java.math.BigInteger testBit(int n)
Description
Notes:
- this method throws an Arithmetic exception if n supplied is negative.
Method Syntax
public boolean testBit(int n)
Method Argument
| Data Type | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| int | n | index of bit to test. |
Method Returns
The testBit() method return true if and only if the designated bit is set.
Compatibility
Requires Java 1.1 and up
Java BigInteger testBit(int n) Example
Below is a java code demonstrates the use of testBit(int n) method of BigInteger class. The example presented might be simple however it shows the behavior of the testBit(int n) method.
package com.javatutorialhq.java.examples;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* A java example source code to demonstrate
* the use of testBit(int n) method of BigInteger class
*/
public class BigIntegerTestBitExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize a BigInteger object
BigInteger val1 = new BigInteger("17");
/*
* Note: 17 in binary is 10001
*/
// get user input
System.out.print("Enter the bit number you want to test:");
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
String input = s.nextLine();
s.close();
/*
* convert the input to Integer, unboxing feature will be used to
* transform Integer to primitive int
*/
Integer inputBitNumber = Integer.parseInt(input);
// test if the index specified is set
boolean result = val1.testBit(inputBitNumber);
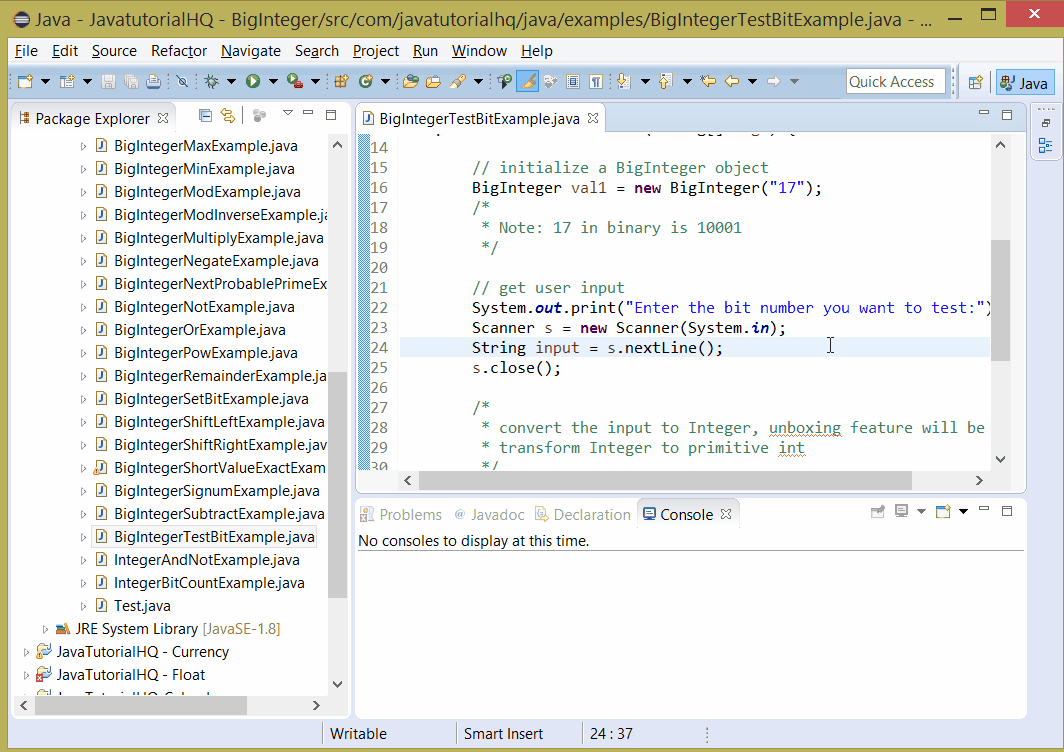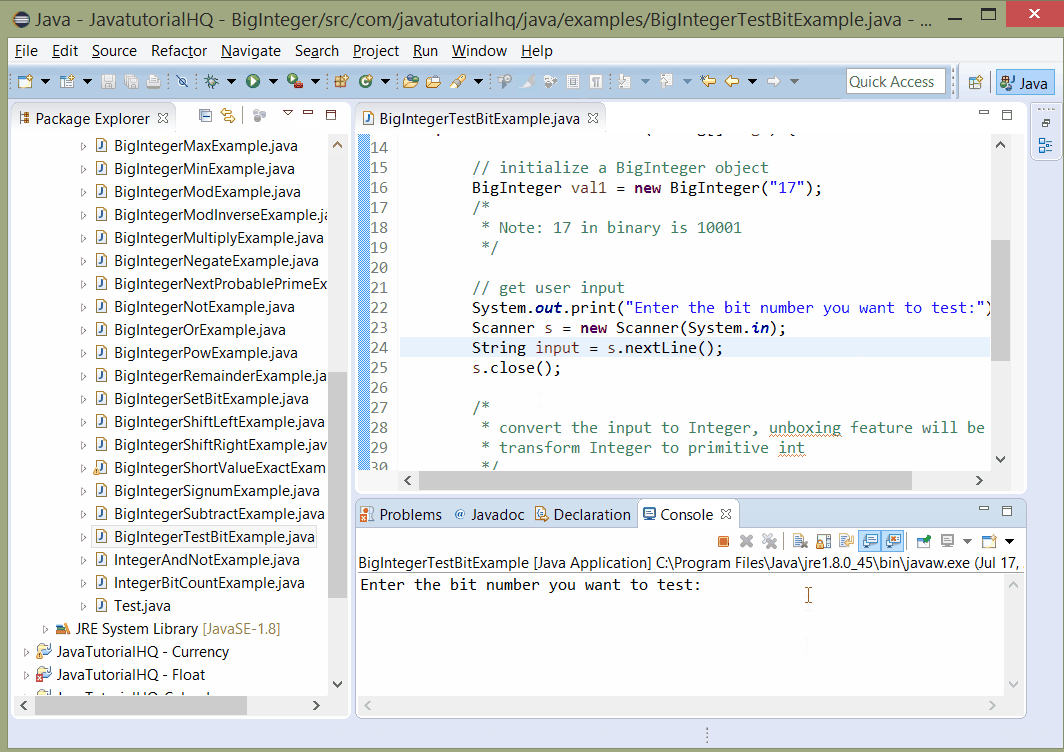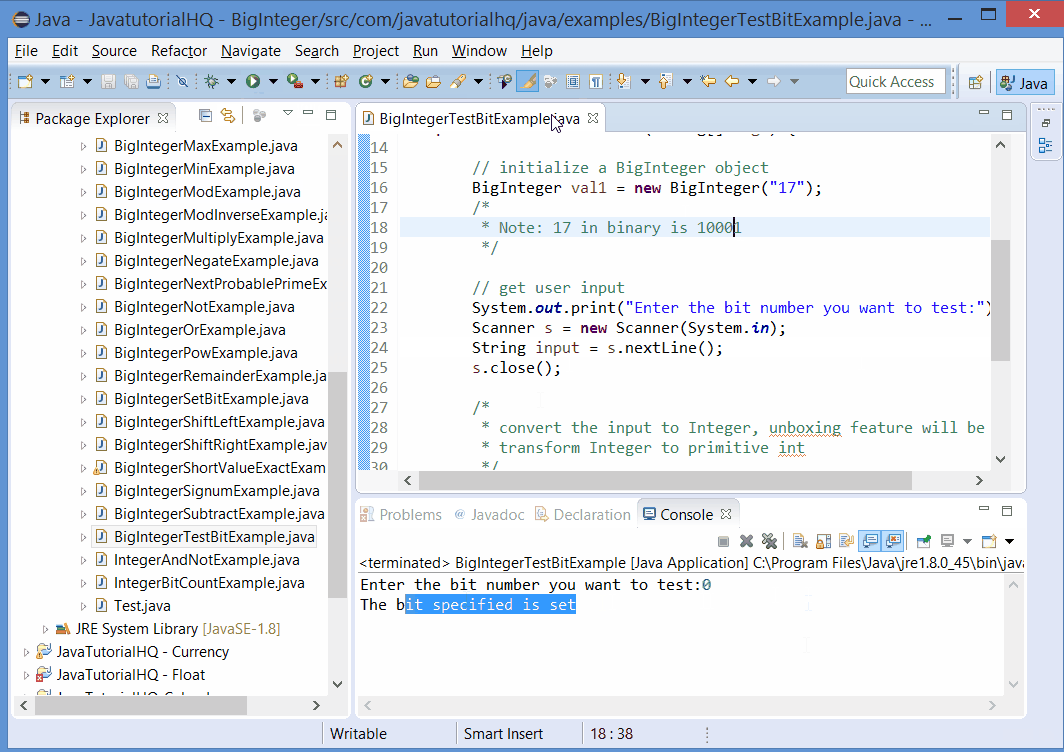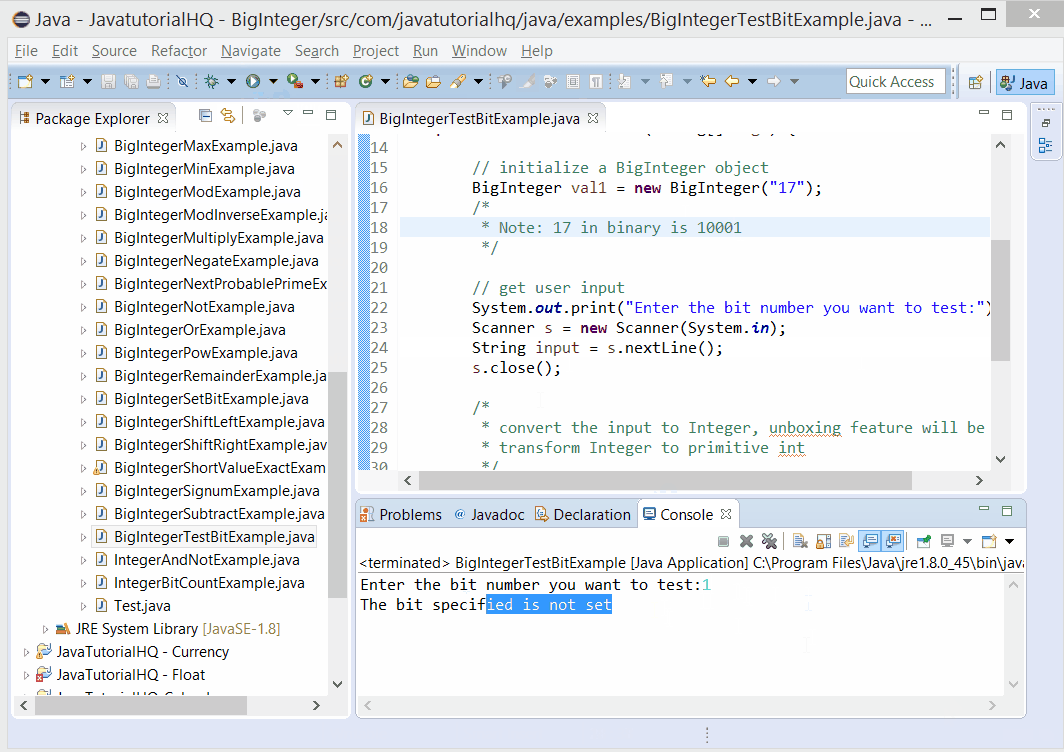
if(result){
System.out.println("The bit specified is set");
}else{
System.out.println("The bit specified is not set");
}
}
}
This example is a lot simpler than it looks. The first part is the declaration of a BigInteger. User are then asked to provide the index of bit to test. The result is evaluated by testing the output of testBit using if condition. If the result is true, a message “The bit specified is set” otherwise a message “The bit specified is not set” is printed on the console.