java.math.BigInteger gcd(BigInteger val)
Description
A quick background on Greatest Comnon Divisor
The greatest common divisor (gcd) of two or more integers, when at least one of them is not zero, is the largest positive integer that divides the numbers without a remainder. For example, the GCD of 8 and 12 is 4.
Method Syntax
public BigInteger gcd(BigInteger val)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BigInteger | val | value with which the GCD is to be computed. |
Method Returns
The divide() method returns GCD(abs(this), abs(val)
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.1 and up
Java BigInteger gcd(BigInteger val) Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of gcd(BigInteger val) method of BigInteger class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the gcd(BigInteger val) method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of gcd(BigInteger val)
* method of BigInteger class
*/
public class BigIntegerGCDExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ask for user input
System.out.print("Enter the first value:");
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
String input1 = s.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter the second value:");
String input2 = s.nextLine();
s.close();
// convert the string input to BigInteger
BigInteger val1 = new BigInteger(input1);
BigInteger val2 = new BigInteger(input2);
// get the GCD
BigInteger gcd = val1.gcd(val2);
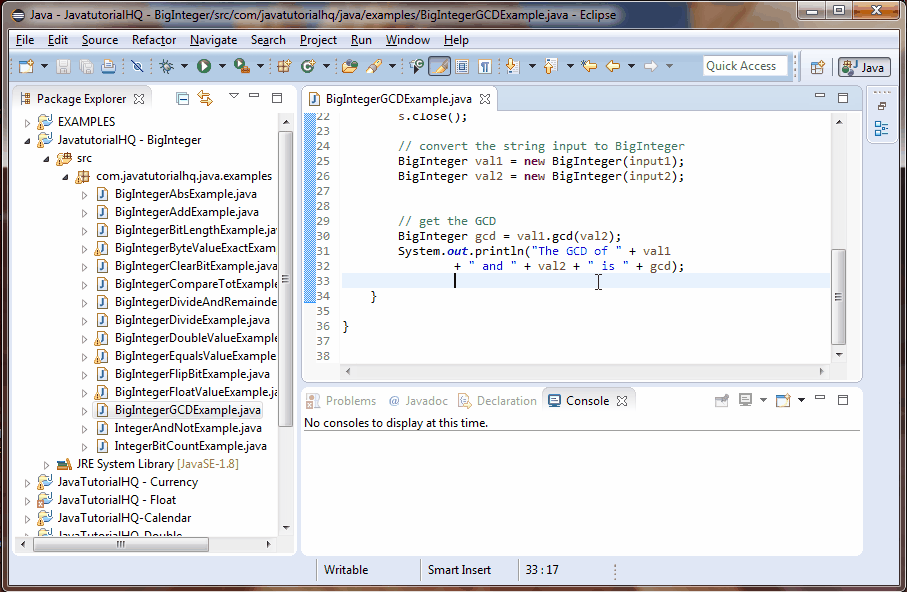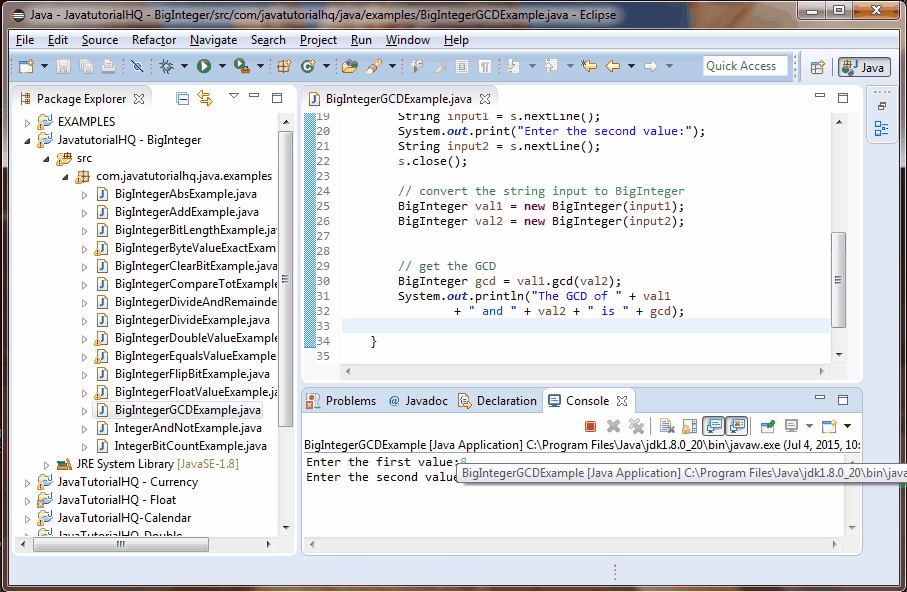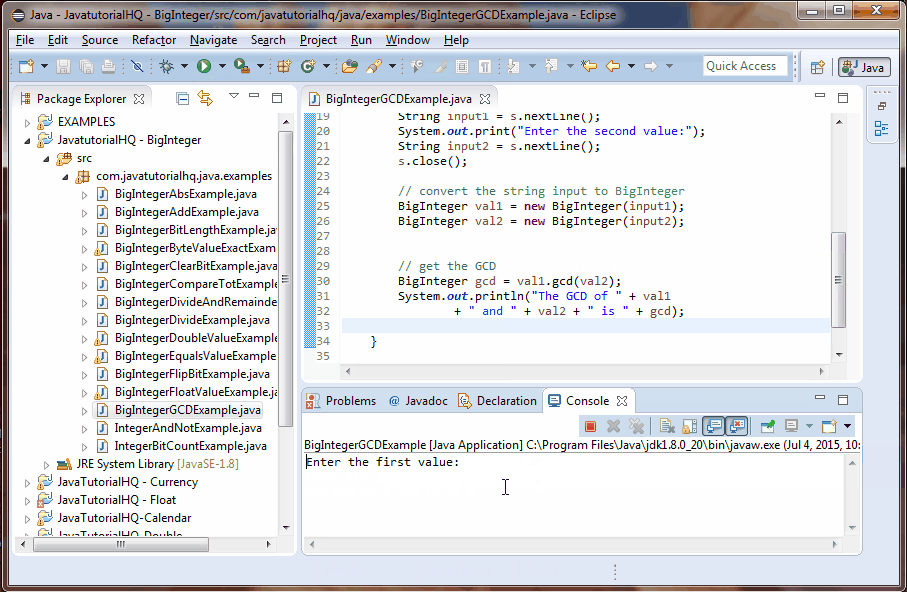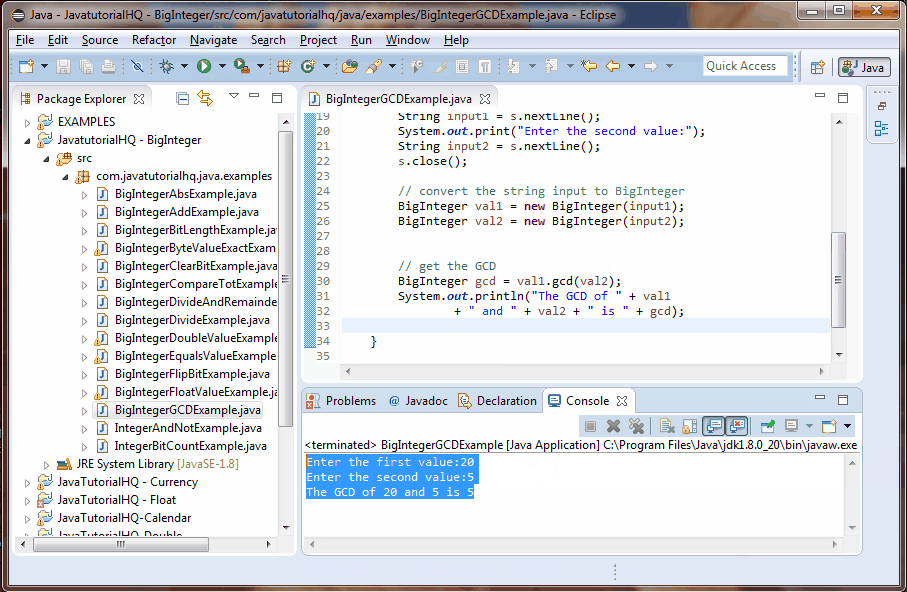
System.out.println("The GCD of " + val1
+ " and " + val2 + " is " + gcd);
}
}
This example is a lot simpler than it looks. We simply ask the user for two inputs and then convert these into BigInteger. The greatest common divisior were derived using the gcd() method.