java.math.BigInteger intValueExact()
Description
For reference the int range is from 2147483647 to -2147483648 and these information is readily available through the Integer constants Integer.MIN_VALUE and Integer.MAX_VALUE.
Method Syntax
public int intValueExact()
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method Returns
The intValueExact() method returns this BigInteger converted to primitive int.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.8 and up
Java BigInteger intValueExact() Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of intValueExact() method of BigInteger class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the intValueExact() method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of intValue() method of BigInteger class
*/
public class BigIntegerIntValueExactExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare and initialize our BigInteger values
BigInteger val1 = new BigInteger("12");
BigInteger val2 = new BigInteger("150");
//BigInteger val2 = new BigInteger("21474832647");
// get the int equivalent of each BigInteger
int intVal1 = val1.intValueExact();
int intVal2 = val2.intValueExact();
// print the operation
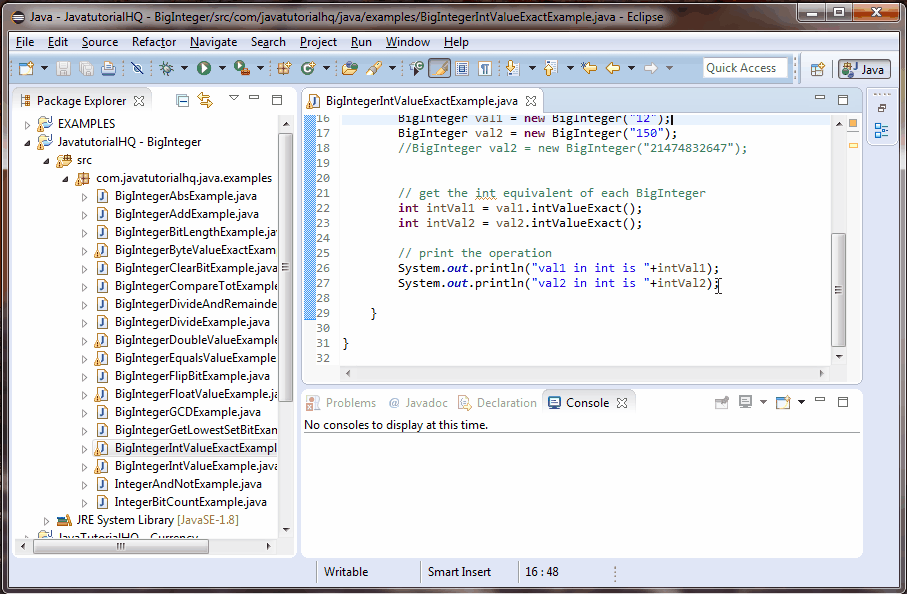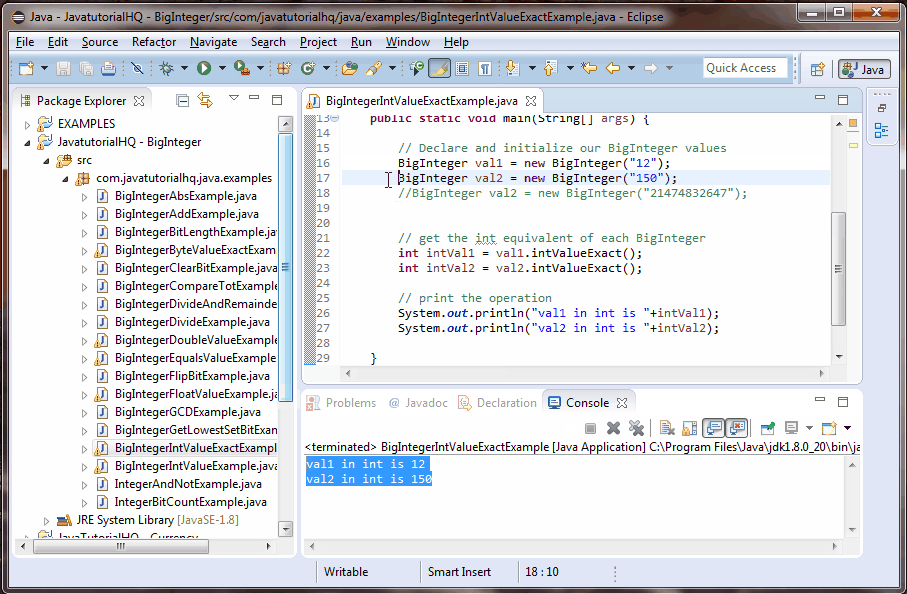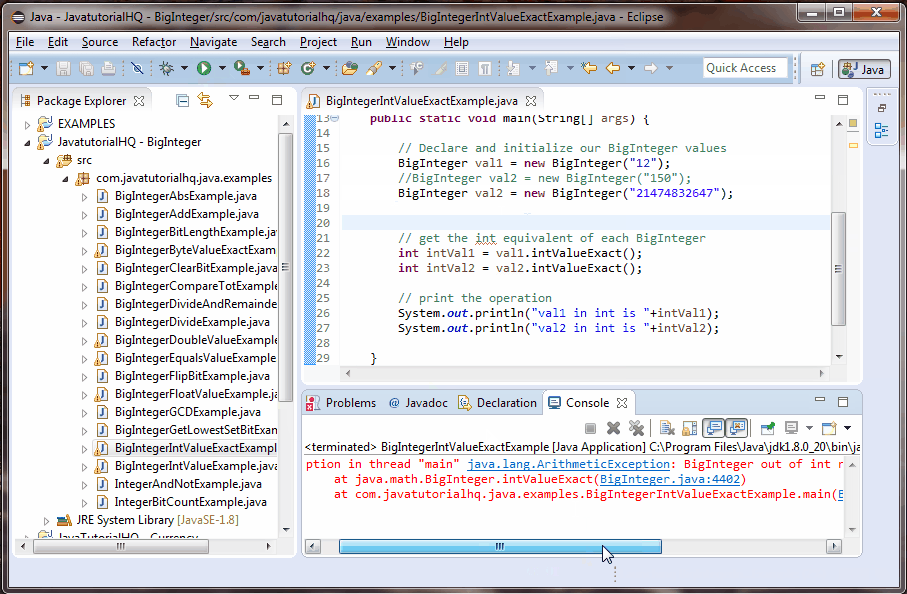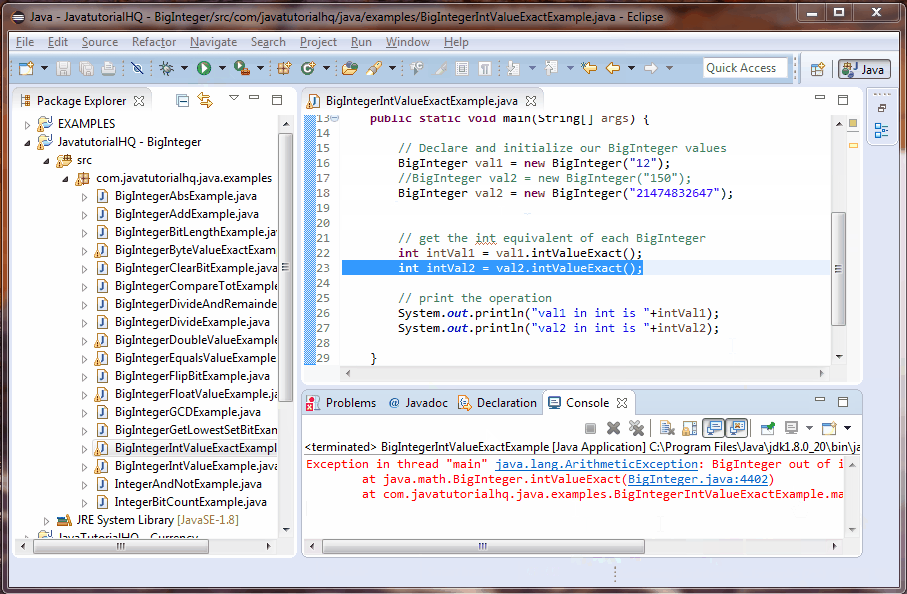
System.out.println("val1 in int is "+intVal1);
System.out.println("val2 in int is "+intVal2);
}
}
This example is a lot simpler than it looks. We only initialize two BigInteger, one is certainly within range and the other is also within range but we have included a value that is certainly outside of range. We have commented it because it will throw an ArithmeticException. This swill clearly be simulated on below example output.