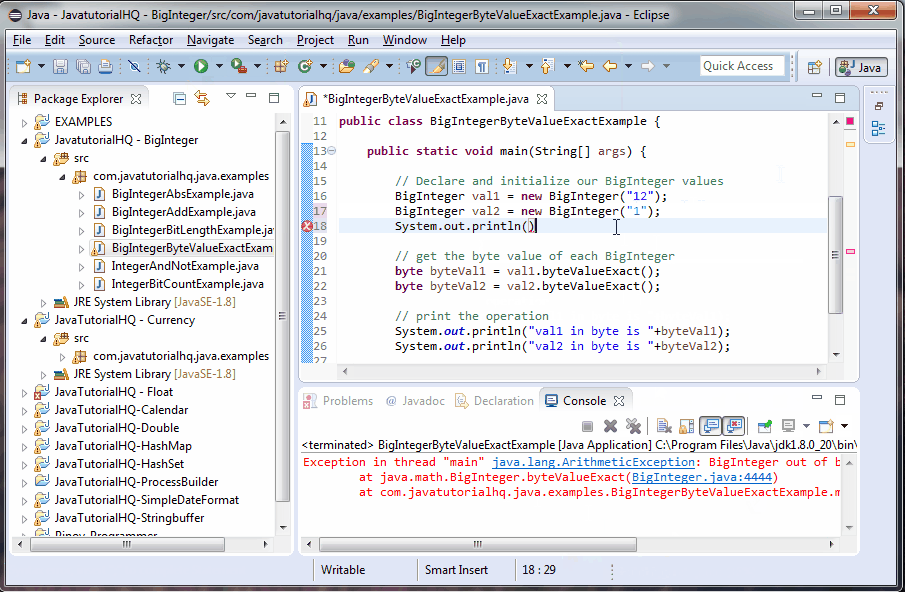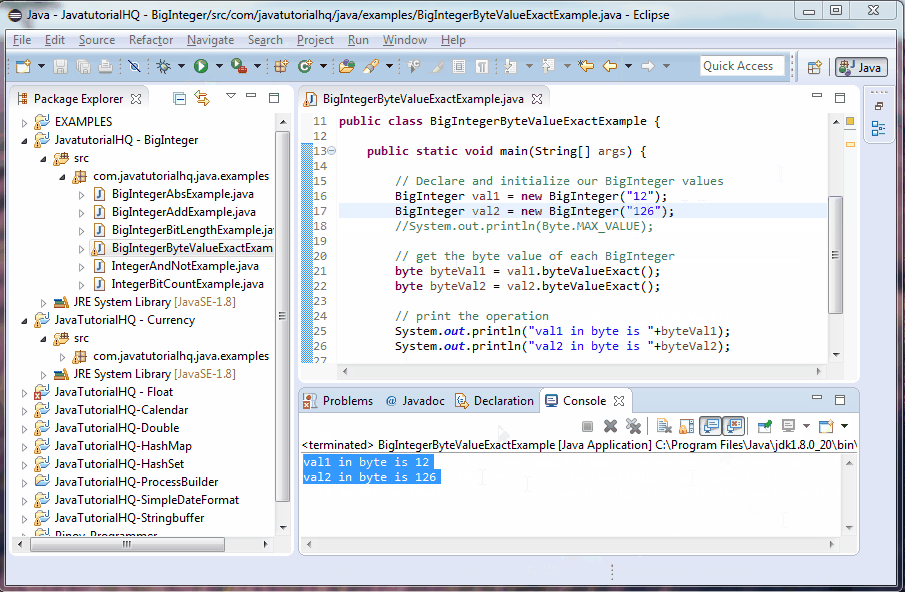
This example is a lot simpler than it looks. We only initialize two BigInteger values, one that we know is in range of bytes and the other is outside the range. The result of the byteValue is printed out.